Random Martian ridges on a lava plain
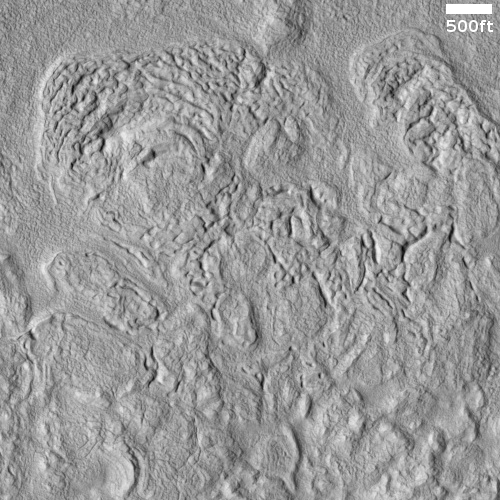
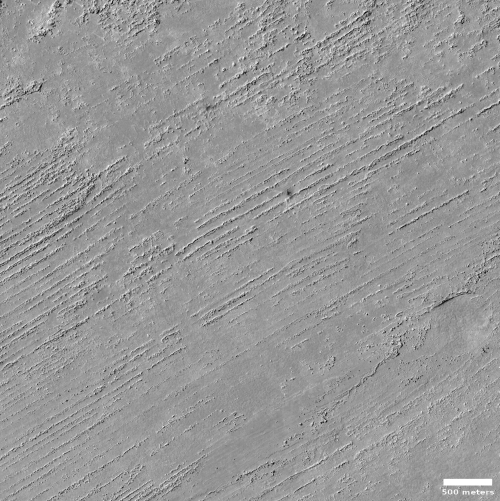
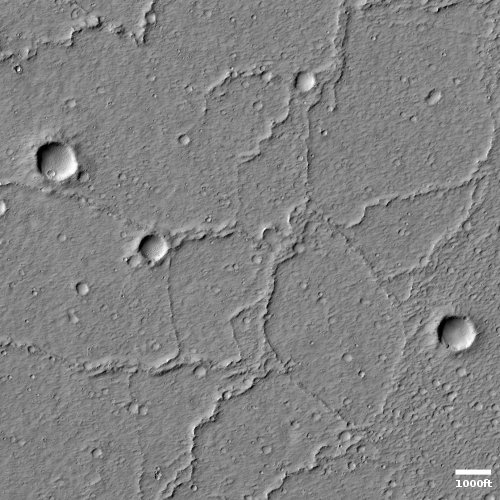
Cool image time! The photo to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on December 30, 2021 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). This was a terrain sample image, taken not as part of any specific research project but to fill a gap in the camera’s schedule and thus keep its temperature maintained properly. When the MRO team needs to take such pictures, they try to pick locations that might be interesting and previously unphotographed, but often the location is neither.
In this case this terrain sample captured a flat lava plain interspersed with sinuous ridges going in all directions. On top of this is a scattering of smaller impact craters, which obviously occurred after the lava had flowed and solidified.
What caused the ridges?
» Read more
Cool image time! The photo to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on December 30, 2021 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). This was a terrain sample image, taken not as part of any specific research project but to fill a gap in the camera’s schedule and thus keep its temperature maintained properly. When the MRO team needs to take such pictures, they try to pick locations that might be interesting and previously unphotographed, but often the location is neither.
In this case this terrain sample captured a flat lava plain interspersed with sinuous ridges going in all directions. On top of this is a scattering of smaller impact craters, which obviously occurred after the lava had flowed and solidified.
What caused the ridges?
» Read more