Luna Lee – Voodoo Child
A evening pause: The Jimi Hendrix song, played on a customized gayageum. I do not think the Koreans who created this instrument ever expected this kind of music to come from it.
Hat tip Mike Nelson.
A evening pause: The Jimi Hendrix song, played on a customized gayageum. I do not think the Koreans who created this instrument ever expected this kind of music to come from it.
Hat tip Mike Nelson.
The British parliament has voted 438 to 20 to approve prime minister Boris Johnson’s demand that they hold general elections on December 12th in exchange for getting an extension to remain in the European Union until the end of January.
Though polls suggest that the public supports Johnson strongly in his effort to leave the EU, an actual election is something completely different. We shall now see if it will really happen.
Personally, I am pessimistic. The opposition to Brexit, like the opposition to Trump in the U.S., has never accepted the results of their previous defeats. I doubt any who voted against Brexit then have changed their mind since, while their unrelenting effort (like the resistance to Trump) has likely worn down its support.
On Christmas Eve 1968 three Americans became the first humans to visit another world. What they did to celebrate was unexpected and profound, and will be remembered throughout all human history. Genesis: the Story of Apollo 8, Robert Zimmerman's classic history of humanity's first journey to another world, tells that story, and it is now available as both an ebook and an audiobook, both with a foreword by Valerie Anders and a new introduction by Robert Zimmerman.
The print edition can be purchased at Amazon or any other book seller. If you want an autographed copy the price is $60 for the hardback and $45 for the paperback, plus $8 shipping for each. Go here for purchasing details. The ebook is available everywhere for $5.99 (before discount) at amazon, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
"Not simply about one mission, [Genesis] is also the history of America's quest for the moon... Zimmerman has done a masterful job of tying disparate events together into a solid account of one of America's greatest human triumphs."--San Antonio Express-News
A federal judge has reinstated the $250 million lawsuit by Covington teenager Nicolas Sandmann against the Washington Post for slandering him during its news coverage.
U.S. District Judge William Bertelsman agreed to permit discovery on three of 33 allegedly libelous statements in The Post’s coverage of the Jan. 18 incident pertaining to teenager Nicholas Sandmann. The Post has insisted that its reporting was fair and accurate.
All three flagged statements from the newspaper’s coverage refer to Omaha Nation elder Nathan Phillips being blocked or impeded by Nicholas, a student at Covington Catholic High School, during their viral encounter at the Lincoln Memorial stairs.
Since the video of the event quite clearly shows that Sandmann never blocked anyone, that if anything Nathan Phillips pursued Sandmann, the Post is now very vulnerable to losing the suit. This decision also suggests that Sandmann’s lawsuits against CNN and NBC will also go forward.
Using raw Juno images, citizen scientist Gerald Eichstädt has created the processed and color enhanced image to the right, cropped to post here. From the Juno press release:
This view from NASA’s Juno spacecraft captures colorful, intricate patterns in a jet stream region of Jupiter’s northern hemisphere known as “Jet N3.”
Jupiter’s cloud tops do not form a simple, flat surface. Data from Juno helped scientists discover that the swirling bands in the atmosphere extend deep into the planet, to a depth of about 1,900 miles (3,000 kilometers). At center right, a patch of bright, high-altitude “pop-up” clouds rises above the surrounding atmosphere.
Some of the darker areas are darker mostly because they are lower and therefore in shadow.
The raw image was taken on May 29, 2019 when Juno was about 6,000 miles away. Unfortunately, they do not provide a scale, but I suspect that the image is probably close to the size of the entire Earth.
Now available in hardback and paperback as well as ebook!
From the press release: In this ground-breaking new history of early America, historian Robert Zimmerman not only exposes the lie behind The New York Times 1619 Project that falsely claims slavery is central to the history of the United States, he also provides profound lessons about the nature of human societies, lessons important for Americans today as well as for all future settlers on Mars and elsewhere in space.
“Zimmerman’s ground-breaking history provides every future generation the basic framework for establishing new societies on other worlds. We would be wise to heed what he says.” —Robert Zubrin, founder of the Mars Society.
