Lucy’s first encounter with an asteroid produced surprises

At the 55th annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference presently being held in Texas, the science team for the Lucy asteroid mission presented their first papers outlining what they learned during the spacecraft’s first asteroid encounter, flying past the main belt asteroid Dinkinesh on November 1, 2023.
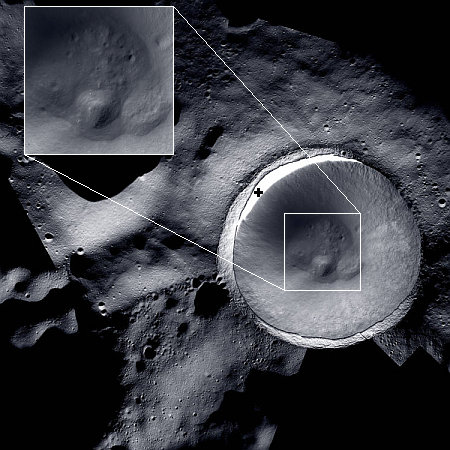
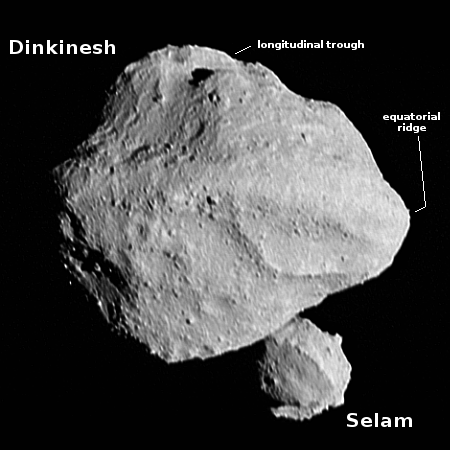
To the right is the the best image taken at closest approach, at about 270 miles distance, annotated to include the analysis of Dinkinesh’s shape by scientists. As noted in the summary paper [pdf], the asteroid is about a half mile in diameter, and appears to have an equatorial ridge, similar to the ridges found on the near-Earth rubble-pile asteroids Bennu or Ryugu. Dinkinesh is not a rubble pile, however. Though boulder-strewn, it appears more solid, and even has what the scientists call a longitudinal trough, as indicated in the picture.
The ridge overlays the trough implying that it is the younger of the two structures. However, there is as yet no information to better constrain their relative ages, and thus they could potentially have formed in the same event. Indeed, Dinkinesh’s ridge and trough are likely the result of mass failure and the reaccretion of material, and may both be linked to the formation of Selam.
That flyby had produced one major surprise, the existence of a smaller satellite asteroid orbiting Dinkinesh, now dubbed Selam. It is shown in the lower left, as it appeared from behind the main asteroid as Lucy flew past. A later picture however revealed an even greater surprise.
» Read more

At the 55th annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference presently being held in Texas, the science team for the Lucy asteroid mission presented their first papers outlining what they learned during the spacecraft’s first asteroid encounter, flying past the main belt asteroid Dinkinesh on November 1, 2023.
To the right is the the best image taken at closest approach, at about 270 miles distance, annotated to include the analysis of Dinkinesh’s shape by scientists. As noted in the summary paper [pdf], the asteroid is about a half mile in diameter, and appears to have an equatorial ridge, similar to the ridges found on the near-Earth rubble-pile asteroids Bennu or Ryugu. Dinkinesh is not a rubble pile, however. Though boulder-strewn, it appears more solid, and even has what the scientists call a longitudinal trough, as indicated in the picture.
The ridge overlays the trough implying that it is the younger of the two structures. However, there is as yet no information to better constrain their relative ages, and thus they could potentially have formed in the same event. Indeed, Dinkinesh’s ridge and trough are likely the result of mass failure and the reaccretion of material, and may both be linked to the formation of Selam.
That flyby had produced one major surprise, the existence of a smaller satellite asteroid orbiting Dinkinesh, now dubbed Selam. It is shown in the lower left, as it appeared from behind the main asteroid as Lucy flew past. A later picture however revealed an even greater surprise.
» Read more