Intuitive Machines wants to land VIPER rover on Moon
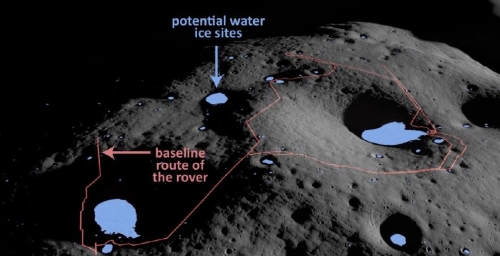
VIPER’s now canceled planned route at the Moon’s south pole
The lunar lander startup Intuitive Machines has now revealed it is putting together an industry partnership to bid on flying NASA’s VIPER lunar rover on its own largest lander, still under development.
In an Aug. 13 earnings call about its second quarter financial results, Intuitive Machines executives said they were planning to respond to a request for information (RFI) that NASA issued Aug. 9 seeking input from companies and organizations interested in taking over the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) mission that the agency said in July it would cancel.
Steve Altemus, chief executive of Intuitive Machines, said on the call that his company, which also responded to an earlier call for “expressions of interest” from NASA regarding VIPER, is working with other companies, universities and international partners on responding to NASA’s RFI. He did not identify any of those prospective partners.
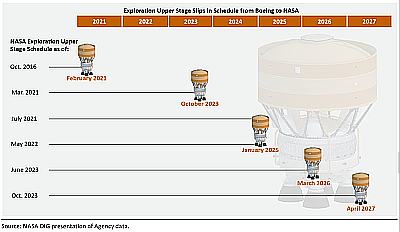
…NASA, in its RFI, said that prospective partners would be responsible for the costs of any final testing and other work on the rover itself, as well as delivering it to the lunar surface and operating it once there. NASA, in its July 17 announcement that it would cancel VIPER, said the agency would save at least $84 million by halting work now on the rover, now complete and undergoing environmental testing.
Whether this company can raise the capital to finish this mission, now that NASA has said it cannot, remains unclear. That it is trying, and NASA is not, illustrates however why NASA should get out of the business of building anything and just buy it from the private sector. NASA’s attempt to build VIPER went 3Xs over budget and is considerably behind schedule. Now the private sector see profits in finishing the job, which will in turn save the agency considerable money. Imagine if NASA had done this from the beginning. The savings would have been even greater, and VIPER might right now be even closer to launch.

VIPER’s now canceled planned route at the Moon’s south pole
The lunar lander startup Intuitive Machines has now revealed it is putting together an industry partnership to bid on flying NASA’s VIPER lunar rover on its own largest lander, still under development.
In an Aug. 13 earnings call about its second quarter financial results, Intuitive Machines executives said they were planning to respond to a request for information (RFI) that NASA issued Aug. 9 seeking input from companies and organizations interested in taking over the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) mission that the agency said in July it would cancel.
Steve Altemus, chief executive of Intuitive Machines, said on the call that his company, which also responded to an earlier call for “expressions of interest” from NASA regarding VIPER, is working with other companies, universities and international partners on responding to NASA’s RFI. He did not identify any of those prospective partners.
…NASA, in its RFI, said that prospective partners would be responsible for the costs of any final testing and other work on the rover itself, as well as delivering it to the lunar surface and operating it once there. NASA, in its July 17 announcement that it would cancel VIPER, said the agency would save at least $84 million by halting work now on the rover, now complete and undergoing environmental testing.
Whether this company can raise the capital to finish this mission, now that NASA has said it cannot, remains unclear. That it is trying, and NASA is not, illustrates however why NASA should get out of the business of building anything and just buy it from the private sector. NASA’s attempt to build VIPER went 3Xs over budget and is considerably behind schedule. Now the private sector see profits in finishing the job, which will in turn save the agency considerable money. Imagine if NASA had done this from the beginning. The savings would have been even greater, and VIPER might right now be even closer to launch.