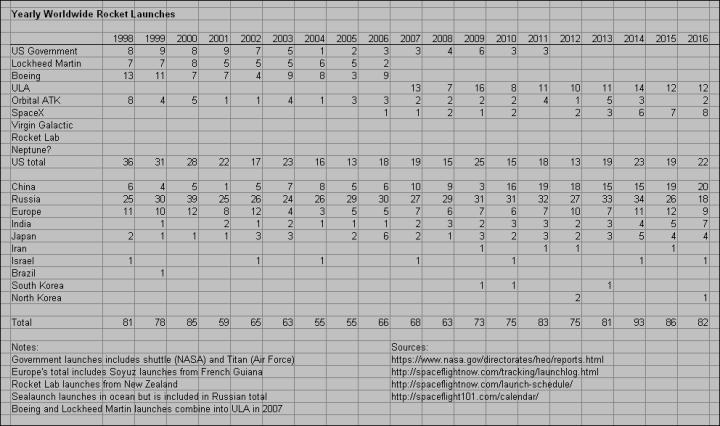
Google Lunar X-Prize finalists named
The competition heats up: The five finalists for the Google Lunar X-Prize have now been set.
Five teams remain in the running: Israel’s SpaceIL, Florida-based Moon Express, an international team known as Synergy Moon, India’s Team Indus and Japan’s Hakuto.
SpaceIL plans to fly on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, which recently returned to flight following a launch pad accident. Team Indus and Hakuto will share a ride on an Indian PSLV launcher. Moon Express is banking on a launch from startup Rocket Lab, which is developing a small rocket called Electron. Whether it wins the XPrize or not, Moon Express is building a business to provide lunar transportation and services, such as research and mineral extraction, Chief Executive Bob Richards said in an interview. Synergy Moon is counting on one of its partners, Mojave, Calif.-based Interorbital Systems, for its launch aboard a new rocket known as Neptune.
To win, one of these teams must fly its mission before the end of 2017.
The competition heats up: The five finalists for the Google Lunar X-Prize have now been set.
Five teams remain in the running: Israel’s SpaceIL, Florida-based Moon Express, an international team known as Synergy Moon, India’s Team Indus and Japan’s Hakuto.
SpaceIL plans to fly on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, which recently returned to flight following a launch pad accident. Team Indus and Hakuto will share a ride on an Indian PSLV launcher. Moon Express is banking on a launch from startup Rocket Lab, which is developing a small rocket called Electron. Whether it wins the XPrize or not, Moon Express is building a business to provide lunar transportation and services, such as research and mineral extraction, Chief Executive Bob Richards said in an interview. Synergy Moon is counting on one of its partners, Mojave, Calif.-based Interorbital Systems, for its launch aboard a new rocket known as Neptune.
To win, one of these teams must fly its mission before the end of 2017.