Detection of the wake of Betelgeuse’s companion star
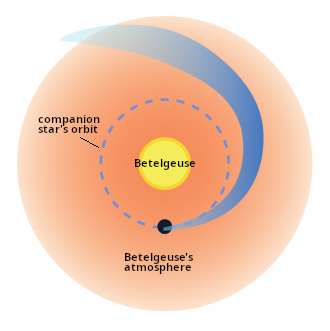
Astronomers believe they have detected evidence of the wake created by Betelgeuse’s companion star as it plows through the primary star’s vast atmosphere.
You can read their paper here [pdf]. The cartoon to the right, annotated by me to post here, is figure 5 of the paper, looking down at Betelgeuse’s pole. It is not to scale. The scientists have nicknamed the companion Siwarha.
The team detected Siwarha’s wake by carefully tracking changes in the star’s light over nearly eight years. These changes show the effects of the previously unconfirmed companion as it plows through the outer atmosphere of Betelgeuse. This discovery resolves one of the biggest mysteries about the giant star, helping scientists to explain how it behaves and evolves while opening new doors to understanding other massive stars nearing the end of their lives.
Located roughly 650 light-years away from Earth in the constellation Orion, Betelgeuse is a red supergiant star so large that more than 400 million Suns could fit inside. Because of its enormous size and proximity, Betelgeuse is one of the few stars whose surface and surrounding atmosphere can be directly observed by astronomers, making it an important and accessible laboratory for studying how giant stars age, lose mass, and eventually explode as supernovae.
Using NASA’s Hubble and ground-based telescopes at the Fred Lawrence Whipple Observatory and Roque de Los Muchachos Observatory, the team was able to see a pattern of changes in Betelgeuse, which provided clear evidence of a long-suspected companion star and its impact on the red supergiant’s outer atmosphere. Those include changes in the star’s spectrum, or the specific colors of light given off by different elements, and the speed and direction of gases in the outer atmosphere due to a trail of denser material, or wake. This trail appears just after the companion crosses in front of Betelgeuse every six years, or about 2,100 days, confirming theoretical models.
Betelgeuse is essentially a giant blob that undulates like a blob of water floating in weightlessness on ISS. Knowing the location and orbit of this companion will help astronomers better understand the central star’s periodic inexplicable changes.
On Christmas Eve 1968 three Americans became the first humans to visit another world. What they did to celebrate was unexpected and profound, and will be remembered throughout all human history. Genesis: the Story of Apollo 8, Robert Zimmerman's classic history of humanity's first journey to another world, tells that story, and it is now available as both an ebook and an audiobook, both with a foreword by Valerie Anders and a new introduction by Robert Zimmerman.
The print edition can be purchased at Amazon or from any other book seller. If you want an autographed copy the price is $60 for the hardback and $45 for the paperback, plus $8 shipping for each. Go here for purchasing details. The ebook is available everywhere for $5.99 (before discount) at amazon, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit. If you buy it from ebookit you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
The audiobook is also available at all these vendors, and is also free with a 30-day trial membership to Audible.
"Not simply about one mission, [Genesis] is also the history of America's quest for the moon... Zimmerman has done a masterful job of tying disparate events together into a solid account of one of America's greatest human triumphs."--San Antonio Express-News

Astronomers believe they have detected evidence of the wake created by Betelgeuse’s companion star as it plows through the primary star’s vast atmosphere.
You can read their paper here [pdf]. The cartoon to the right, annotated by me to post here, is figure 5 of the paper, looking down at Betelgeuse’s pole. It is not to scale. The scientists have nicknamed the companion Siwarha.
The team detected Siwarha’s wake by carefully tracking changes in the star’s light over nearly eight years. These changes show the effects of the previously unconfirmed companion as it plows through the outer atmosphere of Betelgeuse. This discovery resolves one of the biggest mysteries about the giant star, helping scientists to explain how it behaves and evolves while opening new doors to understanding other massive stars nearing the end of their lives.
Located roughly 650 light-years away from Earth in the constellation Orion, Betelgeuse is a red supergiant star so large that more than 400 million Suns could fit inside. Because of its enormous size and proximity, Betelgeuse is one of the few stars whose surface and surrounding atmosphere can be directly observed by astronomers, making it an important and accessible laboratory for studying how giant stars age, lose mass, and eventually explode as supernovae.
Using NASA’s Hubble and ground-based telescopes at the Fred Lawrence Whipple Observatory and Roque de Los Muchachos Observatory, the team was able to see a pattern of changes in Betelgeuse, which provided clear evidence of a long-suspected companion star and its impact on the red supergiant’s outer atmosphere. Those include changes in the star’s spectrum, or the specific colors of light given off by different elements, and the speed and direction of gases in the outer atmosphere due to a trail of denser material, or wake. This trail appears just after the companion crosses in front of Betelgeuse every six years, or about 2,100 days, confirming theoretical models.
Betelgeuse is essentially a giant blob that undulates like a blob of water floating in weightlessness on ISS. Knowing the location and orbit of this companion will help astronomers better understand the central star’s periodic inexplicable changes.
On Christmas Eve 1968 three Americans became the first humans to visit another world. What they did to celebrate was unexpected and profound, and will be remembered throughout all human history. Genesis: the Story of Apollo 8, Robert Zimmerman's classic history of humanity's first journey to another world, tells that story, and it is now available as both an ebook and an audiobook, both with a foreword by Valerie Anders and a new introduction by Robert Zimmerman.
The print edition can be purchased at Amazon or from any other book seller. If you want an autographed copy the price is $60 for the hardback and $45 for the paperback, plus $8 shipping for each. Go here for purchasing details. The ebook is available everywhere for $5.99 (before discount) at amazon, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit. If you buy it from ebookit you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
The audiobook is also available at all these vendors, and is also free with a 30-day trial membership to Audible.
"Not simply about one mission, [Genesis] is also the history of America's quest for the moon... Zimmerman has done a masterful job of tying disparate events together into a solid account of one of America's greatest human triumphs."--San Antonio Express-News


So this study will allow us to explic the inexplicable!
I seem to remember reading about how the Sun could last longer if it were “stirred” with super-high yield nukes.
This companion could have the opposite effect.
On gravity:
https://www.secretprojects.co.uk/threads/cool-science.41252/page-6#post-867322
Jeff—
We should keep in mind that Betelgeuse is a massively huge and young star and has already exhausted all of its hydrogen and is currently fusing helium into carbon and oxygen.
And the high temperature required to burn helium means it can only do it one way–very fast.
As for detonating a ‘super-bomb’ on our Sun– wouldn’t cause a “scratch,” and it’s doubtful we could even tell if it detonated or was turned into plasma as the intense gravity pulled it toward the center.
Stellar Physics: Helium Fusion
https://youtu.be/bV-YZ441z4Q
16:35
Even with starlifting to pull the heavy stuff that we would want to “mine” out of the sun, it’s so vast that it would take a very long time to remove enough to change the sun’s lifecycle. I doubt we’ll even try until most asteroids are gone and probably several moons, too.
On the other hand, a K2 civilization needs a lot of raw material and the sun is going to live a very long time (in human terms). Yanking a couple quintillion tons of iron out of the sun per year would eventually make a difference.
On the bright side, it’s not anything that needs worrying about in our lifetimes (even with radical life extension).