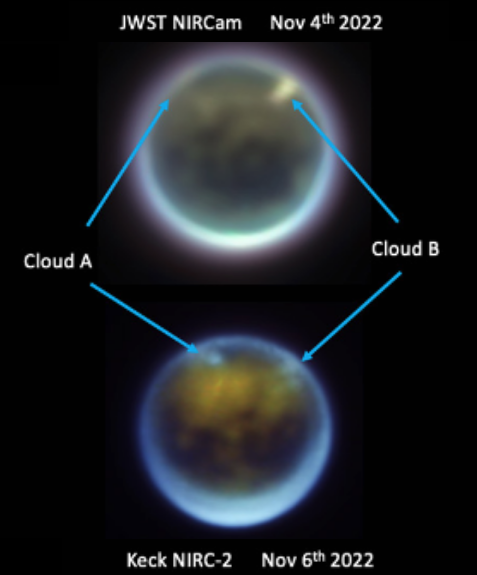
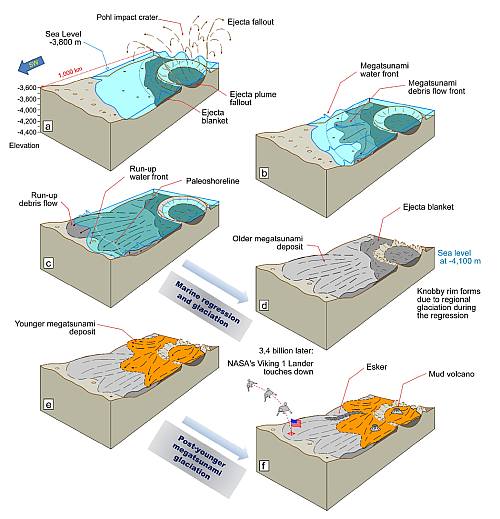
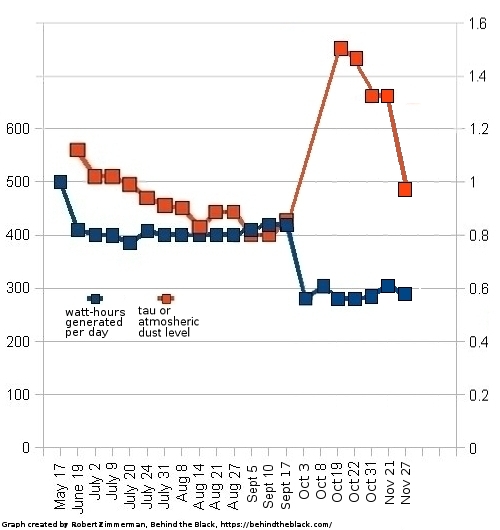
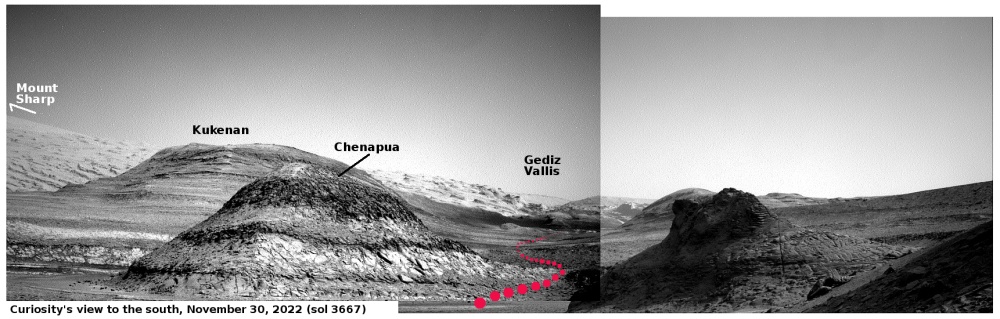
Martian glaciers below 30 degrees latitude
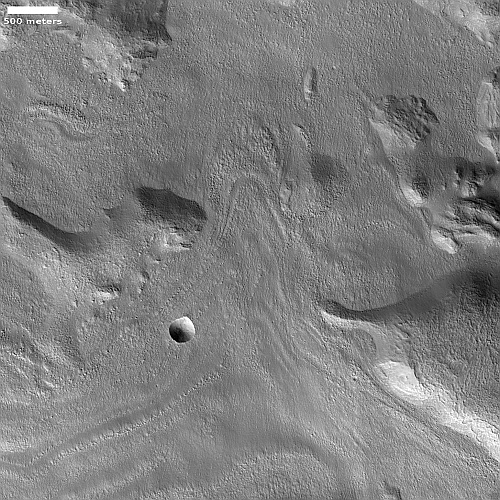
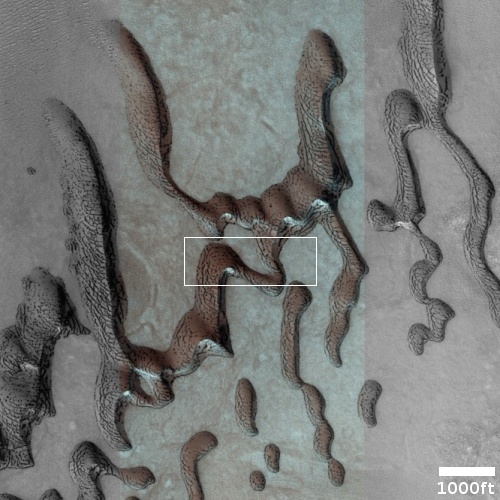
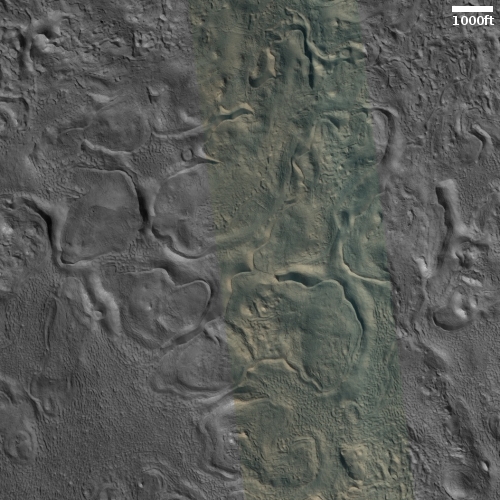
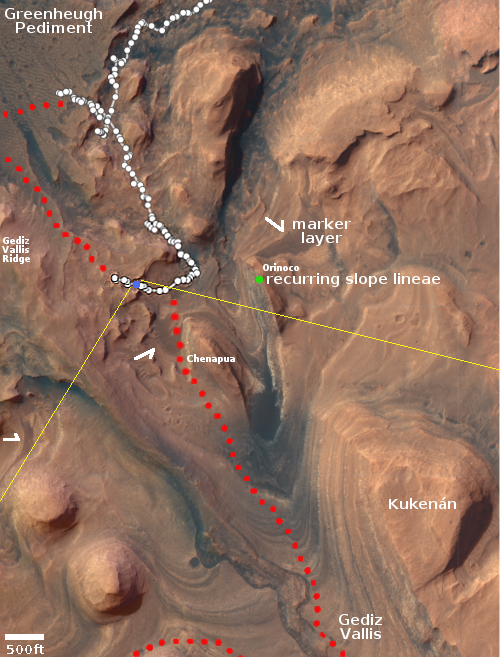
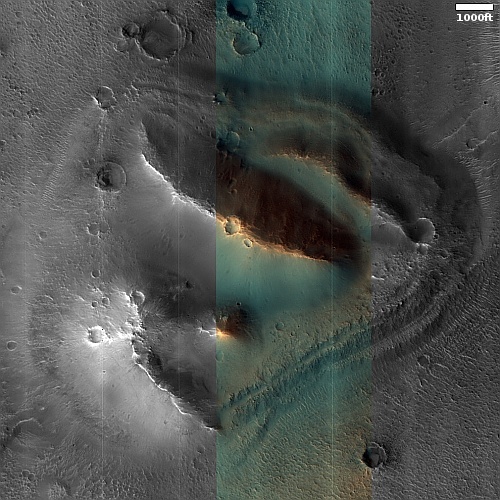
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on September 28, 2022 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). While it shows what looks like a somewhat typical Martian glacial flow pushing through a gap between hills, this glacial flow is not typical. It sits at just under 30 degrees north latitude, closer to the equator than almost any glacial feature on Mars. Moreover, the younger impact crater on top suggests this glacier has been here for some time. Though the impact is younger than the crater, it is not that young, as the dark streaks normally seen in the first years after impact are gone.
Thus, this glacier suggests that not only can near surface Martian ice exist closer than 30 degrees latitude from the equator, it can survive there for a considerable amount of time.
Nor is this glacial flow, so close to the equator, unusual for this region of Mars.
» Read more
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on September 28, 2022 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). While it shows what looks like a somewhat typical Martian glacial flow pushing through a gap between hills, this glacial flow is not typical. It sits at just under 30 degrees north latitude, closer to the equator than almost any glacial feature on Mars. Moreover, the younger impact crater on top suggests this glacier has been here for some time. Though the impact is younger than the crater, it is not that young, as the dark streaks normally seen in the first years after impact are gone.
Thus, this glacier suggests that not only can near surface Martian ice exist closer than 30 degrees latitude from the equator, it can survive there for a considerable amount of time.
Nor is this glacial flow, so close to the equator, unusual for this region of Mars.
» Read more