All editions are available at Amazon, Barnes & Noble, and all book vendors, with the ebook priced at $5.99 before discount. All editions can also be purchased direct from the ebook publisher, ebookit, in which case you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
Autographed printed copies are also available at discount directly from the author (hardback $29.95; paperback $14.95; Shipping cost for either: $6.00). Just send an email to zimmerman @ nasw dot org.
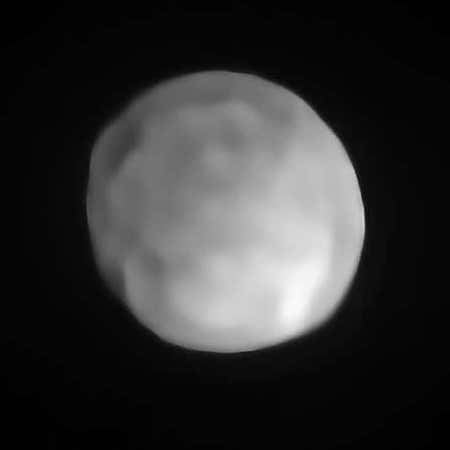

A new image of the asteroid Hygiea has revealed that this main belt object is actually spherical, making it the smallest spherical asteroid so far discovered and suggesting that it could be defined as a planet.
The image, taken by the Very Large Telescope (VLT) in Chile, is to the right. The asteroid was first discovered in 1849 and is the fourth largest in the asteroid belt, after Ceres, Pallas, and Vesta, with a diameter of 267 miles.
The image once again challenges the definition of what makes a planet. It also makes difficult the vague term “dwarf planet.” At what point does a dwarf become a full planet? This has never been clarified, which is why I tend to avoid using the term dwarf planet.
In my many interviews of planetary scientists, they generally dismiss the IAU’s poor definition of a planet and define a planet as anything that has settled into a spherical shape. In the case of Hygiea, that seems to apply.
An evening pause: It is always important to recognize that our heavy machinery is really nothing more than an extension of our hands and arms. This video proves it.
Hat tip Martin Kaselis.
Leaving Earth: Space Stations, Rival Superpowers, and the Quest for Interplanetary Travel, can be purchased as an ebook everywhere for only $3.99 (before discount) at amazon, Barnes & Noble, all ebook vendors, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit.
If you buy it from ebookit you don't support the big oppressive tech companies and I get a bigger cut much sooner.
"Leaving Earth is one of the best and certainly the most comprehensive summary of our drive into space that I have ever read. It will be invaluable to future scholars because it will tell them how the next chapter of human history opened." -- Arthur C. Clarke
This very interesting article does a nice job of reviewing the history of ISIS since 2010, the year that the Obama administration released just killed ISIS leader Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, using multiple news sources and stories.
Here is a rough timeline:
Obama presidency:
2008: ISIS forces estimated to be about 700 fighters, holding practically no ground.
2010: al-Baghdadi is released.
2011: al-Baghdadi takes over ISIS.
2014: Obama refers to ISIS as a “JV team.”
2015: ISIS forces estimated to be between 20,000 to 31,000 fighters.
2015: ISIS establishes global terrorism network resulting in terrorist attacks worldwide.
2016: ISIS occupies 17,500 square miles, with 35,000 fighters.
Trump presidency:
2017: (July): ISIS pushed out of Mosul.
2017 (October) ISIS in full retreat to U.S. backed forces, loses its capital Raqqa.
2017 (December): ISIS forces now estimated to be 1,000 fighters, holding 1,900 square miles.
2019: al-Baghadi is killed.
At this moment ISIS remains a threat, but a significantly reduced one from its peak in 2016.
Like Trump or hate him, an objective look at how he has handled this issue versus Obama’s handling once again puts the victory mark in Trump’s column. Obama’s policy made things worse in the Arab Middle East. Trump has so far improved things.
