FAA confirms “no significant impact” to environment for Starship/Superheavy at Boca Chica
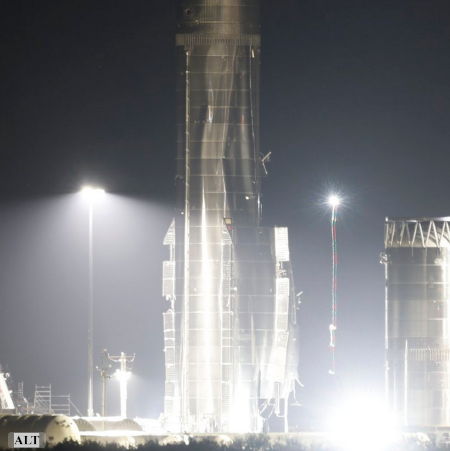
The FAA today released [pdf] its final environmental assessment reviewing SpaceX’s request to expand operations of Starship/Superheavy at Boca Chica, confirming that it has determined there will be “no significant impact” to environment.
The 2022 PEA and April 2025 Tiered EA examined the potential for significant environmental impacts from Starship-Super Heavy launch operations at the Boca Chica Launch Site and defined the regulatory setting for impacts associated with Starship-Super Heavy. The areas evaluated for environmental impacts in this Tiered EA include noise and noise‐compatible land use; aviation emissions and air quality; hazardous materials, solid waste, and pollution prevention; and socioeconomics. In each of these areas, the FAA has concluded that no significant impacts would occur as a result of the Proposed Action.
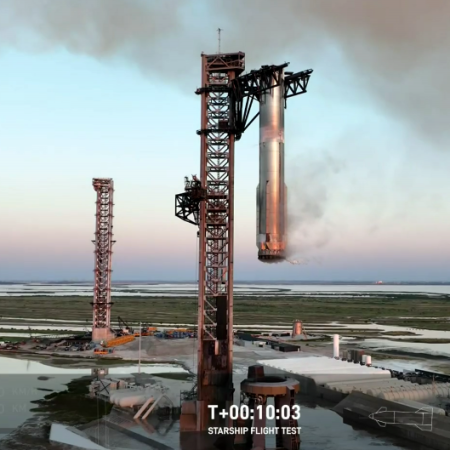
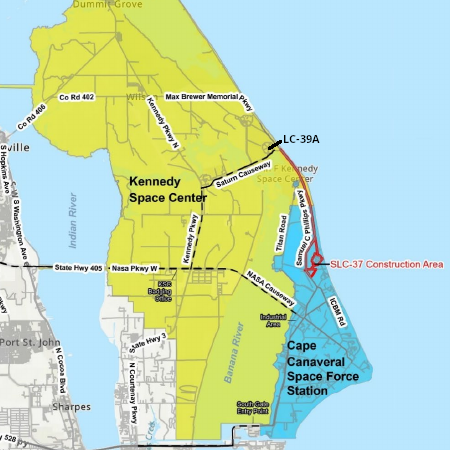
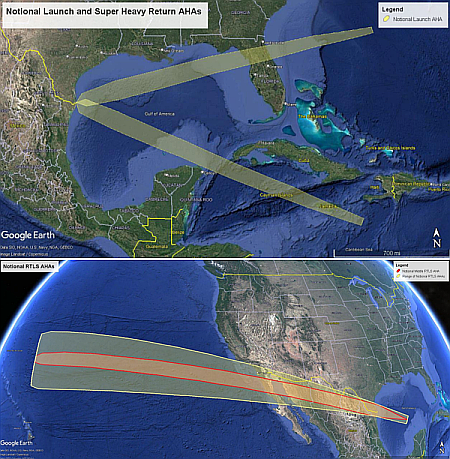
The approval will allow SpaceX to do 25 launches per year (three of which are at night). The approval also appears to lay the groundwork for bringing Superheavy back not only to Boca Chica, but to Florida. It also lays the groundwork for bringing Starship back to Boca Chica after completing an orbital flight, to be caught by the tower chopsticks.
The FAA today released [pdf] its final environmental assessment reviewing SpaceX’s request to expand operations of Starship/Superheavy at Boca Chica, confirming that it has determined there will be “no significant impact” to environment.
The 2022 PEA and April 2025 Tiered EA examined the potential for significant environmental impacts from Starship-Super Heavy launch operations at the Boca Chica Launch Site and defined the regulatory setting for impacts associated with Starship-Super Heavy. The areas evaluated for environmental impacts in this Tiered EA include noise and noise‐compatible land use; aviation emissions and air quality; hazardous materials, solid waste, and pollution prevention; and socioeconomics. In each of these areas, the FAA has concluded that no significant impacts would occur as a result of the Proposed Action.
The approval will allow SpaceX to do 25 launches per year (three of which are at night). The approval also appears to lay the groundwork for bringing Superheavy back not only to Boca Chica, but to Florida. It also lays the groundwork for bringing Starship back to Boca Chica after completing an orbital flight, to be caught by the tower chopsticks.