Dawn Aerospace small-scale rocket-powered airplane breaks the sound barrier

The crew and Mk-II Aurora
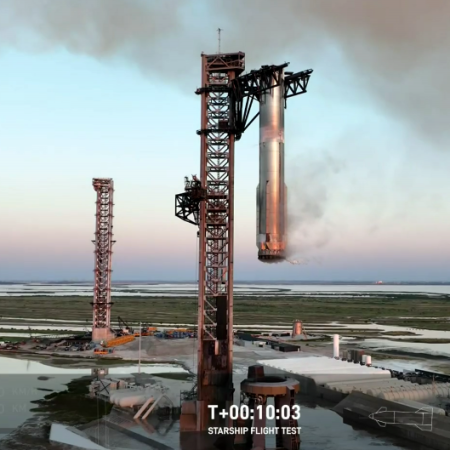
On November 12, 2024, the startup Dawn Aerospace for the first time flew its small-scale rocket-powered Mk-II Aurora unmanned airplane at speeds exceeding the speed of sound, becoming the first commercial airplane since the Concorde to break the sound barrier.
The company, operating as Dawn Hypersonics, achieved the milestone on 12 November 2024, with the Aurora surpassing the speed of sound for the first time, reaching Mach 1.1 and climbing to an altitude of 82,500 feet. This is over twice as high as commercial aircraft and marks the first time a civil aircraft has flown supersonic since Concorde. This achievement signifies a major step toward operational hypersonic travel and daily space access, establishing rocket-powered aircraft as a new class of ultra-high-performance vehicles.
The flight, conducted from New Zealand’s Glentanner Aerodrome near the base of Aoraki Mt Cook, exceeded its test target speeds and altitude of Mach 1.05 and 75,000 feet. The Aurora also set a global record, becoming the fastest aircraft to climb from ground level to 20 km (66,000 feet), completing the ascent in just 118.6 seconds. This beats the previous record, held by a highly modified F-15 ‘Streak Eagle’ in the 1970s, by 4.2 seconds.
It appears the company’s goals have changed and become less ambitious, at least for the moment. According to the company’s press materials now, the goal now is to sell Mk-II (and bigger versions) for suborbital hypersonic research, both for the military and private sector. Back in 2021 however the company described Mk-II as merely a preliminary test vehicle leading to the construction of a larger fullscale two-stage-to-orbit version that would take off and land on a runway and could be used to launch satellites to orbit.
In a sense, nothing might have really changed, other than the company realizing that it should try to make money on the Mk-II now, even as it flies and tests it in preparation for eventually building the larger orbital version. If Dawn begins to win contracts using this prototype, it will then have the resources (as well as the ability to raise more investment capital) to advance to larger more powerful version.

The crew and Mk-II Aurora
On November 12, 2024, the startup Dawn Aerospace for the first time flew its small-scale rocket-powered Mk-II Aurora unmanned airplane at speeds exceeding the speed of sound, becoming the first commercial airplane since the Concorde to break the sound barrier.
The company, operating as Dawn Hypersonics, achieved the milestone on 12 November 2024, with the Aurora surpassing the speed of sound for the first time, reaching Mach 1.1 and climbing to an altitude of 82,500 feet. This is over twice as high as commercial aircraft and marks the first time a civil aircraft has flown supersonic since Concorde. This achievement signifies a major step toward operational hypersonic travel and daily space access, establishing rocket-powered aircraft as a new class of ultra-high-performance vehicles.
The flight, conducted from New Zealand’s Glentanner Aerodrome near the base of Aoraki Mt Cook, exceeded its test target speeds and altitude of Mach 1.05 and 75,000 feet. The Aurora also set a global record, becoming the fastest aircraft to climb from ground level to 20 km (66,000 feet), completing the ascent in just 118.6 seconds. This beats the previous record, held by a highly modified F-15 ‘Streak Eagle’ in the 1970s, by 4.2 seconds.
It appears the company’s goals have changed and become less ambitious, at least for the moment. According to the company’s press materials now, the goal now is to sell Mk-II (and bigger versions) for suborbital hypersonic research, both for the military and private sector. Back in 2021 however the company described Mk-II as merely a preliminary test vehicle leading to the construction of a larger fullscale two-stage-to-orbit version that would take off and land on a runway and could be used to launch satellites to orbit.
In a sense, nothing might have really changed, other than the company realizing that it should try to make money on the Mk-II now, even as it flies and tests it in preparation for eventually building the larger orbital version. If Dawn begins to win contracts using this prototype, it will then have the resources (as well as the ability to raise more investment capital) to advance to larger more powerful version.