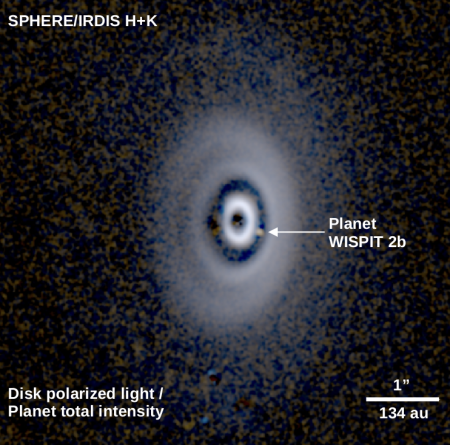
For the first time since 2018, scientists have obtained a clear detection of an exoplanet inside the accretion disk surrounding a Sunlike star. Furthermore, the planet sits inside a gap in that accretion disk, the first time such an exoplanet has been found.
The image to the right, taken from figure one of the research paper [pdf], shows the exoplanet, dubbed WISPIT 2b. The star, located about 435 light years away, has a mass only slightly larger than our Sun, and is considered a close match. The planet itself is estimated to be about the mass of Jupiter, though its orbit within that gap is much farther away, 57 astronomical units versus 5.2. It is these details that make the discovery significant. From the paper’s conclusion:
As the planet resides in the cleared gap and its mass is consistent with the modeled planet mass required to open such a gap, we argue that it likely formed in situ through core accretion and that there is no rapid migration on dynamical timescales. Future follow-up observations of WISPIT 2b with ALMA and [Webb] will enable studies of its atmosphere and the impact of the embedded planet on the disk’s gas kinematics and surface density structure. This will allow us to calibrate ALMA observations of other embedded planet candidates, to unlock the full potential of this complementary technique.
…The discovery of WISPIT 2b embedded in the gap of a seemingly unperturbed disk demonstrates, for the first time, that wide-separation gas giants, discovered by direct imaging around older systems, can indeed form in situ. Thus, WISPIT 2b marks a promising starting point to study wide separation planets in time.
It has long been theorized that gas giants can form much farther from their star, and then migrate inward as the system evolves. This discovery counters that supposition, or least demonstrates that it does not have to occur in every new solar system.
The image also shows that the accretion disk has a second gap farther out, as well as a cleared area close to the star, comparable in size to our solar system. Though other exoplanets have not been detected yet, these gaps suggest they exist, thus indicating that a solar system comparable to our own is now forming.