Scientists: Martian gullies formed by CO2 frost, not water flows
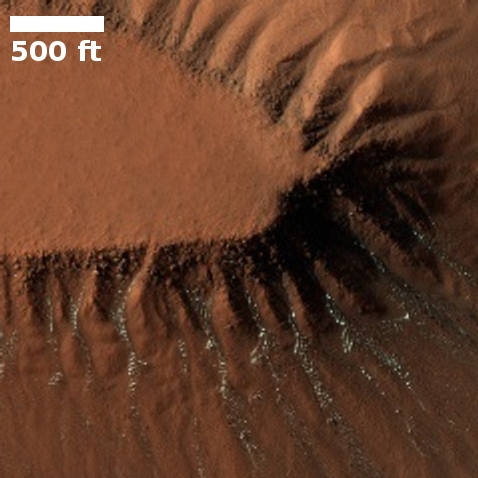

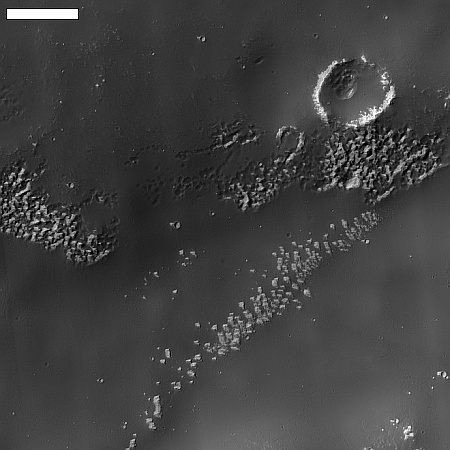
Dry ice frost on Martian cliffs. From a 2020 post.
Click for full image.
A new analysis of the gullies found on cliffs on Mars, usually on the interior rims of craters, has concluded that carbon dioxide frost is the cause of the erosion, not ancient flows of water.
This conclusion eliminates the need for liquid flowing water in the Martian past, at least in conjunction with gullies. From the paper’s conclusion:
These results show that CO2 frost is capable of producing Martian gully morphologies. Since flows powered by this process are known to be ongoing and capable of transporting the necessary volume of material, it is the simplest explanation for their formation. Variations in the frequency and fluidity of flows could have occurred over time due to variations in the CO2 cycle. CO2-driven gully formation would indicate that there was not necessarily regular, recurring meltwater during high-obliquity periods. This removes a constraint on recent climate, and also addresses a paradox: if obliquity regularly exceeds the current value as generally thought, and if gullies formed via snow melting at high obliquity, the Late Amazonian Epoch should have included regular snowmelt and widespread aqueous processes. Gully formation by CO2 frost processes is consistent with a cold-desert Late Amazonian with rare or small amounts of liquid water and little aqueous weathering, consistent with the observed mineralogy.
…Gullies, one of the most-discussed lines of evidence for liquid water on Mars, may in fact have no direct connection to H2O. CO2 frost-fluidized gully formation also has broader implications for geomorphology, widening an emerging field of new landform types and processes without Earth analogs. Similar processes could occur on other worlds with erodible substrates on steep slopes and volatile ices at their frost point, although we currently lack the high-resolution images needed to test this hypothesis. Such ices include N2 on Pluto and Triton, and SO2 on Io. [emphasis mine]
In other words, though the gullies appear at first glance to our Earth eyes to have been caused by water flowing downhill, in fact the data now suggests the annual CO2 frost cycle of Mars is the prime cause, even in the distant past. No surface water was required. And since no one has yet come up with a good model for liquid surface water even existing in the Martian past (the atmosphere being too cold and thin), this conclusion helps eliminate this conflict.
The paper also notes the lack of water likely eliminates the need for any planetary protection efforts at these gullies, as the lack of water makes the likelihood of any microbiology nil.
As these conclusions are based on lab work and analysis of images, there remains great uncertainty. Nonetheless, the results help reinforce the arguments that the geological features we see on Mars were formed not by flowing liquid water but by other processes, such as glaciers of ice.

Dry ice frost on Martian cliffs. From a 2020 post.
Click for full image.
A new analysis of the gullies found on cliffs on Mars, usually on the interior rims of craters, has concluded that carbon dioxide frost is the cause of the erosion, not ancient flows of water.
This conclusion eliminates the need for liquid flowing water in the Martian past, at least in conjunction with gullies. From the paper’s conclusion:
These results show that CO2 frost is capable of producing Martian gully morphologies. Since flows powered by this process are known to be ongoing and capable of transporting the necessary volume of material, it is the simplest explanation for their formation. Variations in the frequency and fluidity of flows could have occurred over time due to variations in the CO2 cycle. CO2-driven gully formation would indicate that there was not necessarily regular, recurring meltwater during high-obliquity periods. This removes a constraint on recent climate, and also addresses a paradox: if obliquity regularly exceeds the current value as generally thought, and if gullies formed via snow melting at high obliquity, the Late Amazonian Epoch should have included regular snowmelt and widespread aqueous processes. Gully formation by CO2 frost processes is consistent with a cold-desert Late Amazonian with rare or small amounts of liquid water and little aqueous weathering, consistent with the observed mineralogy.
…Gullies, one of the most-discussed lines of evidence for liquid water on Mars, may in fact have no direct connection to H2O. CO2 frost-fluidized gully formation also has broader implications for geomorphology, widening an emerging field of new landform types and processes without Earth analogs. Similar processes could occur on other worlds with erodible substrates on steep slopes and volatile ices at their frost point, although we currently lack the high-resolution images needed to test this hypothesis. Such ices include N2 on Pluto and Triton, and SO2 on Io. [emphasis mine]
In other words, though the gullies appear at first glance to our Earth eyes to have been caused by water flowing downhill, in fact the data now suggests the annual CO2 frost cycle of Mars is the prime cause, even in the distant past. No surface water was required. And since no one has yet come up with a good model for liquid surface water even existing in the Martian past (the atmosphere being too cold and thin), this conclusion helps eliminate this conflict.
The paper also notes the lack of water likely eliminates the need for any planetary protection efforts at these gullies, as the lack of water makes the likelihood of any microbiology nil.
As these conclusions are based on lab work and analysis of images, there remains great uncertainty. Nonetheless, the results help reinforce the arguments that the geological features we see on Mars were formed not by flowing liquid water but by other processes, such as glaciers of ice.