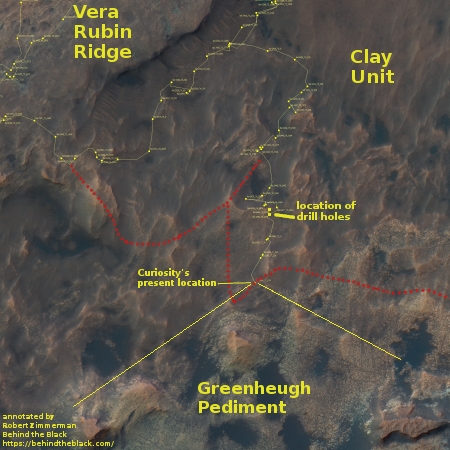
Summary: Curiosity finally on the move after several months drilling two adjacent holes in the clay unit. Yutu-2 continues roving west, has it now operates during its eleventh lunar day on the far side of the Moon.
For the updates in 2018 go here. For a full list of updates before February 8, 2018, go here.
Click for original full image.
For the overall context of Curiosity’s travels, see my March 2016 post, Pinpointing Curiosity’s location in Gale Crater.
I have not done any of my regular rover updates since May 30, 2019 because it was simpler to do individual updates for both Curiosity and Yutu-2, the only working rovers presently on other worlds. (If things had gone well, which they did not, we would have had two other lunar rovers in the past six months, one from Israel and one from India, but both crashed during landing.)
However, since Curiosity is finally on the move after spending several months at one location, where it drilled two holes in the clay unit (the material from one used in a wet cup experiment to look for organic life) it is time to update my readers on where Curiosity is and where it is heading.
The first image above and to the right is an annotated overview of Curiosity’s present position, moving south to a line of buttes which scientists have determined delineates the transition from the clay unit to a new geological layer they have dubbed the Greenheugh Pedimont. The yellow lines indicate the area seen in the panorama below, created from two photographs (here and here) taken by the rover’s navigation camera.
» Read more
Another Democratic stronghold collapsing: Despite an $800 million dollar budget deficit, Chicago’s Democratic mayor is likely going to negotiate a big money increase to its striking school union.
I like the article’s title: “Chicago Mayor Learning that Eventually, You Run Out of Other People’s Money.”
The union is demanding an additional $38 million from the city, over and above what its members presently get. And based on the track record of every big-city Democratic mayor for the past half century, I guarantee they are going to get it, even though the city simply doesn’t have the money.
This quote also illustrates another consistent pattern since World War II:
In their eagerness to sate the appetite for tax dollars, public unions’ ever-escalating demands have made Chicago the only major city of the top five to lose population over the previous decade.
People always flee leftist strongholds, whether they be the Soviet Union, East Germany, North Korea, California, New York, or Chicago. And the only way any of these socialist/communist hellholes found they could stop the exodus was to make their territories the equivalent of prisons, surrounded by barbed wire and armed guards.
Capitalism in space: According to SpaceX’s CEO Gwynne Shotwell at a conference on October 25, the company is targeting the first unmanned cargo landing of Starship on the Moon by 2021, with manned missions shortly thereafter.
Shotwell, speaking at Baron Fund’s annual investment conference at the Metropolitan Opera House on Friday, gave an update on SpaceX’s goals for Starship. “We want Starship in orbit next year; we want to land it on the moon before 2022 with cargo and with people shortly thereafter,” Shotwell said.
However, much like Musk in his presentation last month, Shotwell hedged her estimate, saying that “every time I make a prediction about schedule I turn myself into a liar.”
If they even come close to doing this they will certainly make NASA’s SLS rocket look ridiculous. They began serious development of Starship in early 2019. Even if development takes twice as long as Shotwell’s prediction, they will be landing on the Moon in about six years, in 2025. SLS has been in development since 2004, and its total cost once launched is expected to be more than $25 billion, a cost that does not include an extra $1.6 billion NASA has said it needs to land on the Moon by 2024 and that Congress has so far refused to appropriate.
SpaceX meanwhile has raised $1.3 billion, from private sources, to build Starship.
If you were a customer which product would you buy?
Capitalism in space: SpaceX’s Crew Dragon capsule, planned for a launch abort test in December, has successfully completed a set of static fire engine tests of two of its SuperDraco launch abort engines.
They next plan a static fire test of all eight engines, followed by that launch abort flight. If all goes well with both, the only thing blocking SpaceX from launching its first manned mission early in 2020 will be the paperwork NASA is demanding they fill out prior to flight.
In a setback for its renewed digging effort, the mole drill on InSight has apparently bounced out of its drilled hole during the most recent drilling, soon after engineers had increased the rate of hammer strokes.
