Computer simulations suggest Jupiter and Saturn have fundamentally different interiors
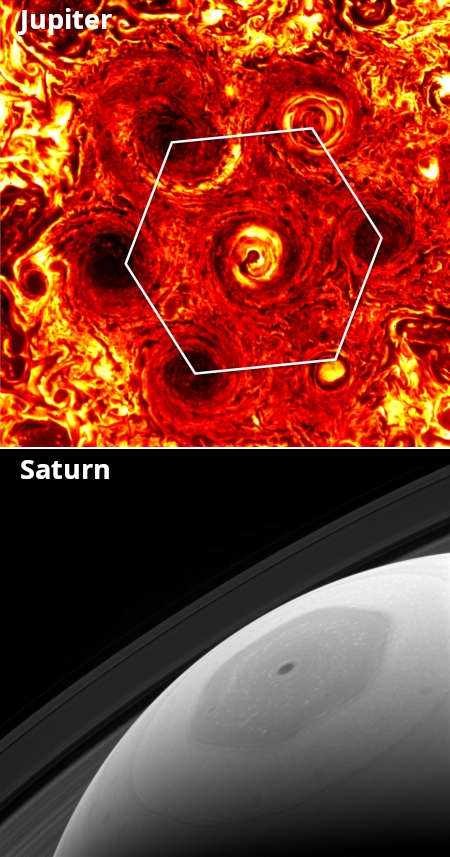
The uncertainty of science: In attempting to explain why the polar vortexes of Jupiter and Saturn are so different, scientists running large computer simulations have found that the difference could be because Jupiter’s interior is “softer” than Saturn’s.
The two images to the right illustrate the different polar vortexes of both planets. Jupiter’s (top) is made up of multiple chaotic small storms that form a hexagon-like ring around the pole. Saturn’s (bottom) is a single very coherent hexagon-shaped storm.
Over multiple different simulations, they observed that some scenarios evolved to form a single large polar vortex, like Saturn, whereas others formed multiple smaller vortices, like Jupiter. After analyzing the combinations of parameters and variables in each scenario and how they related to the final outcome, they landed on a single mechanism to explain whether a single or multiple vortices evolve: As random fluid motions start to coalesce into individual vortices, the size to which a vortex can grow is limited by how soft the bottom of the vortex is. The softer, or lighter the gas is that is rotating at the bottom of a vortex, the smaller the vortex is in the end, allowing for multiple smaller-scale vortices to coexist at a planet’s pole, similar to those on Jupiter.
Conversely, the harder or denser a vortex bottom is, the larger the system can grow, to a size where eventually it can follow the planet’s curvature as a single, planetary-scale vortex, like the one on Saturn.
If this mechanism is indeed what is at play on both gas giants, it would suggest that Jupiter could be made of softer, lighter material, while Saturn may harbor heavier stuff in its interior.
This conclusion however runs completely counter to what we should expect. Jupiter has a much great mass, and one would assume from this that its interior would therefore be denser and thus harder.

The uncertainty of science: In attempting to explain why the polar vortexes of Jupiter and Saturn are so different, scientists running large computer simulations have found that the difference could be because Jupiter’s interior is “softer” than Saturn’s.
The two images to the right illustrate the different polar vortexes of both planets. Jupiter’s (top) is made up of multiple chaotic small storms that form a hexagon-like ring around the pole. Saturn’s (bottom) is a single very coherent hexagon-shaped storm.
Over multiple different simulations, they observed that some scenarios evolved to form a single large polar vortex, like Saturn, whereas others formed multiple smaller vortices, like Jupiter. After analyzing the combinations of parameters and variables in each scenario and how they related to the final outcome, they landed on a single mechanism to explain whether a single or multiple vortices evolve: As random fluid motions start to coalesce into individual vortices, the size to which a vortex can grow is limited by how soft the bottom of the vortex is. The softer, or lighter the gas is that is rotating at the bottom of a vortex, the smaller the vortex is in the end, allowing for multiple smaller-scale vortices to coexist at a planet’s pole, similar to those on Jupiter.
Conversely, the harder or denser a vortex bottom is, the larger the system can grow, to a size where eventually it can follow the planet’s curvature as a single, planetary-scale vortex, like the one on Saturn.
If this mechanism is indeed what is at play on both gas giants, it would suggest that Jupiter could be made of softer, lighter material, while Saturn may harbor heavier stuff in its interior.
This conclusion however runs completely counter to what we should expect. Jupiter has a much great mass, and one would assume from this that its interior would therefore be denser and thus harder.
