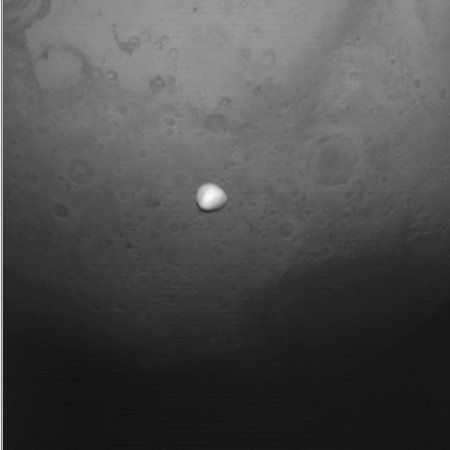
Hera photographs two main belt asteroids on its way to Didymos/Dimorphos
The science team for the European Space Agency’s Hera asteroid probe, on its way to the binary asteroid Didymos/Dimorphos in late 2026, has successfully taken images of two different main belt asteroids, demonstrating once again that its camera and pointing capabilities are operating as expected.
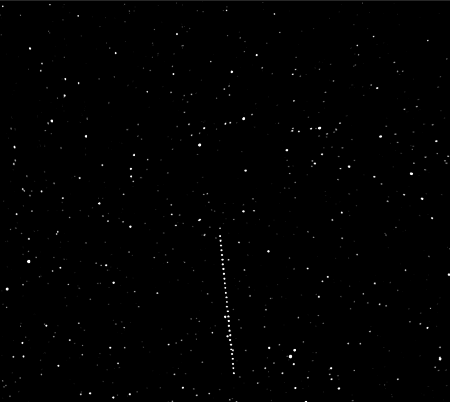
The image to the right, cropped, reduced, and enhanced, shows all the observations of Otero, the first asteroid observed, as it moved upward in the field of view. The result was that vertical line of dots.
On 11 May 2025, as Hera cruised through the main asteroid belt beyond the orbit of Mars, the spacecraft turned its attention toward Otero, a rare A-type asteroid discovered almost 100 years ago.
From a distance of approximately three million kilometres, Otero appeared as a moving point of light – easily mistaken for a star if not for its subtle motion across the background sky. Hera captured images of Otero using its Asteroid Framing Camera – a navigational and scientific instrument that will be used to guide the spacecraft during its approach to Didymos next year.
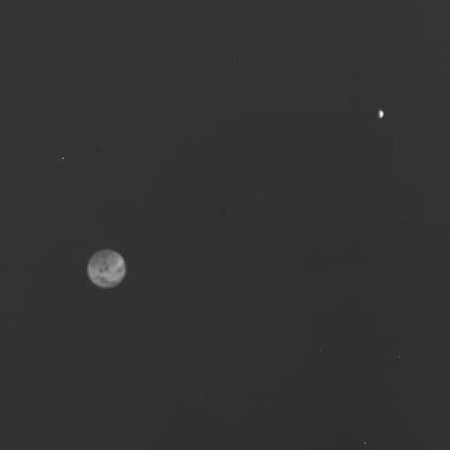
The second observation of asteroid Kellyday was even less spectacular visually, but because that asteroid was forty times fainter than Otero, the observation was more challenging, and thus its success more significant.
Hera will arrive at the Didymos/Dimorphos binary asteroid in 2026, where it will make close-up observations of the changes the asteroids have undergone following Dart’s impact of Dimorphos in 2022. Subsequent ground- and space-based observations have been extensive and on-going, but the close-up view will be ground-breaking.
The science team for the European Space Agency’s Hera asteroid probe, on its way to the binary asteroid Didymos/Dimorphos in late 2026, has successfully taken images of two different main belt asteroids, demonstrating once again that its camera and pointing capabilities are operating as expected.
The image to the right, cropped, reduced, and enhanced, shows all the observations of Otero, the first asteroid observed, as it moved upward in the field of view. The result was that vertical line of dots.
On 11 May 2025, as Hera cruised through the main asteroid belt beyond the orbit of Mars, the spacecraft turned its attention toward Otero, a rare A-type asteroid discovered almost 100 years ago.
From a distance of approximately three million kilometres, Otero appeared as a moving point of light – easily mistaken for a star if not for its subtle motion across the background sky. Hera captured images of Otero using its Asteroid Framing Camera – a navigational and scientific instrument that will be used to guide the spacecraft during its approach to Didymos next year.
The second observation of asteroid Kellyday was even less spectacular visually, but because that asteroid was forty times fainter than Otero, the observation was more challenging, and thus its success more significant.
Hera will arrive at the Didymos/Dimorphos binary asteroid in 2026, where it will make close-up observations of the changes the asteroids have undergone following Dart’s impact of Dimorphos in 2022. Subsequent ground- and space-based observations have been extensive and on-going, but the close-up view will be ground-breaking.