
Click for original image.
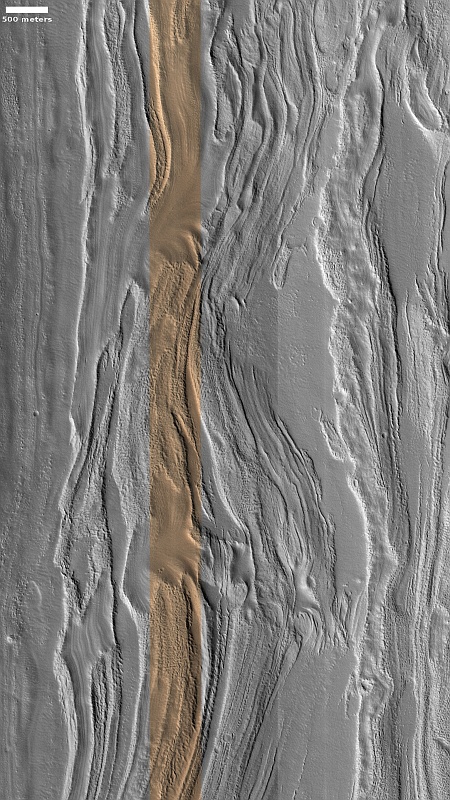
Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on October 27, 2024 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
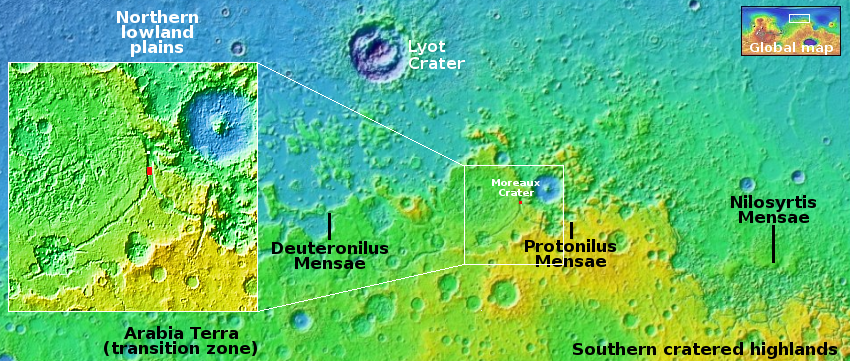
The red dot on the overview map above marks the location, about 35 miles southwest of the rim of 80-mile-wide Moreau Crater. This location is also deep within the 2,000-mile-long northern mid-latitude strip I label glacier country, as almost every high resolution picture from MRO shows glacial features.
This picture is no different, in that it shows the typical lineated parallel grooves seen on the surface of glaciers both on Earth and Mars, and especially found on glaciers flowing within a narrow canyon, as this glacier is. The parallel grooves are caused by the waxing and waning of the glacier. Each layer represents a past period when ice was being deposited on the surface, with the grooves indicates times when that ice was sublimating away. The graceful curves of the grooves is due to the drift of the glacier itself downhill.
This canyon is about seven miles wide at this point, formed from the confluence of two southerly tributaries to the south. The downward grade is to the north, but the low point is not where you would expect, out into the northern lowland plains. Instead, I have marked the low point in the inset with a white dot, inside the canyon itself. It appears this glacier drains into this low spot, but then this debris-covered ice appears to vanish.
It can’t really vanish, but there is a geological mystery here that involves the alien nature of Mars. For some reason the glacier dies at this point, its material sublimating away. Is there a drainage here that sends the ice to the north by underground passages? Your guess is as good as mine.
The lineated nature of this glacial flow however is no mystery in one respect. It is quite beautiful, as seen from space.