Natalia Osipova and Carlos Acosta – Giselle: Act II
An evening pause: This performance by Royal Ballet and Opera company took place in 2015.
Hat tip Judd Clark.
An evening pause: This performance by Royal Ballet and Opera company took place in 2015.
Hat tip Judd Clark.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.

NASA’s failed Moon spacesuits
A new NASA inspector report issued today [pdf] has found that the single contractor NASA uses to maintain the spacesuits on ISS, Collins Aerospace, has increasingly been unable to do the job, and NASA has no alternative contractor to turn to. From the report’s executive summary:
We previously reported on NASA’s spacesuit management in 2017 and 2021, finding that the Agency faced a wide array of risks to sustaining the EMUs [the spacesuits], including design inadequacies, health risks, and low inventories of spacesuit life support systems, ultimately leading to NASA’s efforts to design and develop next-generation suits to replace the existing EMUs. Specifically, the EMU design flaws have increased the chance of and led to unexpected water in helmets, thermal regulation malfunctions, and astronaut injuries. Given that spacesuits are necessary to meet future ISS maintenance needs until its planned decommissioning in 2030, it is critical that NASA effectively manages the contract performance and subsequent safety risks associated with ESOC [the contract with Collins].
…Until the ISS’s planned decommission at the end of the decade, NASA will continue to require spacewalking capabilities to perform upgrades and corrective and preventative maintenance to the Station. However, Collins’ performance on ESOC increases programmatic risks to NASA as it attempts to conduct safe spacewalks outside the ISS and maintain critical EMU life support component inventories. The contractor is experiencing considerable schedule delays, cost overruns, and quality issues that significantly increase the risk to maintaining NASA’s spacewalking capability.
Collins was awarded this five-year cost-plus maintenance contract in 2010 for $324 million. Since then NASA has been repeatedly extending it, so that it now runs through 2027 and has funneled $1.4 billion into Collins’ bank account. Yet Collins has repeatedly failed to deliver necessary repair parts, even as there have been more frequent problems on ISS, including several cases where spacewalks had to be aborted because an astronaut’s life was in danger. Here are just a few examples cited in the report:
» Read more
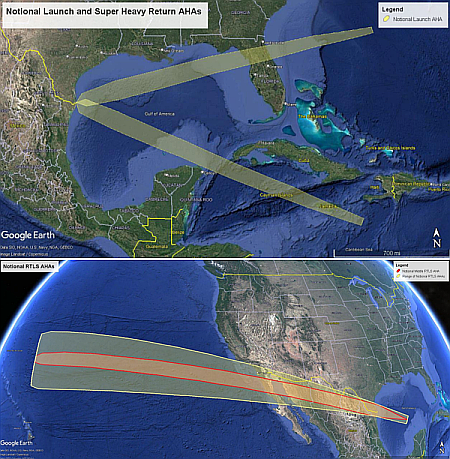
The planned return trajectories for both
Superheavy and Starship on future tests
In an update posted yesterday on SpaceX’s website, the company revealed that it is targeting October 13, 2025 for the eleventh orbital test flight of its Starship/Superheavy rocket.
The update also provided details about the company will test during this flight, including the reuse of a second Superheavy booster.
The booster on this flight test previously flew on Flight 8 and will launch with 24 flight-proven Raptor engines. Its primary test objective will be demonstrating a unique landing burn engine configuration planned to be used on the next generation Super Heavy. It will attempt this while on a trajectory to an offshore landing point in the Gulf of America and will not return to the launch site for catch.
Upon return the booster will start off by firing thirteen engines, the five, and finally three just before landing, to test refinements to its return to Earth.
Starship meanwhile will mostly repeat with variations the test program from flight 10, including the deployment of dummy Starlink satellites, the relight of one of its Raptor engines, and the testing of different thermal protection systems. It will once again fly a low orbital path that will bring it down in the Indian Ocean, either under control or not. This Starship prototype is the last of version two, so there are a limited number of things it can test.
