China launches another 11 satellites for one of its mega-constellations
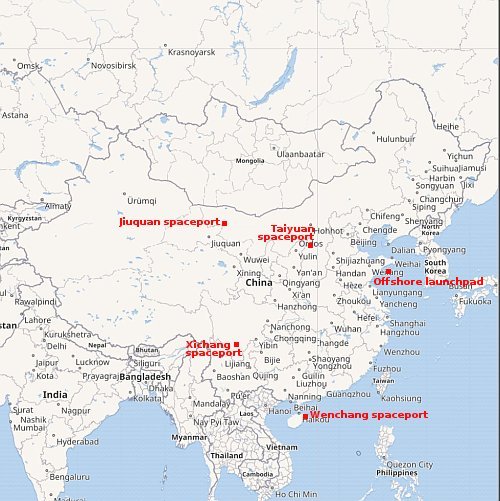
China today successfully placed another 11 satellites into orbit for one of its internet satellite constellations designed to compete with Starlink, its Smart Dragon-3 rocket lifting off from a launch platform off the eastern coast of China.
This was the fourth launch of satellites for Geely constellation. Though the rocket’s lower stages dropped into the South China Sea as well as the Pacific, doing no harm to habitable areas (as China routinely does when it launches from its interior spaceports), earlier this week the president of the Philippines, Ferdinand Marcos Jr., complained about China’s habit of not giving its neighbors sufficient warning prior to its coastal launches.
Marcos issued the statement after China launched its Long March 12 rocket on Monday [from its coastal Wenchang spaceport], which left debris within Philippine maritime territory. During an interview with the Philippine media delegation covering his state visit to India, the President said this was not the first time suspected Chinese rocket debris had ended up in Philippine waters.
“Well, it’s not the first time that this has happened. And, actually, if you look at the incidents, they did not commit any violations. There have been no casualties,” Marcos said. “We just wish that perhaps they could warn us a little earlier so that we know the path of the rocket, where the path is, and if they will release stages, where they will fall,” he added.
All par for the course for China. It not only doesn’t really care if it crashes rocket stages on the heads of its own people, it cares even less about dropping stages on neighboring countries.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
97 SpaceX
43 China
11 Rocket Lab
9 Russia
SpaceX still leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 97 to 74.

China today successfully placed another 11 satellites into orbit for one of its internet satellite constellations designed to compete with Starlink, its Smart Dragon-3 rocket lifting off from a launch platform off the eastern coast of China.
This was the fourth launch of satellites for Geely constellation. Though the rocket’s lower stages dropped into the South China Sea as well as the Pacific, doing no harm to habitable areas (as China routinely does when it launches from its interior spaceports), earlier this week the president of the Philippines, Ferdinand Marcos Jr., complained about China’s habit of not giving its neighbors sufficient warning prior to its coastal launches.
Marcos issued the statement after China launched its Long March 12 rocket on Monday [from its coastal Wenchang spaceport], which left debris within Philippine maritime territory. During an interview with the Philippine media delegation covering his state visit to India, the President said this was not the first time suspected Chinese rocket debris had ended up in Philippine waters.
“Well, it’s not the first time that this has happened. And, actually, if you look at the incidents, they did not commit any violations. There have been no casualties,” Marcos said. “We just wish that perhaps they could warn us a little earlier so that we know the path of the rocket, where the path is, and if they will release stages, where they will fall,” he added.
All par for the course for China. It not only doesn’t really care if it crashes rocket stages on the heads of its own people, it cares even less about dropping stages on neighboring countries.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
97 SpaceX
43 China
11 Rocket Lab
9 Russia
SpaceX still leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 97 to 74.