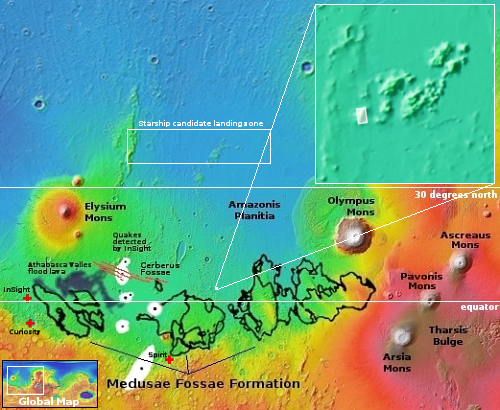
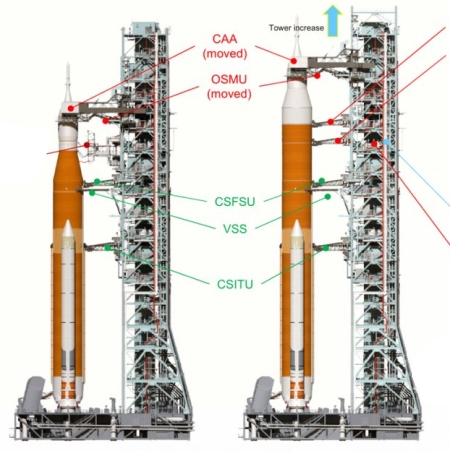
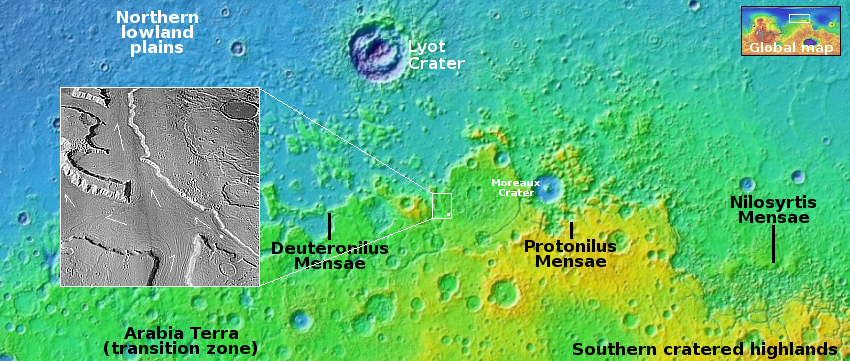
First New Glenn launch, set for October 13, 2024, only has an 8-day launch window
According to an article from Aviation Week today, in order for Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket to get its payload of two Mars orbiters on their way to Mars it must launch within a very short window lasting only eight days, beginning on the present launch date of October 13, 2024.
The Oct. 13-21 launch window is an ambitious goal. The aft and mid modules of New Glenn’s reusable first stage were recently attached, clearing the path for installation of the vehicle’s seven methane-fueled BE-4 engines, CEO Dave Limp noted in an Aug. 23 update on the X social media site.
A static hot-fire at New Glenn’s Florida launch complex is planned prior to launch. The company did not release the status of the New Glenn upper stage, which is to be powered by a pair of BE-3U engines fueled by liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen. A hot-fire of the second stage is also pending.
This launch will be the first ever for New Glenn. To get ready for that tight launch window it appears a great deal of work must be done in the next six weeks, some of which Blue Origin engineers will be doing for the very first time.
If there are any issues and that launch window is missed, the two NASA Escapade orbiters, built by Rocket Lab, will face a two-year delay until the next window to get to Mars re-opens. At that point New Glenn will likely do this launch with a dummy payload, since it needs to get off the ground in order to fulfill other launch contracts, including a 27-launch contract with Amazon for its Kuiper satellite constellation.
According to an article from Aviation Week today, in order for Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket to get its payload of two Mars orbiters on their way to Mars it must launch within a very short window lasting only eight days, beginning on the present launch date of October 13, 2024.
The Oct. 13-21 launch window is an ambitious goal. The aft and mid modules of New Glenn’s reusable first stage were recently attached, clearing the path for installation of the vehicle’s seven methane-fueled BE-4 engines, CEO Dave Limp noted in an Aug. 23 update on the X social media site.
A static hot-fire at New Glenn’s Florida launch complex is planned prior to launch. The company did not release the status of the New Glenn upper stage, which is to be powered by a pair of BE-3U engines fueled by liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen. A hot-fire of the second stage is also pending.
This launch will be the first ever for New Glenn. To get ready for that tight launch window it appears a great deal of work must be done in the next six weeks, some of which Blue Origin engineers will be doing for the very first time.
If there are any issues and that launch window is missed, the two NASA Escapade orbiters, built by Rocket Lab, will face a two-year delay until the next window to get to Mars re-opens. At that point New Glenn will likely do this launch with a dummy payload, since it needs to get off the ground in order to fulfill other launch contracts, including a 27-launch contract with Amazon for its Kuiper satellite constellation.