Astronomers detect exoplanet shaping the protoplanetary disk surrounding a baby star
Astronomers using two different instruments on the Very Large Telescope (VLT) in Chile have now directly detected what they think is an exoplanet as it shapes the spiral arms of a baby star’s protoplanetary disk.
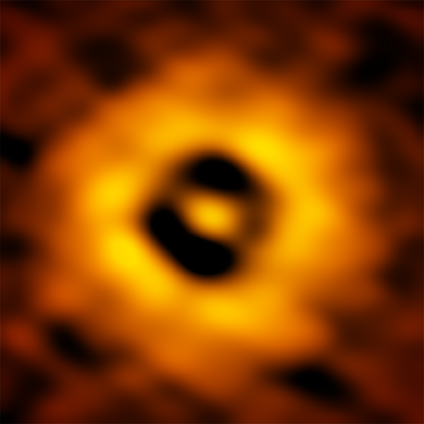
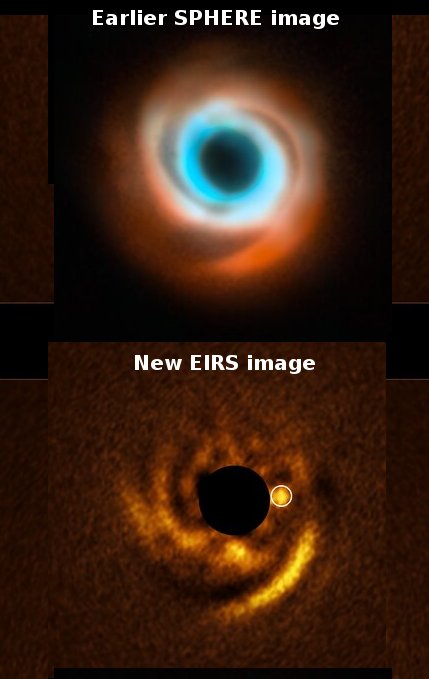
In the case of HD 135344B’s disc, swirling spiral arms had previously been detected by another team of astronomers using SPHERE (Spectro-Polarimetric High-contrast Exoplanet REsearch), an instrument on ESO’s VLT. However, none of the previous observations of this system found proof of a planet forming within the disc.
Now, with observations from the new VLT’s Enhanced Resolution Imager and Spectrograph (ERIS) instrument, the researchers say they may have found their prime suspect. The team spotted the planet candidate right at the base of one of the disc’s spiral arms, exactly where theory had predicted they might find the planet responsible for carving such a pattern.
The newly detected object however might be a brown dwarf and not an exoplanet. More observations are required to reduce the uncertainty.
Astronomers using two different instruments on the Very Large Telescope (VLT) in Chile have now directly detected what they think is an exoplanet as it shapes the spiral arms of a baby star’s protoplanetary disk.
In the case of HD 135344B’s disc, swirling spiral arms had previously been detected by another team of astronomers using SPHERE (Spectro-Polarimetric High-contrast Exoplanet REsearch), an instrument on ESO’s VLT. However, none of the previous observations of this system found proof of a planet forming within the disc.
Now, with observations from the new VLT’s Enhanced Resolution Imager and Spectrograph (ERIS) instrument, the researchers say they may have found their prime suspect. The team spotted the planet candidate right at the base of one of the disc’s spiral arms, exactly where theory had predicted they might find the planet responsible for carving such a pattern.
The newly detected object however might be a brown dwarf and not an exoplanet. More observations are required to reduce the uncertainty.