German rocket startup Isar wins another launch contract

Spectrum falling seconds after its launch
in March 2025
The German rocket startup Isar Aerospace today won a new launch contract from the satellite aggregator SEOPS for a 2028 launch of its new Spectrum rocket.
SEOPS today announced during SpaceTech Expo it has purchased a dedicated launch on Isar Aerospace’s ‘Spectrum’ rocket. Targeted for launch in 2028, this marks SEOPS’ first collaboration with Isar Aerospace, expanding the company’s European launch capabilities.
SEOPS acts as an agent for satellite companies building small cubesats, arranging the launches for them because these companies often don’t have the resources or experience to do the job themselves. The choice of Isar’s Spectrum rocket suggests SEOPS wants to encourage new launch options, since Isar has only launched Spectrum once, and that launch was a failure. This contract acts to strengthen Isar’s future by giving it a powerful customer. It also gives SEOPS a European launch option, something that will attract European smallsat makers to it.
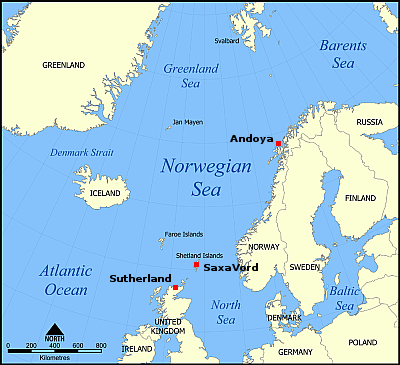
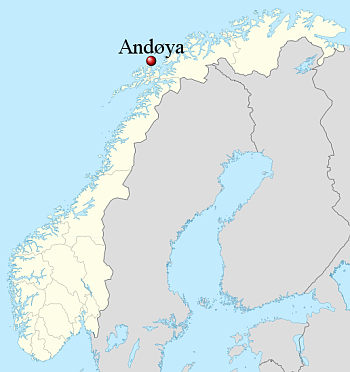
Isar is presently preparing Spectrum for its second launch out of Norway’s Andoya spaceport, with road closure announcements suggesting it will occur prior to December 21, 2025. If successful Isar will be the first new European rocket company in decades to reach orbit. It will also be the first German company to do so, ever. And it will give Andoya spaceport first place in the race to become Europe’s first orbital spaceport.

Spectrum falling seconds after its launch
in March 2025
The German rocket startup Isar Aerospace today won a new launch contract from the satellite aggregator SEOPS for a 2028 launch of its new Spectrum rocket.
SEOPS today announced during SpaceTech Expo it has purchased a dedicated launch on Isar Aerospace’s ‘Spectrum’ rocket. Targeted for launch in 2028, this marks SEOPS’ first collaboration with Isar Aerospace, expanding the company’s European launch capabilities.
SEOPS acts as an agent for satellite companies building small cubesats, arranging the launches for them because these companies often don’t have the resources or experience to do the job themselves. The choice of Isar’s Spectrum rocket suggests SEOPS wants to encourage new launch options, since Isar has only launched Spectrum once, and that launch was a failure. This contract acts to strengthen Isar’s future by giving it a powerful customer. It also gives SEOPS a European launch option, something that will attract European smallsat makers to it.
Isar is presently preparing Spectrum for its second launch out of Norway’s Andoya spaceport, with road closure announcements suggesting it will occur prior to December 21, 2025. If successful Isar will be the first new European rocket company in decades to reach orbit. It will also be the first German company to do so, ever. And it will give Andoya spaceport first place in the race to become Europe’s first orbital spaceport.