Perseverance looks to the far west
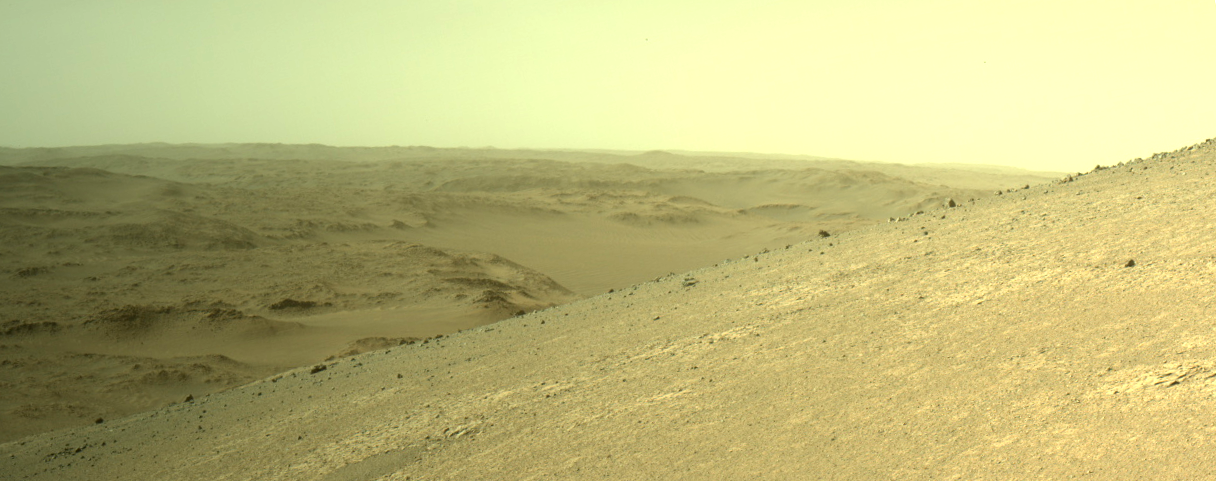
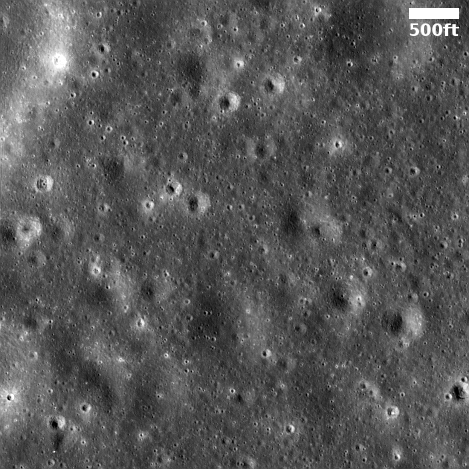
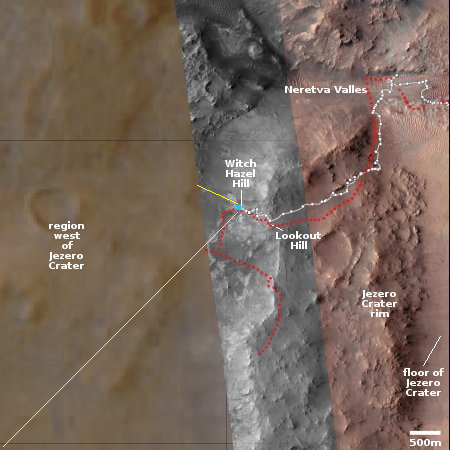
Cool image time! The panorama above, rotated, cropped, and enhanced to post here, was taken today by the left navigation camera on the Mars rover Perseverance. It gives us the first really good high elevation view of the mountainous terrain to the west of Jezero Crater
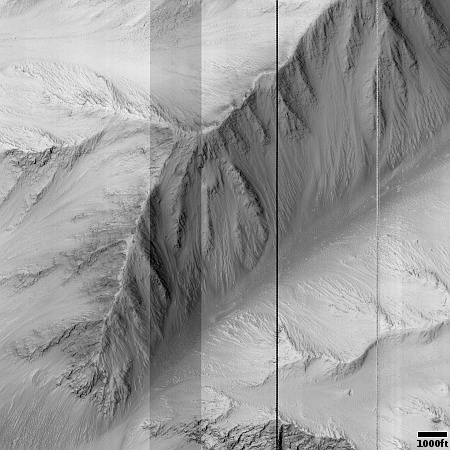
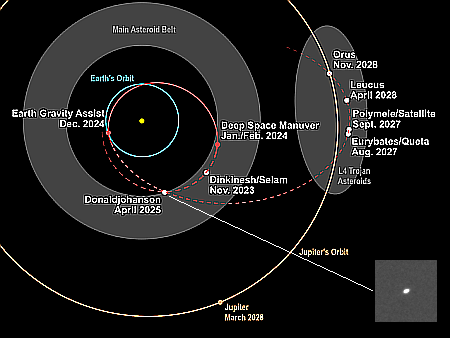
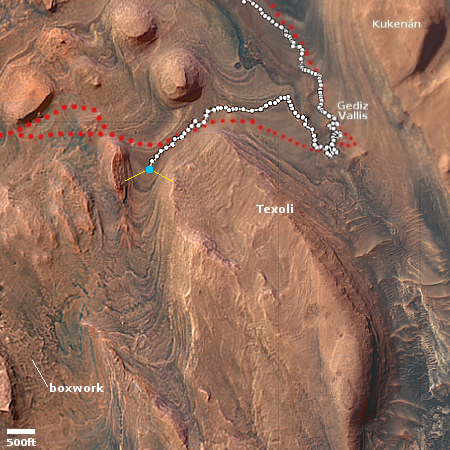
The overview map to the right provides the context. The blue dot marks the rover’s present position, with the white dotted line its past travels and the red dotted line its future planned route. The yellow lines are my approximate guess as to the area covered by the panorama above.
Neither the rover team nor the team running Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) that provides the high resolution images of this region have as yet updated the interactive map to show this western region in high resolution. My guess as to why is that the planned route is not yet heading that way (as indicated by the red dotted line). When Perseverance has finished its exploration of the outer slopes of the rim of Jezero Crater and heads west, this fuzzy area on this map will likely be replaced with high resolution data, similar to the rest of the map.
Nonetheless, if you look close, you can distinguish several geological features seen in the panorama, such as the large crater to the right and the ridge line to the left. Beyond are mountain chains and valleys, as well as many additional craters. This is truly a barren and alien place, though it has enormous potential for eventually becoming a friendlier environment.
All that is required is for humans to live there, with the natural desire to make it so.
Cool image time! The panorama above, rotated, cropped, and enhanced to post here, was taken today by the left navigation camera on the Mars rover Perseverance. It gives us the first really good high elevation view of the mountainous terrain to the west of Jezero Crater
The overview map to the right provides the context. The blue dot marks the rover’s present position, with the white dotted line its past travels and the red dotted line its future planned route. The yellow lines are my approximate guess as to the area covered by the panorama above.
Neither the rover team nor the team running Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) that provides the high resolution images of this region have as yet updated the interactive map to show this western region in high resolution. My guess as to why is that the planned route is not yet heading that way (as indicated by the red dotted line). When Perseverance has finished its exploration of the outer slopes of the rim of Jezero Crater and heads west, this fuzzy area on this map will likely be replaced with high resolution data, similar to the rest of the map.
Nonetheless, if you look close, you can distinguish several geological features seen in the panorama, such as the large crater to the right and the ridge line to the left. Beyond are mountain chains and valleys, as well as many additional craters. This is truly a barren and alien place, though it has enormous potential for eventually becoming a friendlier environment.
All that is required is for humans to live there, with the natural desire to make it so.