Webb tracks volcanic eruptions on Io
Using the Webb Space Telescope, scientists have tracked two different volcanic eruptions on Io that too place from 2022 to 2023, detecting sulfur monoxide both from those eruptions as well as sulfur from the magnetic plasma torus produced as the planet travels through Jupiter’s strong magnetic field. From the paper’s abstract:
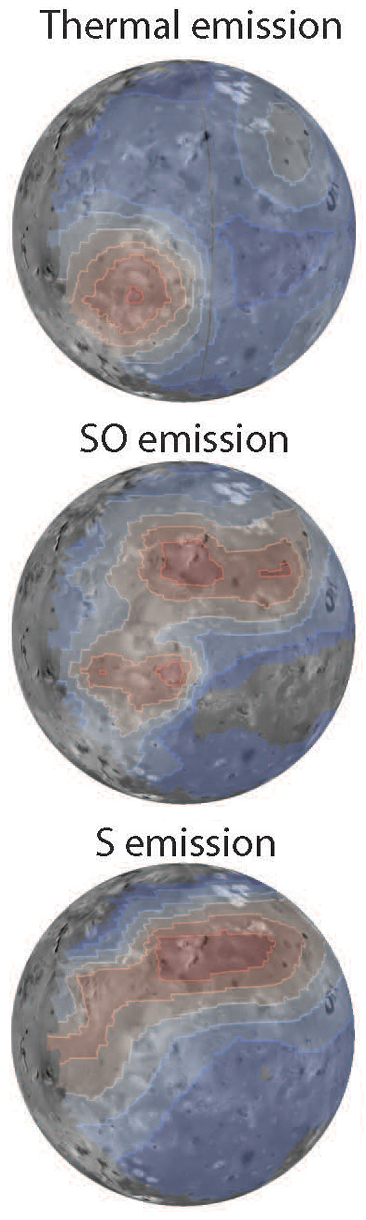
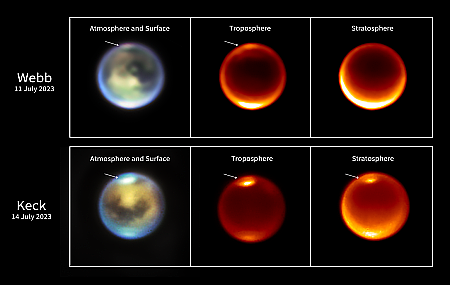
Volcanic thermal emission was detected from Loki Patera and Kanehekili Fluctus [two volcanic vents]. The main changes in the shape of the thermal emission spectra since [Webb] observed Io in November 2022 were consistent with the continued cooling of emplaced lava flows in the Kanehekili Fluctus region, and the crust that had formed on the surface of the lava lake in Loki Patera. Images of Io in the SO 1.707 μm emission band [sulfur monoxide] show a concentration above Kanehekili Fluctus and in two regions in the northern hemisphere. The emissions are sourced from SO molecules ejected from volcanic vents. We further detected, for the first time, sulfur line emissions at 1.08 and 1.13 μm. These emissions are distributed homogeneously across a band in Io’s northern hemisphere. They are mainly produced through excitation by electrons from the plasma torus, penetrating Io’s atmosphere.
The top image to the right shows the heat signature above the two volcanoes, one to the southwest and the second to the northeast. The middle image shows the sulfur monoxide emissions detected by Webb above those volcanoes from their on-going eruptions. The bottom image shows the more diffuse sulfur emissions, mostly in the northern hemisphere, believed produce by interactions with the plasma torus.
This research also relied on data obtained by both the Keck telescopes in Hawaii and the Hubble Space Telescope.
There are of course uncertainties with these results. For example, the conclusion that the more diffuse sulfur is produced by interactions with the plasma torus is not as certain. First, those sulfur emissions still appear closely linked to the volcanoes, which suggests this still could be a source.
Second, the observations also cover only two data points in time, in 2022 and 2023. To get a more precise map of the activity on Io we really need an orbiter there observing the planet on a continuous basis, something that is at this time impossible, not only because no mission is planned but because the hostile radiation environment this close to Jupiter makes the engineering quite challenging. It is this reason why Europa Clipper is not going into orbit around Europa when it arrives there in 2031. Better to orbit Jupiter and only periodically dip into that harsh radiation environment.
Using the Webb Space Telescope, scientists have tracked two different volcanic eruptions on Io that too place from 2022 to 2023, detecting sulfur monoxide both from those eruptions as well as sulfur from the magnetic plasma torus produced as the planet travels through Jupiter’s strong magnetic field. From the paper’s abstract:
Volcanic thermal emission was detected from Loki Patera and Kanehekili Fluctus [two volcanic vents]. The main changes in the shape of the thermal emission spectra since [Webb] observed Io in November 2022 were consistent with the continued cooling of emplaced lava flows in the Kanehekili Fluctus region, and the crust that had formed on the surface of the lava lake in Loki Patera. Images of Io in the SO 1.707 μm emission band [sulfur monoxide] show a concentration above Kanehekili Fluctus and in two regions in the northern hemisphere. The emissions are sourced from SO molecules ejected from volcanic vents. We further detected, for the first time, sulfur line emissions at 1.08 and 1.13 μm. These emissions are distributed homogeneously across a band in Io’s northern hemisphere. They are mainly produced through excitation by electrons from the plasma torus, penetrating Io’s atmosphere.
The top image to the right shows the heat signature above the two volcanoes, one to the southwest and the second to the northeast. The middle image shows the sulfur monoxide emissions detected by Webb above those volcanoes from their on-going eruptions. The bottom image shows the more diffuse sulfur emissions, mostly in the northern hemisphere, believed produce by interactions with the plasma torus.
This research also relied on data obtained by both the Keck telescopes in Hawaii and the Hubble Space Telescope.
There are of course uncertainties with these results. For example, the conclusion that the more diffuse sulfur is produced by interactions with the plasma torus is not as certain. First, those sulfur emissions still appear closely linked to the volcanoes, which suggests this still could be a source.
Second, the observations also cover only two data points in time, in 2022 and 2023. To get a more precise map of the activity on Io we really need an orbiter there observing the planet on a continuous basis, something that is at this time impossible, not only because no mission is planned but because the hostile radiation environment this close to Jupiter makes the engineering quite challenging. It is this reason why Europa Clipper is not going into orbit around Europa when it arrives there in 2031. Better to orbit Jupiter and only periodically dip into that harsh radiation environment.