Swiss company tests three-legged hopper for asteroid exploration on zero-G airplane
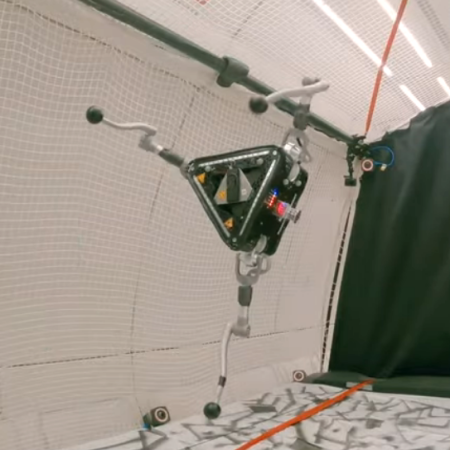

SpaceHopper in flight
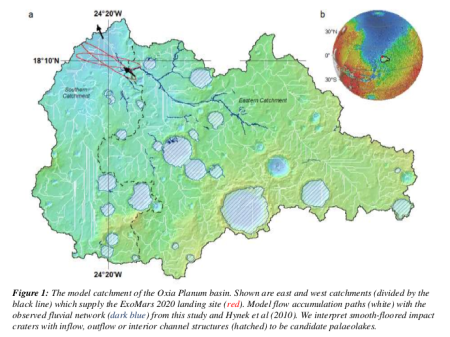
A Swiss company, ETH Zurich, has successfully tested the ability of an unmanned three-legged hopper, designed to explore asteroids by hoping in the light gravity, to orient itself using its legs by flying on a zero-G airplane.
The picture to the right is a screen capture from the video embedded below.
All nine leg motors [three per leg] work together to launch the SpaceHopper high off the asteroid’s surface when jumping. As the robot is subsequently in flight, it maintains its upright orientation by selectively extending or withdrawing its legs to shift its center of mass as needed. Upon landing, its legs flex to absorb impact and to keep the bot from falling over.
During zero-G on the airplane flights the hopper successfully jumped, then used its legs to correctly orient itself afterward.
Developing this hopper was initially a student project, and its success has gotten it upgraded, still led by those students.
» Read more

SpaceHopper in flight
A Swiss company, ETH Zurich, has successfully tested the ability of an unmanned three-legged hopper, designed to explore asteroids by hoping in the light gravity, to orient itself using its legs by flying on a zero-G airplane.
The picture to the right is a screen capture from the video embedded below.
All nine leg motors [three per leg] work together to launch the SpaceHopper high off the asteroid’s surface when jumping. As the robot is subsequently in flight, it maintains its upright orientation by selectively extending or withdrawing its legs to shift its center of mass as needed. Upon landing, its legs flex to absorb impact and to keep the bot from falling over.
During zero-G on the airplane flights the hopper successfully jumped, then used its legs to correctly orient itself afterward.
Developing this hopper was initially a student project, and its success has gotten it upgraded, still led by those students.
» Read more