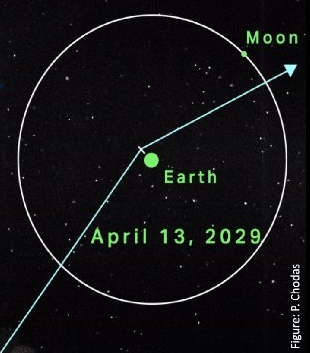
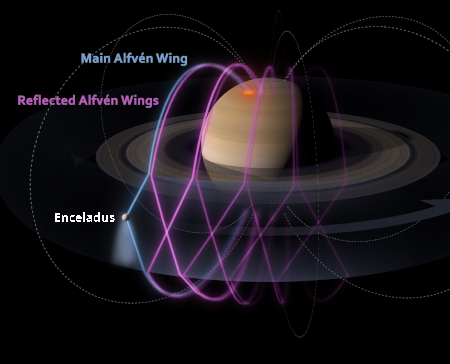
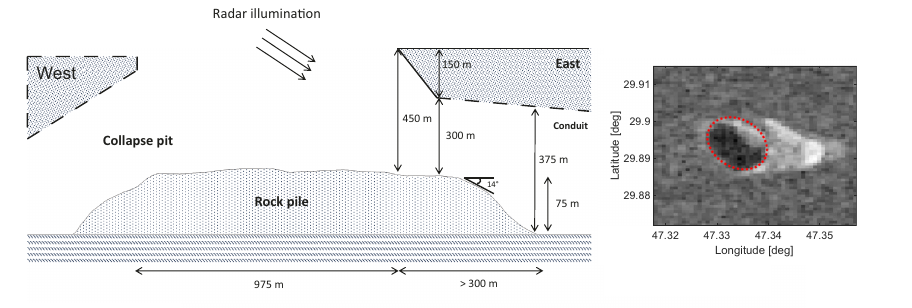
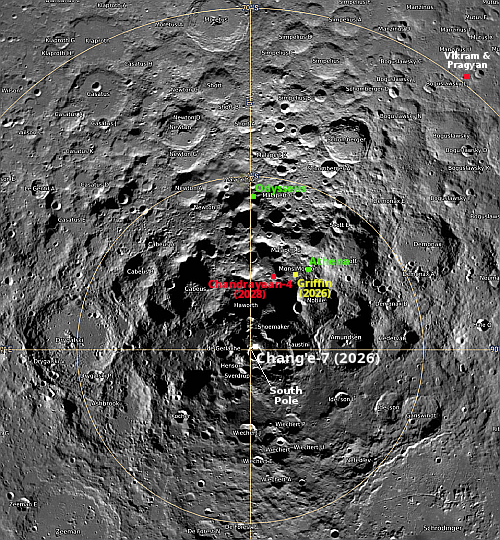
A sculptured Martian landscape
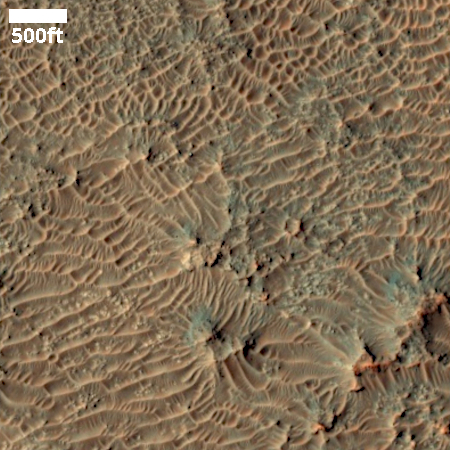
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped and sharpened to post here, was taken on December 4, 2025 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
The science team labels this landscape “olivine-rich plains”, which is a magnesium iron silicate mineral of some industrial value that is quite common on Earth. Its presence here suggests there could be other valuable minerals in this region.
I post the image because the landscape is so weird and beautiful. The orange color suggests these ridges are covered with dust, if not made of dust entirely. The small areas with a greenish tint that appear to mostly appear on north-facing cliffs could be frost, except this is in the southern hemisphere where north-facing cliffs get more sunlight. As it was autumn when this picture was taken frost is an unlikely explanation.
More likely the green indicates exposures of bedrock or coarser boulders.
» Read more
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped and sharpened to post here, was taken on December 4, 2025 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
The science team labels this landscape “olivine-rich plains”, which is a magnesium iron silicate mineral of some industrial value that is quite common on Earth. Its presence here suggests there could be other valuable minerals in this region.
I post the image because the landscape is so weird and beautiful. The orange color suggests these ridges are covered with dust, if not made of dust entirely. The small areas with a greenish tint that appear to mostly appear on north-facing cliffs could be frost, except this is in the southern hemisphere where north-facing cliffs get more sunlight. As it was autumn when this picture was taken frost is an unlikely explanation.
More likely the green indicates exposures of bedrock or coarser boulders.
» Read more