The image to the right shows the mole, the white cylinder on the left, with the scoop of the robot arm mostly covering the hole in its effort to pin the mole in position.
“While digging this weekend the mole backed about halfway out of the ground,” the mission announced via a pair of tweets Oct. 27. “Preliminary assessment points to unexpected soil properties as the main reason.”
…The mission added that one possibility is soil is falling in front of the mole, filling the hole. “Team continues to look over the data and will have a plan in the next few days.”
Without question the alien and fluffy properties of the soil appears to be the problem. Based on how the mole is leaning, I wonder if the left wall of the hole began to widen and collapse, as had the rest of the hole during initial drilling, thus defeating the purpose of the robot arm’s effort to pin the mole in place.
One of the Air Force’s two X-37B reusable mini-shuttle’s has landed, completing a 780-day record mission.
This was the fifth mission of the X-37B Orbital Test Vehicle. It flew for 780 days during this mission, breaking its own record by being in orbit for more than two years. As of today, the total number of days spent on-orbit for the entire test vehicle program is 2,865 days, the Air Force said. The spaceplane originally was designed to fly for just 270 days.
The mission had launched on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket on September 7, 2017, in a deal that had been worked out with the Air Force in June under relatively short notice.
Not surprisingly, there is no word when the next X-37B mission will fly, likely using the Air Force’s other spacecraft.
Capitalism in space: The fourth flight of Exos Aerospace’s suborbital rocket failed yesterday when the rocket’s parachute apparently failed to deploy, sending the rocket crashing to the ground.
A good overview of the company and SARGE’s history can be found here. The live stream of today’s launch is embedded below the fold, cued to just before launch.
This failure appears at this moment to be far more serious than their previous failure, where the rocket shutdown prematurely but safely landed without damage using its chutes.
» Read more
Welcome to Venezuela: PG&E will impose its second planned blackout today for almost a million customers in northern California, all in a vain attempt to prevent wildfires.
Leftist politicians like to blame climate change for these fires, but there is no scientific evidence for such a claim. Instead, the evidence points to the policies of those very leftist politicians, who have been micromanaging PG&E for almost a decade, preventing it from doing proper maintenance, while also forbidding the clearing of brush from state lands.
If you live in California be warned. This is only a taste of what your dismal future is going to be, especially as I see no sign that the voters have any intention of firing these politicians. If anything, election trends have been to give them more power.
Earlier this week Japan announced that it planned to become a partner in NASA’s Artemis program to build a space station in lunar orbit.
That announcement was very vague. Yesterday an official from Mitsubishi Heavy Industries might have offered the first real detail, suggesting that its new H3 rocket, scheduled for its first lift-off in 2020, could be used to launch components for Artemis, as early as 2025. The official described one option for using the H3, sending Japan’s upgraded ISS cargo freighter, the HTV-X, to Gateway in 2025 or 2026.
Launching an HTV-X cargo vessel to the gateway would require two H3 launches, he said. The first launch would send an HTV-X into an orbit around the Earth, he said. The second launch would send up an upper stage with an enlarged fuel tank to dock with the HTV-X and propel it to the Gateway, he said.
What was not stated was who will pay for this. The U.S.? Japan? Either way Mitsubishi, which has failed badly in garnering any of the international commercial satellite business for its H2B rocket, is clearly trying to attract business now for the H3 rocket, supposedly designed to be cheaper to launch.
Capitalism in space: Firefly has agreed to purchase Aerojet Rocketdyne’s AR-1 engine to use in it larger Beta rocket, presently under development.
Though deal also includes help from Aerojet for the development of Firefly’s smaller Alpha rocket,
…the companies made clear that the centerpiece of the agreement was the potential use of the AR1 on Firefly’s Beta rocket, giving Aerojet a customer for the engine while allowing Firefly to increase the performance of the medium-class rocket.
Beta is intended to fill the niche once served by ULA’s Delta 2. “It has left an opportunity for a modern launcher to come in at perhaps a better price point than Delta 2, and can address some of the new missions coming out,” such as small geostationary orbit satellites, he said.
