Belgium company joins Starlab space station consortium

The Starlab design in 2025. Click
for original image.
The Starlab consortium, proposing to build its single-module large Starlab space station that will be launched on Starship, has now added the Belgium company Space Applications Services (SpaceApps) as both a partner and investor.
SpaceApps contributes deep experience in space systems, mission operations and payload integration with capabilities that include avionics, payload development, the end-to-end International Commercial Experiment Cubes (ICECubes) service, as well as mission integration and operations control software. The company also works closely with the European Space Agency and international partners, broadening Starlab’s access to global markets and research communities.
The Starlab consortium already includes the American companies Voyager Space and Northrop Grumman and the European company Airbus. It also has a partnership agreement with the European Space Agency. This new Belgium partnership further cements its place as Europe’s potential future space station after ISS is retired.
This deal is only one of several news stories in the past week signaling progress by this consortium. It has signed the American company Vivace to build the station’s main structure and its partner Northrop Grumman has successfully tested the rendezvous and docking technology its Cygnus cargo capsule will use to dock with Starlab. All in all this station appears to be assembling the pieces its needs.
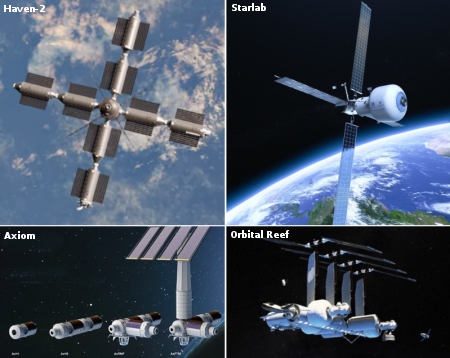
Below is my updated rankings of the four commercial stations under development:
» Read more

The Starlab design in 2025. Click
for original image.
The Starlab consortium, proposing to build its single-module large Starlab space station that will be launched on Starship, has now added the Belgium company Space Applications Services (SpaceApps) as both a partner and investor.
SpaceApps contributes deep experience in space systems, mission operations and payload integration with capabilities that include avionics, payload development, the end-to-end International Commercial Experiment Cubes (ICECubes) service, as well as mission integration and operations control software. The company also works closely with the European Space Agency and international partners, broadening Starlab’s access to global markets and research communities.
The Starlab consortium already includes the American companies Voyager Space and Northrop Grumman and the European company Airbus. It also has a partnership agreement with the European Space Agency. This new Belgium partnership further cements its place as Europe’s potential future space station after ISS is retired.
This deal is only one of several news stories in the past week signaling progress by this consortium. It has signed the American company Vivace to build the station’s main structure and its partner Northrop Grumman has successfully tested the rendezvous and docking technology its Cygnus cargo capsule will use to dock with Starlab. All in all this station appears to be assembling the pieces its needs.
Below is my updated rankings of the four commercial stations under development:
» Read more