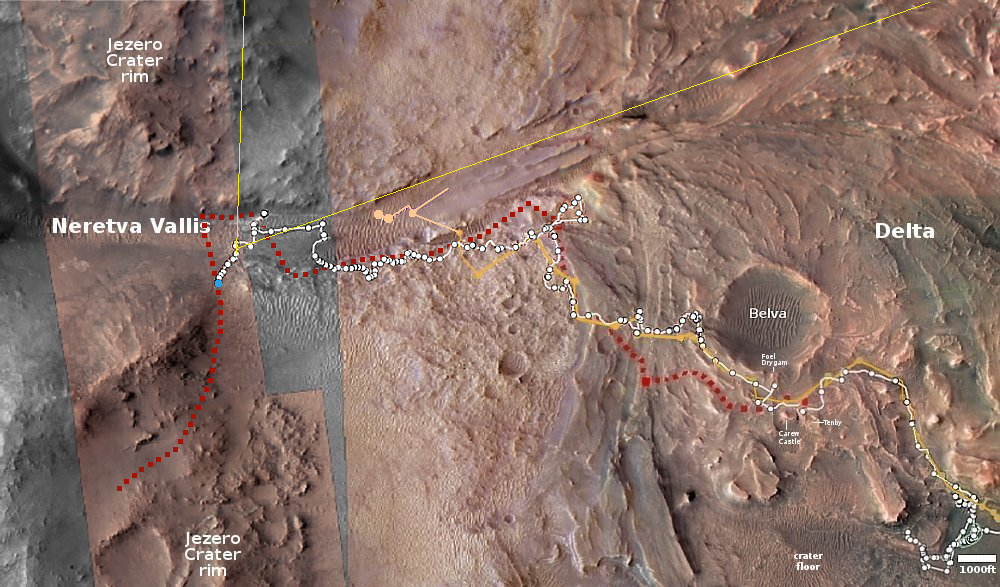
Will NASA give up on Starliner after its present contracts are completed?
According to an article today at Ars Technica, there are indications that NASA will not buy any further flights of Boeing’s Starliner capsule after it finally completes its present three-launch contract.
NASA hasn’t decided if it will require Boeing to launch another test flight before formally certifying Starliner for operational missions. If Starliner performs flawlessly after undocking and successfully lands this weekend, perhaps NASA engineers can convince themselves Starliner is good to go for crew rotation flights once Boeing resolves the thruster problems and helium leaks.
In any event, the schedule for launching an operational Starliner crew flight in less than a year seems improbable. Aside from the decision on another test flight, the agency also must decide whether it will order any more operational Starliner missions from Boeing. These “post-certification missions” will transport crews of four astronauts between Earth and the ISS, orbiting roughly 260 miles (420 kilometers) above the planet.
NASA has only given Boeing the “Authority To Proceed” for three of its six potential operational Starliner missions.
Apparently NASA has not decided whether to commit to any more Starliner operational manned flights behind those first three.
There are obvious good reasons for NASA’s hesitancy, most of which center on Boeing and its inability to get Starliner flying without technical problems. One that isn’t as obvious however is ISS itself. Boeing has taken so long in getting Starliner flying that the end of ISS in 2030 is now looming. There are only so many manned flights that NASA needs to buy before the station is decommissioned. Afterward the agency will still need to hire ferrying services to the new privately owned stations, but it is too far in the future to consider either SpaceX or Boeing for those decisions.
According to an article today at Ars Technica, there are indications that NASA will not buy any further flights of Boeing’s Starliner capsule after it finally completes its present three-launch contract.
NASA hasn’t decided if it will require Boeing to launch another test flight before formally certifying Starliner for operational missions. If Starliner performs flawlessly after undocking and successfully lands this weekend, perhaps NASA engineers can convince themselves Starliner is good to go for crew rotation flights once Boeing resolves the thruster problems and helium leaks.
In any event, the schedule for launching an operational Starliner crew flight in less than a year seems improbable. Aside from the decision on another test flight, the agency also must decide whether it will order any more operational Starliner missions from Boeing. These “post-certification missions” will transport crews of four astronauts between Earth and the ISS, orbiting roughly 260 miles (420 kilometers) above the planet.
NASA has only given Boeing the “Authority To Proceed” for three of its six potential operational Starliner missions.
Apparently NASA has not decided whether to commit to any more Starliner operational manned flights behind those first three.
There are obvious good reasons for NASA’s hesitancy, most of which center on Boeing and its inability to get Starliner flying without technical problems. One that isn’t as obvious however is ISS itself. Boeing has taken so long in getting Starliner flying that the end of ISS in 2030 is now looming. There are only so many manned flights that NASA needs to buy before the station is decommissioned. Afterward the agency will still need to hire ferrying services to the new privately owned stations, but it is too far in the future to consider either SpaceX or Boeing for those decisions.