Webb takes its first infrared image of Mars
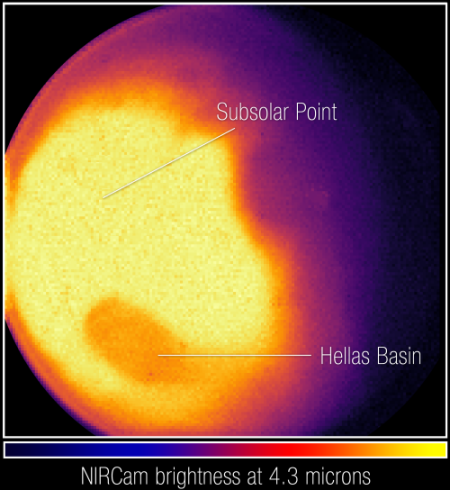
Astronomers have now released the the James Webb Space Telescope’s first infrared image of Mars, taken on September 5, 2022.
The image to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, shows some of the data obtained. Because Mars is so close, it is actually too bright for Webb’s instruments. To get any data, the exposures were very very short, and still the brightest areas — as indicated by large areas of yellow — are overexposed. The cause of the different brightness of Hellas Basin, however, is not simply because the basin — the deepest point on Mars — is cooler.
As light emitted by the planet passes through Mars’ atmosphere, some gets absorbed by carbon dioxide (CO2) molecules. The Hellas Basin – which is the largest well-preserved impact structure on Mars, spanning more than 1,200 miles (2,000 kilometers) – appears darker than the surroundings because of this effect. “This is actually not a thermal effect at Hellas,” explained the principal investigator, Geronimo Villanueva of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, who designed these Webb observations. “The Hellas Basin is a lower altitude, and thus experiences higher air pressure. That higher pressure leads to a suppression of the thermal emission at this particular wavelength range [4.1-4.4 microns] due to an effect called pressure broadening. It will be very interesting to tease apart these competing effects in these data.”
The NASA press release says the scientists are preparing a paper analyzing the spectral data and what it revealed about “dust, icy clouds, what kind of rocks are on the planet’s surface, and the composition of the atmosphere,” I suspect however that Webb’s capabilities for studying Mars are much more limited than implied, and that it will over time take much fewer images of the red planet, compared to Hubble.
Astronomers have now released the the James Webb Space Telescope’s first infrared image of Mars, taken on September 5, 2022.
The image to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, shows some of the data obtained. Because Mars is so close, it is actually too bright for Webb’s instruments. To get any data, the exposures were very very short, and still the brightest areas — as indicated by large areas of yellow — are overexposed. The cause of the different brightness of Hellas Basin, however, is not simply because the basin — the deepest point on Mars — is cooler.
As light emitted by the planet passes through Mars’ atmosphere, some gets absorbed by carbon dioxide (CO2) molecules. The Hellas Basin – which is the largest well-preserved impact structure on Mars, spanning more than 1,200 miles (2,000 kilometers) – appears darker than the surroundings because of this effect. “This is actually not a thermal effect at Hellas,” explained the principal investigator, Geronimo Villanueva of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, who designed these Webb observations. “The Hellas Basin is a lower altitude, and thus experiences higher air pressure. That higher pressure leads to a suppression of the thermal emission at this particular wavelength range [4.1-4.4 microns] due to an effect called pressure broadening. It will be very interesting to tease apart these competing effects in these data.”
The NASA press release says the scientists are preparing a paper analyzing the spectral data and what it revealed about “dust, icy clouds, what kind of rocks are on the planet’s surface, and the composition of the atmosphere,” I suspect however that Webb’s capabilities for studying Mars are much more limited than implied, and that it will over time take much fewer images of the red planet, compared to Hubble.