On the edge of Mars’ glacier country
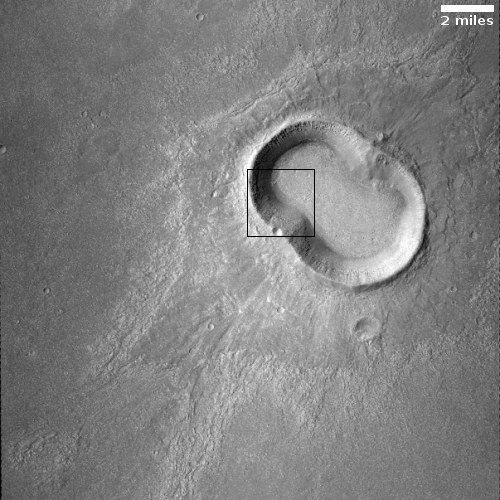
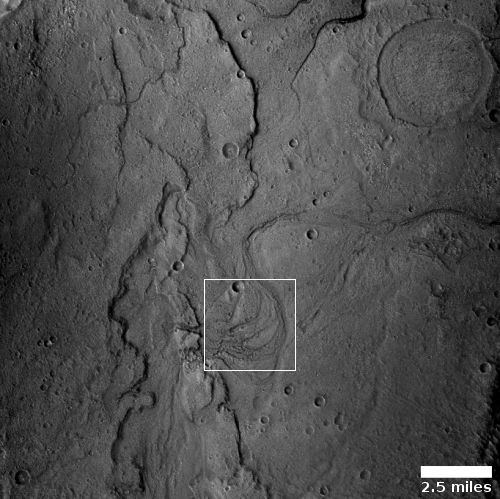
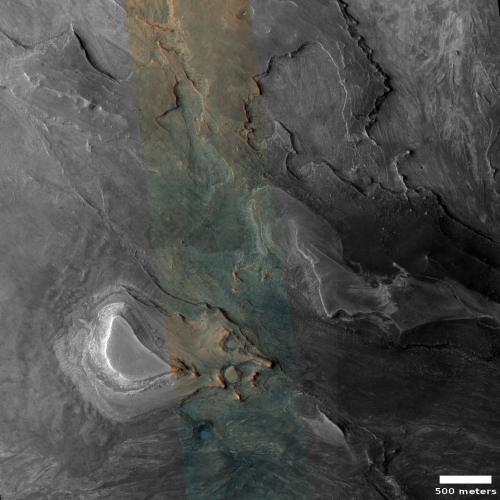
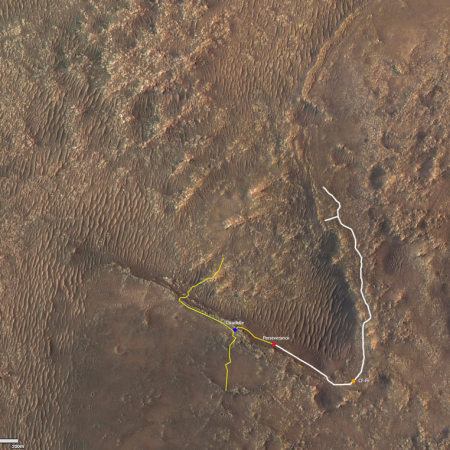
Today’s cool image sits right on the southern edge of Mars’ northern glacier country, at 29 degrees north latitude. The picture to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken of this location on June 4, 2021 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows what appears to be the exposed and scraped bedrock and mesas on the floor of an unnamed 60-mile-wide crater.
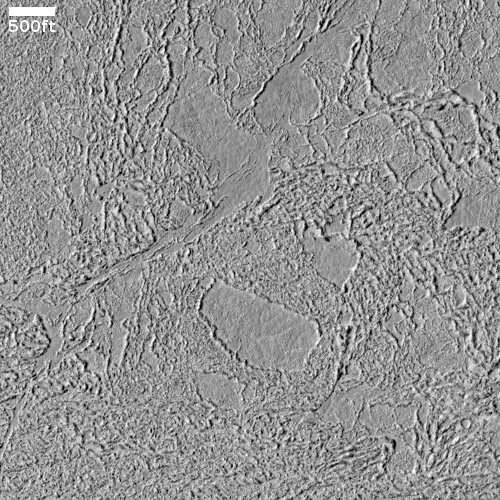
That scraped bedrock is quite beautiful, reminiscent of the bare carved mesas and bedrock one sees throughout the southwest of the United States. To hike from that central valley to the top of the bright mesa would be a fine experience, especially because of the suggested change in colors in the color strip.
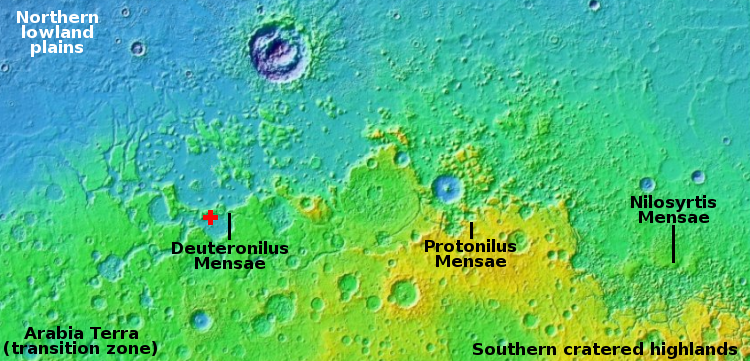
The overview map below gives more context.
» Read more
Today’s cool image sits right on the southern edge of Mars’ northern glacier country, at 29 degrees north latitude. The picture to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken of this location on June 4, 2021 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows what appears to be the exposed and scraped bedrock and mesas on the floor of an unnamed 60-mile-wide crater.
That scraped bedrock is quite beautiful, reminiscent of the bare carved mesas and bedrock one sees throughout the southwest of the United States. To hike from that central valley to the top of the bright mesa would be a fine experience, especially because of the suggested change in colors in the color strip.
The overview map below gives more context.
» Read more