Webb imaged a star before it went supernova
One of the biggest challenges facing astronomers for more than four centuries has been the detection of a star prior to its going supernova. Until very recently, no such detection had ever happened, and so astronomers could only guess at the kind of stars or binary systems that might result in these gigantic stellar explosions.
In recent years the improvement in telescopes, both in orbit and on the ground, has produced some successes, whereby the progenitor star was imaged in archival imagery and found after the explosion. The sample however has been small, and the data limited to only a few wavelengths.
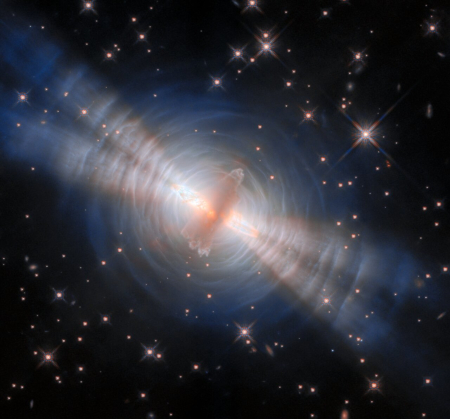
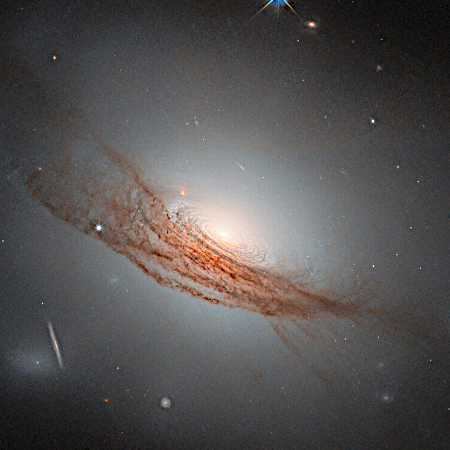
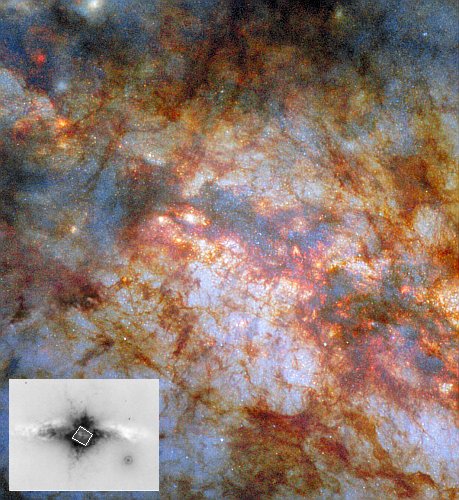
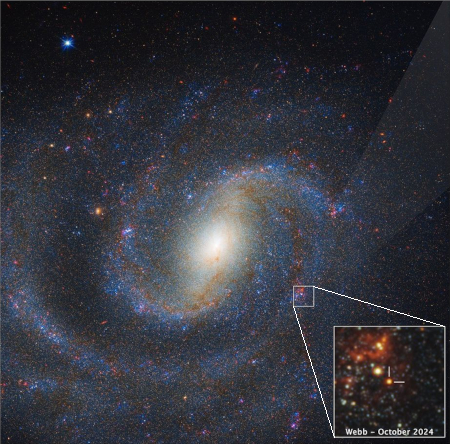
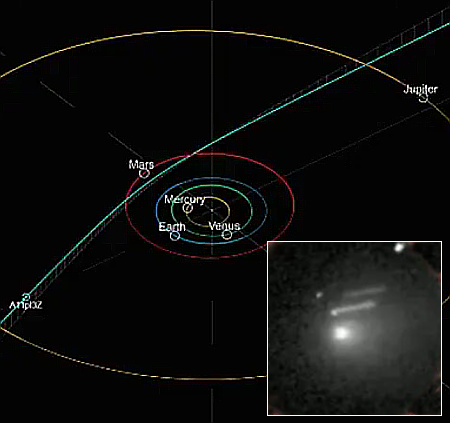
Now, the Webb Space Telescope has made its first detection of a supernova progenitor, in the infrared. That image is to the right, showing the star prior to the June 2025 supernova explosion.
By carefully aligning Hubble and Webb images taken of NGC 1637, the team was able to identify the progenitor star in images taken by Webb’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument) and NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) in 2024. They found that the star appeared surprisingly red – an indication that it was surrounded by dust that blocked shorter, bluer wavelengths of light. “It’s the reddest, most dusty red supergiant that we’ve seen explode as a supernova,” said graduate student and co-author Aswin Suresh of Northwestern University.
This excess of dust could help explain a long-standing problem in astronomy that could be described as the case of the missing red supergiants. Astronomers expect the most massive stars that explode as supernovas to also be the brightest and most luminous. So, they should be easy to identify in pre-supernova images. However, that hasn’t been the case.
One potential explanation is that the most massive aging stars are also the dustiest. If they’re surrounded by large quantities of dust, their light could be dimmed to the point of undetectability. The Webb observations of supernova 2025pht support that hypothesis.
You can read the peer-reviewed paper here [pdf].
One of the biggest challenges facing astronomers for more than four centuries has been the detection of a star prior to its going supernova. Until very recently, no such detection had ever happened, and so astronomers could only guess at the kind of stars or binary systems that might result in these gigantic stellar explosions.
In recent years the improvement in telescopes, both in orbit and on the ground, has produced some successes, whereby the progenitor star was imaged in archival imagery and found after the explosion. The sample however has been small, and the data limited to only a few wavelengths.
Now, the Webb Space Telescope has made its first detection of a supernova progenitor, in the infrared. That image is to the right, showing the star prior to the June 2025 supernova explosion.
By carefully aligning Hubble and Webb images taken of NGC 1637, the team was able to identify the progenitor star in images taken by Webb’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument) and NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) in 2024. They found that the star appeared surprisingly red – an indication that it was surrounded by dust that blocked shorter, bluer wavelengths of light. “It’s the reddest, most dusty red supergiant that we’ve seen explode as a supernova,” said graduate student and co-author Aswin Suresh of Northwestern University.
This excess of dust could help explain a long-standing problem in astronomy that could be described as the case of the missing red supergiants. Astronomers expect the most massive stars that explode as supernovas to also be the brightest and most luminous. So, they should be easy to identify in pre-supernova images. However, that hasn’t been the case.
One potential explanation is that the most massive aging stars are also the dustiest. If they’re surrounded by large quantities of dust, their light could be dimmed to the point of undetectability. The Webb observations of supernova 2025pht support that hypothesis.
You can read the peer-reviewed paper here [pdf].