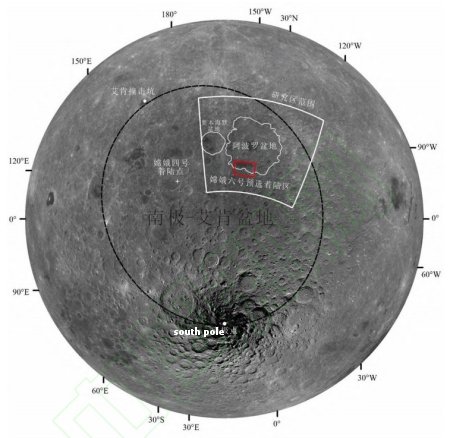
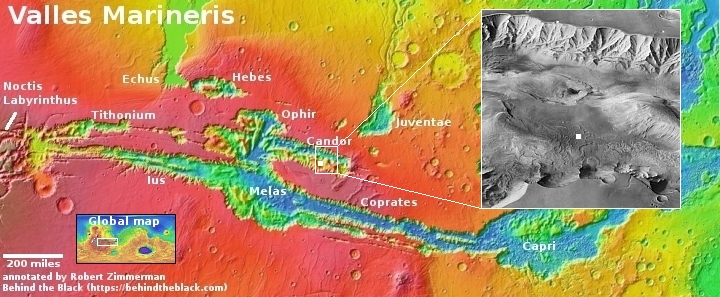
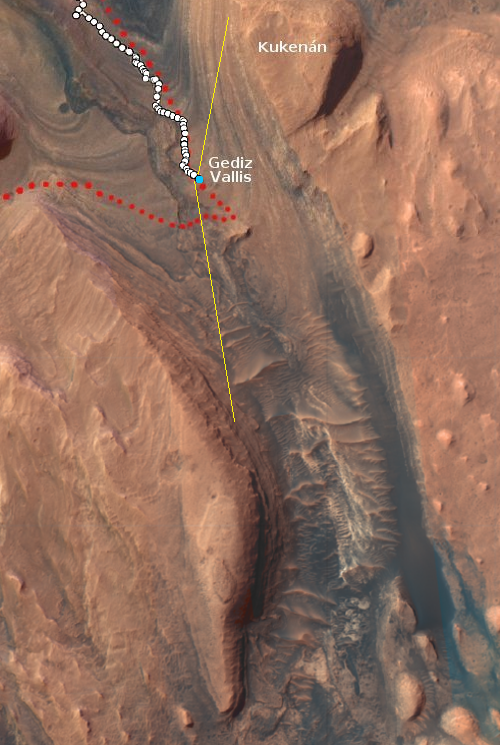
A French rocket startup enters the competition
A new French rocket startup, Hyprspace, has assembled the engine and body of a first stage demonstrator, dubbed Terminator, to be used to test that new engine in preparation for the first suborbital test launch.
On 4 May 2024, the company shared the first glimpse of the Terminator demonstrator at its facility in Le Haillan, France. According to the update, teams had worked through double shifts over a three-week period to prepare the demonstrator for its test firing. The test will be conducted at a Direction générale de l’armement missile test facility in Gironde, France. HyPrSpace has not yet revealed when the test is expected to take place.
This engine will eventually be used in the company’s planned orbital Baguette-1 rocket for launching smallsats.
We now have at least five European rocket startups, three in Germany (Rocket Factory Augsburg, Isar, Hyimpulse), one in Spain (PLD), and one in France (Hyprspace). We also have Avio in Italy taking over ownership from Arianespace of its Vega family of rockets. That company is about to begin static fire testing a Vega-C upper stage, its engine nozzle completely redesigned following a launch failure. It hopes to resume flying by the end of the year.
A new French rocket startup, Hyprspace, has assembled the engine and body of a first stage demonstrator, dubbed Terminator, to be used to test that new engine in preparation for the first suborbital test launch.
On 4 May 2024, the company shared the first glimpse of the Terminator demonstrator at its facility in Le Haillan, France. According to the update, teams had worked through double shifts over a three-week period to prepare the demonstrator for its test firing. The test will be conducted at a Direction générale de l’armement missile test facility in Gironde, France. HyPrSpace has not yet revealed when the test is expected to take place.
This engine will eventually be used in the company’s planned orbital Baguette-1 rocket for launching smallsats.
We now have at least five European rocket startups, three in Germany (Rocket Factory Augsburg, Isar, Hyimpulse), one in Spain (PLD), and one in France (Hyprspace). We also have Avio in Italy taking over ownership from Arianespace of its Vega family of rockets. That company is about to begin static fire testing a Vega-C upper stage, its engine nozzle completely redesigned following a launch failure. It hopes to resume flying by the end of the year.