A blob in space
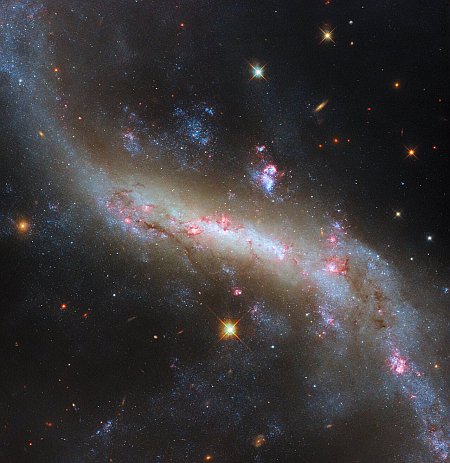
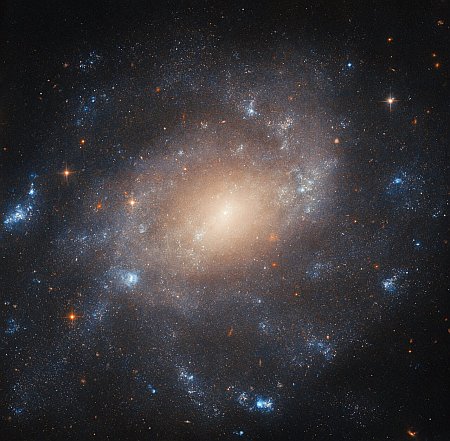
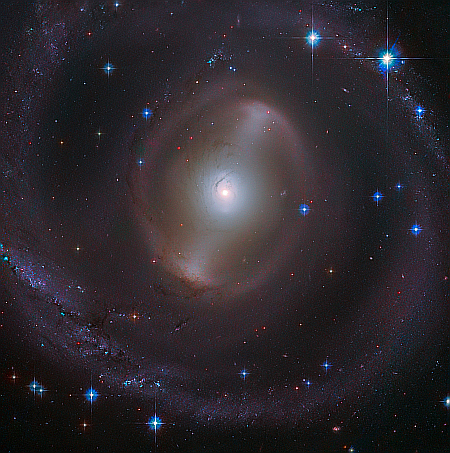
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken by the Hubble Space Telescope of the dwarf galaxy NGC 5238.
Its unexciting, blob-like appearance, resembling more an oversized star cluster than a galaxy, belies a complicated structure which has been the subject of much research by astronomers. Here, the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope is able to pick out the galaxy’s countless stars, as well as its associated globular clusters — the glowing spots both inside and around the galaxy that are swarmed by yet more stars.
NGC 5238 is theorised to have recently — here meaning no more than a billion years ago! — had a close encounter with another galaxy. The evidence for this is the tidal distortions of NGC 5238’s shape, the kind produced by two galaxies pulling on each other as they interact. There’s no nearby galaxy which could have caused this disturbance, so the hypothesis is that the culprit is a smaller satellite galaxy that was devoured by NGC 5238.
Astronomers are hoping to use this image to detect the two different populations of stars within this blob that come from those once interacting galaxies.
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken by the Hubble Space Telescope of the dwarf galaxy NGC 5238.
Its unexciting, blob-like appearance, resembling more an oversized star cluster than a galaxy, belies a complicated structure which has been the subject of much research by astronomers. Here, the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope is able to pick out the galaxy’s countless stars, as well as its associated globular clusters — the glowing spots both inside and around the galaxy that are swarmed by yet more stars.
NGC 5238 is theorised to have recently — here meaning no more than a billion years ago! — had a close encounter with another galaxy. The evidence for this is the tidal distortions of NGC 5238’s shape, the kind produced by two galaxies pulling on each other as they interact. There’s no nearby galaxy which could have caused this disturbance, so the hypothesis is that the culprit is a smaller satellite galaxy that was devoured by NGC 5238.
Astronomers are hoping to use this image to detect the two different populations of stars within this blob that come from those once interacting galaxies.