Kenya to build its own spaceport
Kenya spaceports
The Kenyan government has now initiated a project to establish a second commercial spaceport on the country’s coast, located near the town of Kipini.
As stated in the document made public on December 16, 2025, the government is looking to recruit a skilled transaction advisor who is capable of analyzing the technical, financial, legal, environmental, and social feasibility of the construction of the spaceport based on a PPP model. The strategy utilizes Kenya’s location on the equator, which provides some benefits in satellite launches, among them lower fuel consumption, lower launch costs, and easier satellite placement in low-inclined orbits around the earth’s equatorial region.
…Under the plan, the transaction advisor will prepare a detailed feasibility study in line with the PPP Act, 2021. The study will include concept designs, launch vehicle options, infrastructure requirements, lifecycle cost estimates, and a phased implementation plan for the facility.
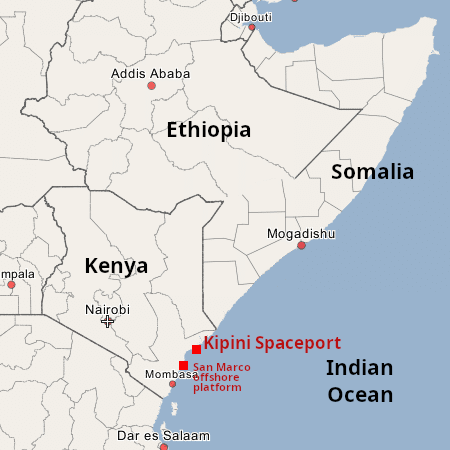
As shown on the map to the right, this new facility would be to the north of the San Marco offshore platform that had been used for eight launches by Italy from the ’60s to the ’80s and that the Italian rocket company Avio is now planning to re-open.
The Kenyan government apparently wants to build its own a launch site that it can offer to others to use.

Kenya spaceports
The Kenyan government has now initiated a project to establish a second commercial spaceport on the country’s coast, located near the town of Kipini.
As stated in the document made public on December 16, 2025, the government is looking to recruit a skilled transaction advisor who is capable of analyzing the technical, financial, legal, environmental, and social feasibility of the construction of the spaceport based on a PPP model. The strategy utilizes Kenya’s location on the equator, which provides some benefits in satellite launches, among them lower fuel consumption, lower launch costs, and easier satellite placement in low-inclined orbits around the earth’s equatorial region.
…Under the plan, the transaction advisor will prepare a detailed feasibility study in line with the PPP Act, 2021. The study will include concept designs, launch vehicle options, infrastructure requirements, lifecycle cost estimates, and a phased implementation plan for the facility.
As shown on the map to the right, this new facility would be to the north of the San Marco offshore platform that had been used for eight launches by Italy from the ’60s to the ’80s and that the Italian rocket company Avio is now planning to re-open.
The Kenyan government apparently wants to build its own a launch site that it can offer to others to use.