Hubble’s 2021 survey of the outer solar system
NASA today released the annual survey of images taken each year by the Hubble Space Telescope of the large planets that comprise the outer solar system, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
These Hubble images are part of yearly maps of each planet taken as part of the Outer Planets Atmospheres Legacy program, or OPAL. The program provides annual, global views of the outer planets to look for changes in their storms, winds, and clouds. Hubble’s longevity, and unique vantage point, has given astronomers a unique chance to check in on the outer planets on a yearly basis. Knowledge from the OPAL program can also be extended far beyond our own solar system in the study of atmospheres of planets that orbit stars other than our Sun.
The four photos, all either cropped or reduced slightly to post here, are to the right. Each shows some changes in these planets since the previous survey images the year before.
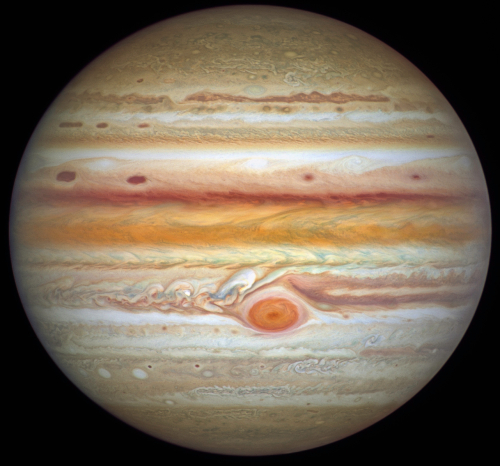
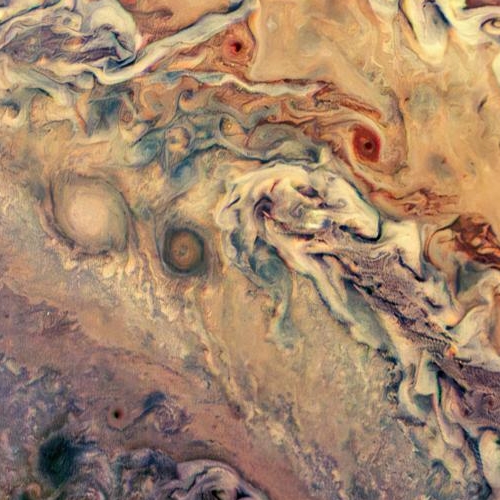
On Jupiter for example the equatorial region shows several new storms, with that band remaining a deep orange color longer than expected.
On Saturn the various bands have continued to show the frequent and extreme color changes that the telescope has detected since it began these survey images back in the 1990s.
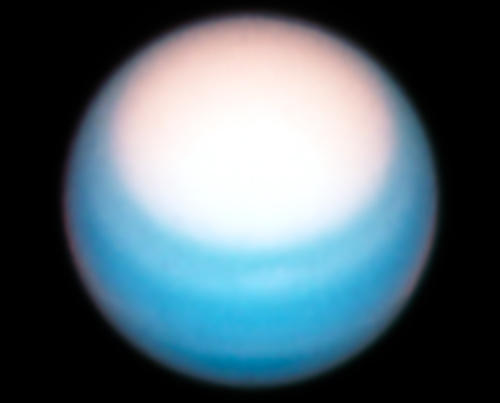
The photo of Uranus meanwhile looks at the gas giant’s northern polar regions, where it is presently spring. The increased sunlight and ultraviolet radiation has thus caused the upper atmosphere at the pole to brighten. The photo also confirms that the size of this bright “polar hood” continues to remain the same, never extending beyond the 43 degree latitude where scientists suspect a jet streams acts to constrain it.
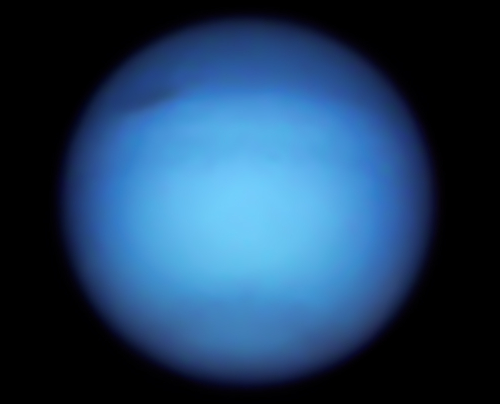
The image of Neptune, the farthest and thus hardest planet for Hubble to see, found that the dark spot in the planet’s northern hemisphere appears to have stopped moving south and now appears to be heading north. Also,
In 2021, there are few bright clouds on Neptune, and its distinct blue with a singular large dark spot is very reminiscent of what Voyager 2 saw in 1989.
NASA today released the annual survey of images taken each year by the Hubble Space Telescope of the large planets that comprise the outer solar system, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
These Hubble images are part of yearly maps of each planet taken as part of the Outer Planets Atmospheres Legacy program, or OPAL. The program provides annual, global views of the outer planets to look for changes in their storms, winds, and clouds. Hubble’s longevity, and unique vantage point, has given astronomers a unique chance to check in on the outer planets on a yearly basis. Knowledge from the OPAL program can also be extended far beyond our own solar system in the study of atmospheres of planets that orbit stars other than our Sun.
The four photos, all either cropped or reduced slightly to post here, are to the right. Each shows some changes in these planets since the previous survey images the year before.
On Jupiter for example the equatorial region shows several new storms, with that band remaining a deep orange color longer than expected.
On Saturn the various bands have continued to show the frequent and extreme color changes that the telescope has detected since it began these survey images back in the 1990s.
The photo of Uranus meanwhile looks at the gas giant’s northern polar regions, where it is presently spring. The increased sunlight and ultraviolet radiation has thus caused the upper atmosphere at the pole to brighten. The photo also confirms that the size of this bright “polar hood” continues to remain the same, never extending beyond the 43 degree latitude where scientists suspect a jet streams acts to constrain it.
The image of Neptune, the farthest and thus hardest planet for Hubble to see, found that the dark spot in the planet’s northern hemisphere appears to have stopped moving south and now appears to be heading north. Also,
In 2021, there are few bright clouds on Neptune, and its distinct blue with a singular large dark spot is very reminiscent of what Voyager 2 saw in 1989.