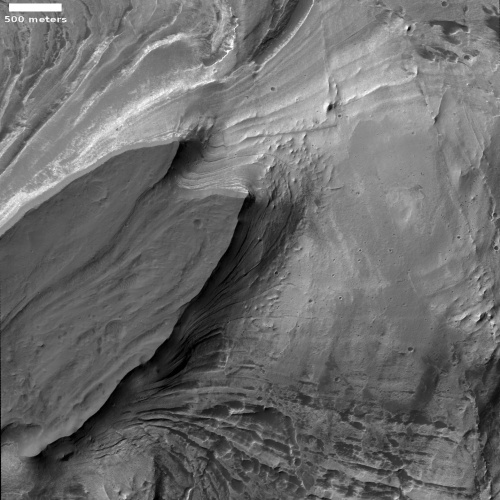
Hubble image shows several dozen boulders flung from Dimorphos
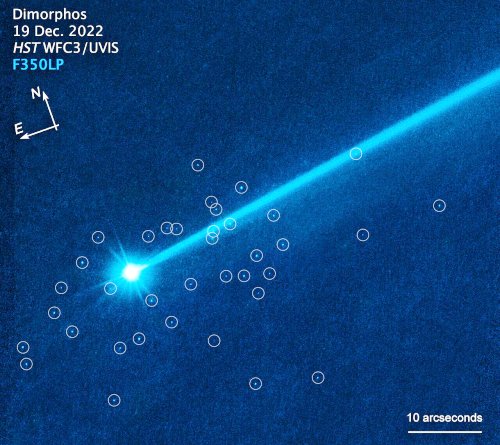
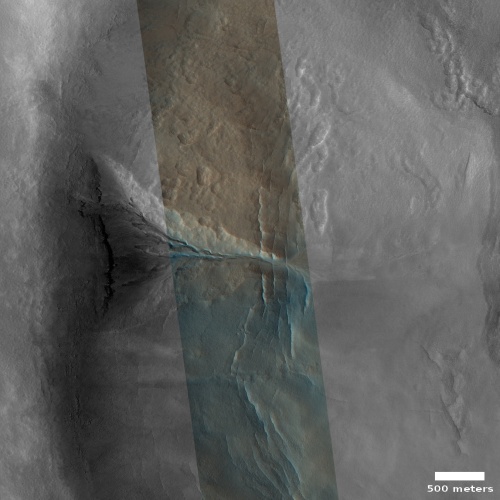
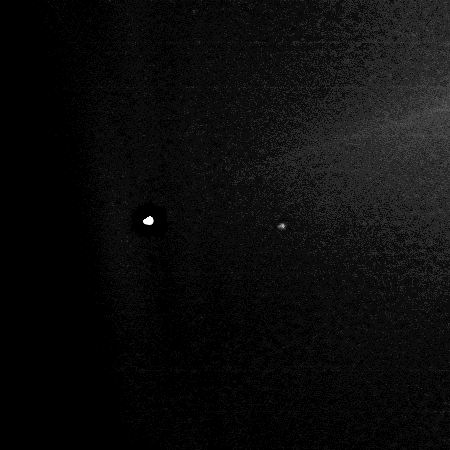
Using the Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers have photographed several dozen boulders that were flung off of the asteroid Dimorphos following the impact by the space probe DART. The picture to the right, reduced and brightened to more clearly show those boulders, was taken on December 19, 2022, four months after DART’s impact.
These are among the faintest objects Hubble has ever photographed inside the Solar System. The ejected boulders range in size from 1 meter to 6.7 meters across, based on Hubble photometry. They are drifting away from the asteroid at around a kilometre per hour.
The blue streak is the dust tail that has streamed off of Dimorphos since the impact, pushed away from the sun by the solar wind.
Using the Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers have photographed several dozen boulders that were flung off of the asteroid Dimorphos following the impact by the space probe DART. The picture to the right, reduced and brightened to more clearly show those boulders, was taken on December 19, 2022, four months after DART’s impact.
These are among the faintest objects Hubble has ever photographed inside the Solar System. The ejected boulders range in size from 1 meter to 6.7 meters across, based on Hubble photometry. They are drifting away from the asteroid at around a kilometre per hour.
The blue streak is the dust tail that has streamed off of Dimorphos since the impact, pushed away from the sun by the solar wind.