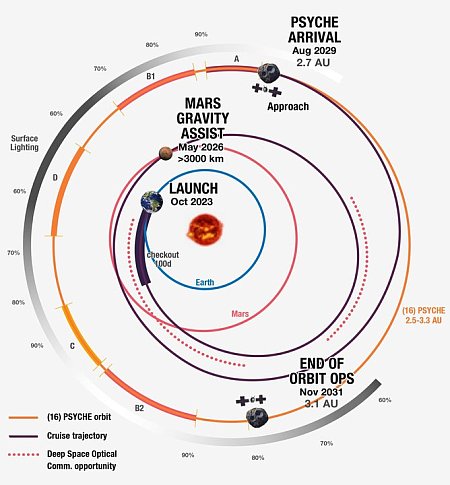
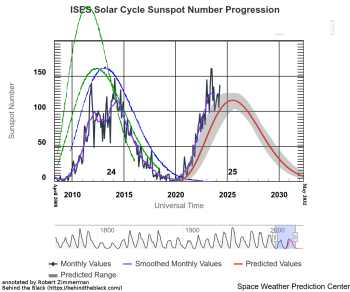
Astronomers discover nearby Earth-sized exoplanet only slightly hotter than Earth
Using the TESS space telescope as well as a number of ground-based telescopes astronomers have discovered an Earth-sized exoplanet only 40 light years away that has a surface temperature estimated to be about 107 degrees Fahrenheit, assuming it has no atmosphere.
The host star, called Gliese 12, is a cool red dwarf located almost 40 light-years away in the constellation Pisces. The star is only about 27% of the Sun’s size, with about 60% of the Sun’s surface temperature. The newly discovered world, named Gliese 12 b, orbits every 12.8 days and is Earth’s size or slightly smaller — comparable to Venus. Assuming it has no atmosphere, the planet has a surface temperature estimated at around 107 degrees Fahrenheit (42 degrees Celsius).
At the moment however scientists do not yet know if the exoplanet has an atmosphere or not. Follow-up observations using the Webb Space Telescope are planned to find this out. Based on the data presently available, the exoplanet could either be like Venus, too hot to sustain life, or like Earth, cooler with water and an atmosphere and thus very habitable.
Gliese 12 b could therefore become one of the primary targets for the first interstellar missions once humanity begins such exploration.
Using the TESS space telescope as well as a number of ground-based telescopes astronomers have discovered an Earth-sized exoplanet only 40 light years away that has a surface temperature estimated to be about 107 degrees Fahrenheit, assuming it has no atmosphere.
The host star, called Gliese 12, is a cool red dwarf located almost 40 light-years away in the constellation Pisces. The star is only about 27% of the Sun’s size, with about 60% of the Sun’s surface temperature. The newly discovered world, named Gliese 12 b, orbits every 12.8 days and is Earth’s size or slightly smaller — comparable to Venus. Assuming it has no atmosphere, the planet has a surface temperature estimated at around 107 degrees Fahrenheit (42 degrees Celsius).
At the moment however scientists do not yet know if the exoplanet has an atmosphere or not. Follow-up observations using the Webb Space Telescope are planned to find this out. Based on the data presently available, the exoplanet could either be like Venus, too hot to sustain life, or like Earth, cooler with water and an atmosphere and thus very habitable.
Gliese 12 b could therefore become one of the primary targets for the first interstellar missions once humanity begins such exploration.