Philae found!
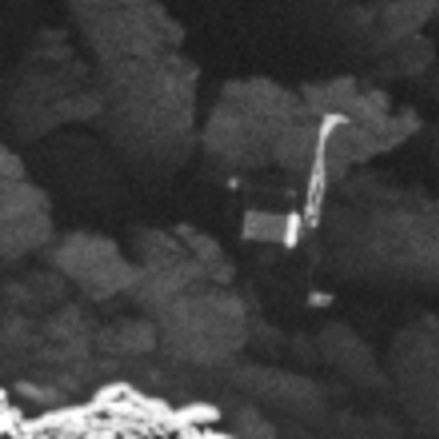

Less than a month before Rosetta’s mission ends the spacecraft’s high resolution camera has finally located Philae in its final resting spot on the surface of Comet 67P/C-G.
The images were taken on 2 September by the OSIRIS narrow-angle camera as the orbiter came within 2.7 km of the surface and clearly show the main body of the lander, along with two of its three legs. The images also provide proof of Philae’s orientation, making it clear why establishing communications was so difficult following its landing on 12 November 2014.
The image on the right clearly shows the lander on its side with one leg sticking up, as theorized by the Rosetta engineers based on the small amount of data they had received before Philae went dead. Furthermore, the wide image at the link above shows that the lander landed exactly as predicted by data, up against a wall — in this case a large boulder — which placed it in shadow most of the time.

Less than a month before Rosetta’s mission ends the spacecraft’s high resolution camera has finally located Philae in its final resting spot on the surface of Comet 67P/C-G.
The images were taken on 2 September by the OSIRIS narrow-angle camera as the orbiter came within 2.7 km of the surface and clearly show the main body of the lander, along with two of its three legs. The images also provide proof of Philae’s orientation, making it clear why establishing communications was so difficult following its landing on 12 November 2014.
The image on the right clearly shows the lander on its side with one leg sticking up, as theorized by the Rosetta engineers based on the small amount of data they had received before Philae went dead. Furthermore, the wide image at the link above shows that the lander landed exactly as predicted by data, up against a wall — in this case a large boulder — which placed it in shadow most of the time.