The target payload capacity of Beta is eight metric tons to low Earth orbit, a size Markusic explained was driven by the market and which, in turn, led to a design change for the rocket. Beta’s original design resembled the Alpha but with two additional first stages as side boosters, a triple-core design like the Delta 4 Heavy or Falcon Heavy. Beta is now a single-core vehicle with an AR1 engine in its first stage.
Aerojet Rocketdyne had gotten a lot of Congressional money to develop the AR-1 with the intent it would be used in ULA’s Vulcan rocket. ULA has instead chosen Blue Origin’s BE-4 engine, leaving Aerojet Rocketdyne high and dry without any customers. This deal might save that company, while making Firefly more competitive and robust. Moreover, because of all that money from Congress, Aerojet has probably been able to offer the engine at cut-rate prices.
A smart deal all around.
Two stories that have been trending like crazy through the conservative news media in the past 24 hours suggest that the investigation by the Justice Department into the anti-Trump spying and coup attempt by the FBI and the CIA might finally be heating up.
I remain somewhat skeptical. The first story is based on two anonymous sources, which makes me very suspicious. I purposely waited before reporting on it because I have found such stories too often turn out to be either fake or unreliable.
I also don’t take the second story very seriously because Horowitz has been promising his FISA report now for months. His promises, and non-delivery, have increasingly reminded me of Richard Branson’s endless promises that “SpaceShipTwo will be flying in space in mere months!”
At the same time, it is important to note both stories. Horowitz’s FISA probe will be released. And Durham’s investigation, under Attorney General William Barr’s direction, has appeared to be so far aggressive and pointed. If both deliver what these stories suggest, then we might finally get some real prosecutions of some real villains, people in the FBI and CIA who conspired for the past three years to try to overturn a legal U.S. election.
NASA today announced that it is building a lunar rover that it will send to the lunar south pole, with a target launch date of December 2022.
About the size of a golf cart, the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, or VIPER, will roam several miles, using its four science instruments — including a 1-meter drill — to sample various soil environments. Planned for delivery to the lunar surface in December 2022, VIPER will collect about 100 days of data that will be used to inform the first global water resource maps of the Moon.
This rover appears to be a traditional NASA project, designed, built, and managed by various NASA agencies that also subcontract the work out to private contractors. As the press release says,
VIPER is a collaboration within and beyond the agency. VIPER is part of the Lunar Discovery and Exploration Program managed by the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters. Ames is managing the rover project, leading the mission’s science, systems engineering, real-time rover surface operations and software development. The hardware for the rover is being designed by the Johnson Space Center, while the instruments are provided by Ames, Kennedy, and commercial partner, Honeybee Robotics. The spacecraft lander and launch vehicle that will deliver VIPER to the surface of the Moon, will be provided through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) contract, delivering science and technology payloads to and near the Moon. [emphasis mine]
The highlighted words however indicate where this project differs from the past. The launch vehicle and lander are not being designed and built by NASA. They will be provided by commercial vendors.
Capitalism in space: According to a report by a Northrop Grumman engineer who has been trying to list these things, the number of companies trying to develop small rockets for the burgeoning smallsat market has grown so large that it is now difficult to track.
Of the 148 small launch vehicles on a popular industry watch list, about 40 efforts “are likely dead but the watch list continues to grow,” Carlos Niederstrasser, a Northrop Grumman master systems engineer, said at the 2019 International Astronautical Congress here.
The problem for Niederstrasser and anyone trying to keep up with the market is that the list continues to grow. “Every time I kill off one [launch vehicle], two more show up,” he said.
…U.S. companies are responsible for 21 of the vehicles Niederstrasser considers active development programs. Seven are from China, four from Spain and three from the United Kingdom. Germany, India and Japan each have two small rocket development programs. Many other countries have a single effort underway.
We should see the shake-out in this new market take place during the next five years. By then at least four rockets should be operational, and the smallsat technology more mature and capable of many things now done by larger satellites.
Buyer beware: With the official completion of a merger of Virgin Galactic with the venture capital company Social Capital Hedosophia this week, it will be possible to buy stock in the company as early as Monday, October 28.
The space-tourism company run by billionaire Sir Richard Branson has been approved to merge with Social Capital Hedosophia, a venture capital firm that helps technology companies list on public markets, according to a Wednesday SEC filing from the company.
