French startup The Exploration Company wins major contract from Germany
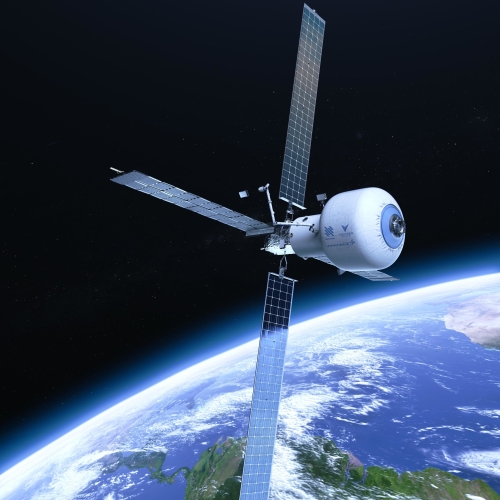
Germany’s space agency, DLR, announced today that it has signed a major contract with the French startup The Exploration Company to use its Nyx reusable capsule, still under development, for in-orbit weightlessness research.
On 20 February, during its DLR TecDays in Bonn, the German aerospace agency announced that it had signed a contract with The Exploration Company and would serve as an anchor customer for its microgravity research service. The contract secures space for 160 kilograms of scientific payloads aboard the inaugural flight of the Nyx Earth capsule in 2028. “We are supporting a startup that provides services that will be particularly valuable in a post-ISS era,” explained Dr. Walther Pelzer, Head of the German Space Agency at DLR.
Nyx’s main customer base was originally to serve as a cargo freighter for all of planned commercial space stations, having already been chosen by the European Space Agency as one of two European companies (the other being Thales-Alenia) to fly cargo demonstration missions to ISS in 2028.
This new contract illustrates the wider possibilities for profit for these capsules that has appeared in the past two years. If you can launch a returnable capsule to bring cargo, why not launch it to do in-orbit research and manufacturing? Varda in the U.S. has already demonstrated this possibility. Others apparently are now recognizing it as well.
Germany’s space agency, DLR, announced today that it has signed a major contract with the French startup The Exploration Company to use its Nyx reusable capsule, still under development, for in-orbit weightlessness research.
On 20 February, during its DLR TecDays in Bonn, the German aerospace agency announced that it had signed a contract with The Exploration Company and would serve as an anchor customer for its microgravity research service. The contract secures space for 160 kilograms of scientific payloads aboard the inaugural flight of the Nyx Earth capsule in 2028. “We are supporting a startup that provides services that will be particularly valuable in a post-ISS era,” explained Dr. Walther Pelzer, Head of the German Space Agency at DLR.
Nyx’s main customer base was originally to serve as a cargo freighter for all of planned commercial space stations, having already been chosen by the European Space Agency as one of two European companies (the other being Thales-Alenia) to fly cargo demonstration missions to ISS in 2028.
This new contract illustrates the wider possibilities for profit for these capsules that has appeared in the past two years. If you can launch a returnable capsule to bring cargo, why not launch it to do in-orbit research and manufacturing? Varda in the U.S. has already demonstrated this possibility. Others apparently are now recognizing it as well.