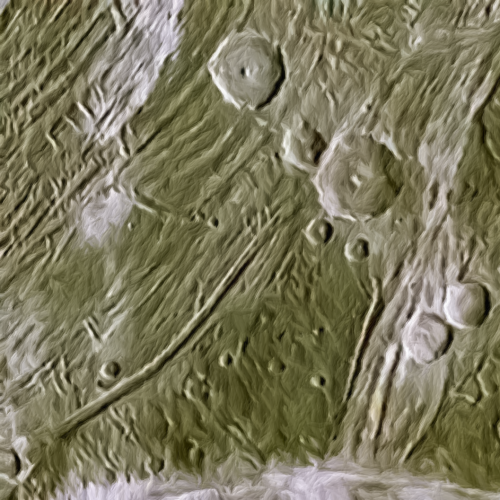
The nearest hill to China’s Zhurong
Cool image time! The science team for the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) today released a pair of images the camera took on June 28, 2021 of the nearest pitted cone to China’s Zhurong rover.
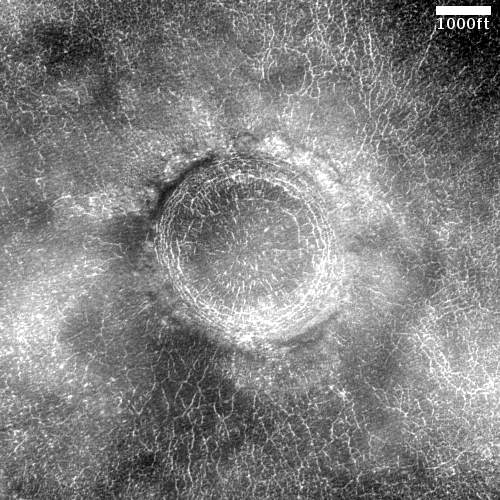
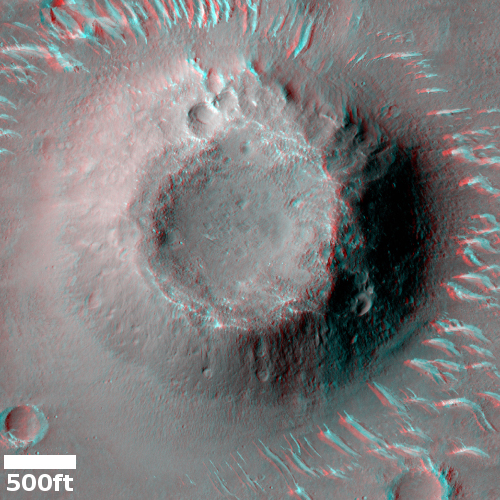
The stereo anaglyph to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, allows you, with blue-red 3D glasses, to see the cone in three dimensions. Quite impressive. As noted by Alfred McEwen of the Lunar & Planetary Laboratory in Arizona in his caption,
This image completed a stereo pair of a region just west of where the Zhurong rover landed in southern Utopia Planitia.
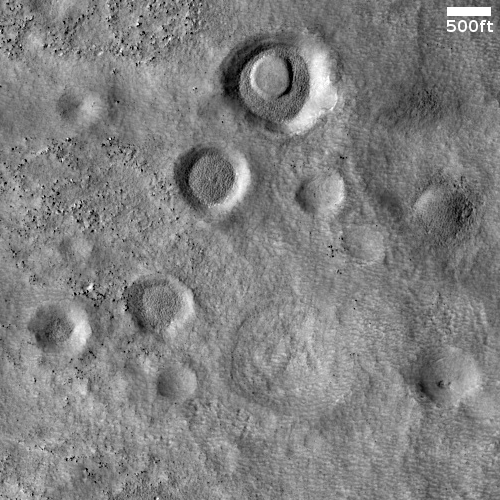
The cutout is from a portion of the stereo anaglyph, showing an enigmatic pitted cone. Is this cone composed of sediments or volcanic materials? The sharp bright features surrounding the cone are aeolian (wind-blown) landforms.
According to McEwan, the hill itself is about 200 to 220 feet high, with the pit at its top about 60-65 feet deep.
While McEwan has told me this cone would be his primary target if he was running Zhurong, it appears the Chinese are instead heading south toward the largest nearby crater, and on the way inspecting the parachute, fairing, and heat shield discarded just prior to landing.
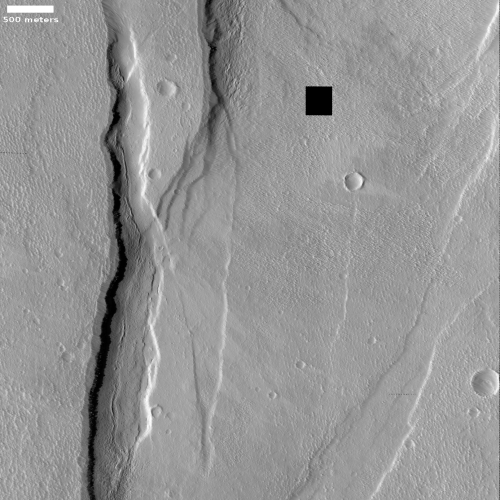
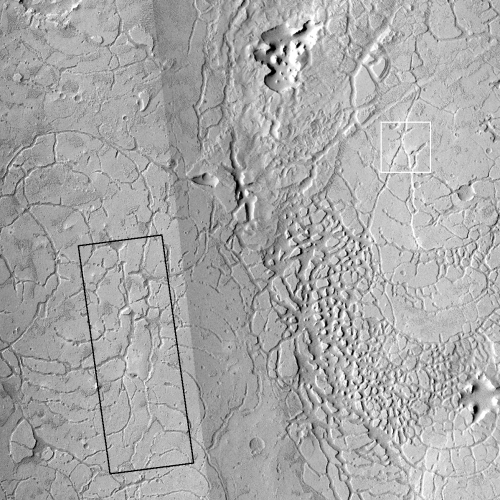
The mosaic below from three MRO context camera images provides a wider overview.
» Read more
Cool image time! The science team for the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) today released a pair of images the camera took on June 28, 2021 of the nearest pitted cone to China’s Zhurong rover.
The stereo anaglyph to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, allows you, with blue-red 3D glasses, to see the cone in three dimensions. Quite impressive. As noted by Alfred McEwen of the Lunar & Planetary Laboratory in Arizona in his caption,
This image completed a stereo pair of a region just west of where the Zhurong rover landed in southern Utopia Planitia.
The cutout is from a portion of the stereo anaglyph, showing an enigmatic pitted cone. Is this cone composed of sediments or volcanic materials? The sharp bright features surrounding the cone are aeolian (wind-blown) landforms.
According to McEwan, the hill itself is about 200 to 220 feet high, with the pit at its top about 60-65 feet deep.
While McEwan has told me this cone would be his primary target if he was running Zhurong, it appears the Chinese are instead heading south toward the largest nearby crater, and on the way inspecting the parachute, fairing, and heat shield discarded just prior to landing.
The mosaic below from three MRO context camera images provides a wider overview.
» Read more