The merger is expected to close Friday. On Monday, Social Capital’s ticker, “IPOA,” will become Virgin Galactic’s, and trade under “SPCE.”
As I say, buyer beware. Virgin Galactic has spent fifteen years spending a lot of investment capital without achieving what it promised to do years ago, fly tourists on suborbital space flights. Along the way we’ve seen Richard Branson make a lot of exciting announcements about how he is about to fly in space, none of which ever happened. Instead, they crashed their spaceship, killing one pilot.
If you want to invest money in this company you should be aware of their so far poor track record.
The head of the House Armed Services committee yesterday questioned the appropriateness of the Air Force awarding Northrop Grumman an ICBM contract without any competition.
[House Armed Services Committee Chairman Adam Smith (D-Washington.)] said he is troubled that only one company, Northrop Grumman, will be bidding for the Ground Based Strategic Deterrent, a program to replace the Minuteman 3 ICBMs that make up the ground-based portion of the nation’s nuclear forces.
Northrop Grumman and Boeing were expected to compete head to head to be GBSD prime contractors but Boeing decided in July it would not submit a proposal because of Northrop’s overwhelming advantage as the nation’s largest manufacturer of solid rocket motors.
Northrop Grumman’s advantage here comes from its purchase of Orbital ATK last year, which provided the company this solid rocket launch capability that apparently no one else has.
Smith’s complaints here also extend to the Air Force’s plans to pick only two companies in the next year to launch all of its satellites for the next half decade, rather than leave the bidding open to all. As Smith noted,
“I have worked with them [the Air Force] on launch and other things and it strikes me that they are way too close to the contractors that they’re working with,” he said. “They seem to show bias,” Smith added. “It could be incompetence. But I think it is more likely that they like their historical partners. This is really, really bad because competition is a good thing.”
Smith appears generally correct. The Air Force made a sweet non-competitive launch deal with ULA back in the early 2000s that cost the taxpayer billions. Now it seems it is doing the same with its ICBM replacement contractor, and also wants to do the same with its satellite launch contracts. I hope Smith is successful in changing the Air Force approach.
Capitalism in space: Even as it prepares for its first orbital demonstration flight, Virgin Orbit today announced that it is considering development of a third stage that will make the rocket capable of launching planetary cubesat missions.
John Fuller, Virgin Orbit advanced concepts director, said the company is deciding between three “highly energetic third stage” options for LauncherOne that would enable the rocket to launch up to 50 kilograms to Mars or 70 kilograms to Venus. The “Exploration 3-Stage Variant” of LauncherOne would also have the ability to launch around 100 kilograms to the moon or toward Lagrange points, he said.
“What we do is we take that third stage and bring the overall impulse of the vehicle up to a point where we can reach very high energies to launch to cis-lunar, interplanetary or even asteroid targets,” Fuller said Oct. 24 at the 70th International Astronautical Congress here.
The company however has still not flown the rocket, and that first flight is now about a year-plus behind schedule. They say they are preparing for the first orbital mission before the end of year but until it happens there is plenty of room for skepticism.
Capitalsm in space: NASA and Boeing have now officially scheduled the launch of Boeing’s Starliner capsule on its first unmanned demo flight to ISS for December 17.
Boeing had announced this date earlier, but it is now official.
The next two months will be a very busy period for tests of the two privately built manned capsules being built by Boeing and SpaceX. Not only will Boeing fly Starliner on its first unmanned orbital mission, the company will also do a pad abort test of Starliner on November 4. SpaceX in turn will be doing a major parachute test campaign for Dragon, as well as a launch abort test, right now roughly scheduled for late November.
If all go well, both companies will be ready for the first manned flights of both capsules in the first quarter of 2020.
An evening pause: Bowen is on the Welsh triple harp. They do two songs, Ar Hyd y Nos (All Through the Night) and the theme from Doctor Who.
Hat tip Marcus A.
Cool image time! In the recent download of images from the high resolution camera of Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), I found the image on the right, rotated, cropped, and reduced to post here. It shows an example of the many glacial flows coming off of the slopes of Euripus Mons, the sixteenth highest mountain on Mars.
We know these are glaciers because data from SHARAD, the ground-penetrating radar instrument MRO, has found significant clean ice below the surface, protected by a debris layer that insulates it. As planetary scientist Alfred McEwen of the Lunar & Planetary Laboratory in Arizona explained to me in a phone interview yesterday,
These are remnant glaciers. Basically they form like glaciers form. They are not active or if they are they are moving so extremely slowly that effectively they are not active.
If you look close, you can see that this particular glacier was made up of multiple flows, with the heads or moraines of each piled up where each flow ended. In addition, this overall glacier appears to have been a major conduit off the mountain, following a gap between more resistant ridges to the east and west.
The sequence of moraines suggest that when the glacier was active, it experienced alternating periods of growth and retreat, with the growth periods being shorter and shorter with time. As a result each new moraine was pushed less distance down the mountain as the previous one.
Euripus Mons is interesting in that it has a very large and distinct apron of material surrounding it, as shown in the overview image below.
» Read more
The Curiosity science team today released a beautiful mosaic of the rover, stitched from 57 different images. The photo at the right, cropped and reduced to post here, is the annotated version of that image. It shows the rover’s two most recent drill holes to the left. As the view looks away from Mount Sharp, you can see in the distance Vera Rubin Ridge, the floor of the crater, and its rim on the far horizon.
The two drill holes are significant because of the chemical experiment that Curiosity is subjecting the material from those holes.
The special chemistry experiment occurred on Sept. 24, 2019, after the rover placed the powderized sample from Glen Etive 2 into SAM. The portable lab contains 74 small cups used for testing samples. Most of the cups function as miniature ovens that heat the samples; SAM then “sniffs” the gases that bake off, looking for chemicals that hold clues about the Martian environment billions of years ago, when the planet was friendlier to microbial life.
But nine of SAM’s 74 cups are filled with solvents the rover can use for special “wet chemistry” experiments. These chemicals make it easier for SAM to detect certain carbon-based molecules important to the formation of life, called organic compounds.
Because there’s a limited number of wet-chemistry cups, the science team has been saving them for just the right conditions. In fact, the experiment at Glen Etive is only the second time Curiosity has performed wet chemistry since touching down on Mars in August 2012.
This time however was the first time they had used a wet chemistry cup on material from a drill hole. That they were able to do this at all is a testament to the brilliant innovative skills of the rover’s engineers. They had been holding off doing a wet chemistry analysis from drill hole material until they got to this point, but on the way the rover’s drill feed mechanism failed. It took more than a year of tests and experimentation before they figured out a way to bypass the feed mechanism by using the arm itself to push the drill bit into the ground. That rescue made possible the wet chemistry experiment that they initiated on September 24.
The results, which are eagerly awaited, won’t be available until next year, as it will take time for the scientists to analyze and publish their results.
Curiosity meanwhile has moved on, leaving this location where it had remained for several months to march in the past week southward back towards its long planned route up Mount Sharp.
According to a new paper, scientists now think the biggest and longest landslides found on Mars might not require a base of ice on which it could slide such extensive distances.
The findings, published today in Nature Communications, show for the first time that the unique structures on Martian landslides from mountains several kilometres high could have formed at high speeds of up to 360 kilometres per hour due to underlying layers of unstable, fragmented rocks.
This challenges the idea that underlying layers of slippery ice can only explain such long vast ridges, which are found on landslides throughout the Solar System.
First author, PhD student Giulia Magnarini (UCL Earth Sciences), said: “Landslides on Earth, particularly those on top of glaciers, have been studied by scientists as a proxy for those on Mars because they show similarly shaped ridges and furrows, inferring that Martian landslides also depended on an icy substrate. “However, we’ve shown that ice is not a prerequisite for such geological structures on Mars, which can form on rough, rocky surfaces. This helps us better understand the shaping of Martian landscapes and has implications for how landslides form on other planetary bodies including Earth and the Moon.”
The lighter gravity of Mars, about one third of Earth’s, is part of the explanation, though many other factors are involved. Either way, this is one more data point in the evidence that the though geology on Mars might look like what we see on Earth, it is likely very different than we expect, due to the alien nature of Mars itself.