Beginning with the 12th test flight, the company will begin flying version 3, and will likely quickly move to full orbital flights and a chopstick catch of Starship at Boca Chica, as shown by the flight paths in the graphic to the right.
During a static fire engine test yesterday in preparation for launch, the rocket startup Firefly lost the first stage when an explosion occurred at what appeared to be the base of the rocket. From the company’s update:
During testing at Firefly’s facility in Briggs, Texas, the first stage of Firefly’s Alpha Flight 7 rocket experienced an event that resulted in a loss of the stage. Proper safety protocols were followed, and all personnel are safe. The company is assessing the impact to its stage test stand, and no other facilities were impacted.
Video of the explosion can be seen here.
This incident will obviously delay the next launch, which had only just been scheduled following the completion of the company’s investigation into its launch failure in April. This explosion also suggests there remain serious issues with the Alpha rocket, which has only had two full successes in six launch attempts.
At the same time, with the successful soft landing of its Blue Ghost lander on the Moon earlier this year, Firefly has demonstrated its engineering can be sound and robust. It just appears that a lot more work needs to be done to get Alpha into shape.
China earlier today successfully launched two test satellites for “experimental verification of Earth observation technologies, its Long March 2D rocket lifting off from its Xichang space port in southwest China.
No word on where the rocket’s lower stages, using very toxic hypergolic fuels, crashed inside China. The two satellites are part of the Shiyan family of satellites that have done rendezvous and proximity operations as well as surveillance of other satellites in orbit.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
126 SpaceX
58 China
13 Russia
12 Rocket Lab
SpaceX still leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 126 to 98.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
A new study suggests that exposing patients with advanced osteoarthritis (OA) to low doses of radiation reduced their pain significantly.
The trial included 114 people with primary knee OA, diagnosed by moderate damage visible on X-rays, and significant pain with walking. They were randomly assigned to one of three groups: very low-dose radiation (0.3 Gy total, spread over six sessions of 0.05 Gy), low-dose radiation (3 Gy total, spread over six sessions of 0.5 Gy), or a sham treatment that did not deliver radiation.
…Each treatment in this trial was 500 mGy, which works out to be 5,000 times the radiation dose of a chest X-ray and around 70 times the dose of a chest CT scan. However, while this sounds like a lot, the treatment delivered in the study is still considered to be low-dose. For radiotherapy cancer treatment, for example, total doses are usually 50 to 70 Gy – so a total of 3 Gy is roughly one-twentieth or less of that.
…Trial participants couldn’t take regular pain meds during the first four months, other than occasional “rescue” meds if needed. No second round of radiation was allowed. The main treatment outcome was how many participants showed significant improvement after four months, as measured by assessments of pain and function.
The 3 Gy group did significantly better than the sham group. About 70% improved vs 42% in the sham group. Over half (57%) of people in the 3 Gy group had a clinically meaningful improvement in joint pain and function scores vs about 31% in the sham group. The 0.3 Gy group didn’t show a statistically significant improvement; about 58% improved. No meaningful differences were seen in blood markers of inflammation or in the amount of pain medication people used. The treatment was deemed to be safe, with no side effects or toxicity reported.
If this result is confirmed, it suggests strongly that especially for the older population there is now a viable treatment for knee pain that avoids surgery and could be far more reliable.
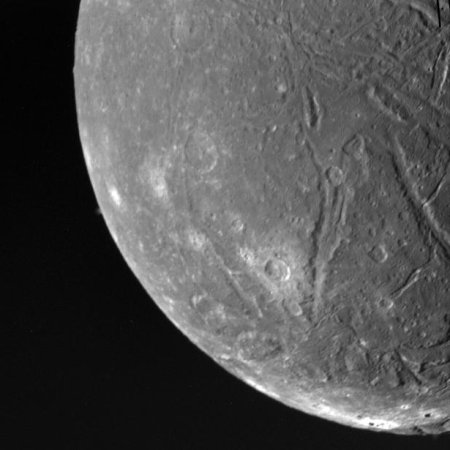

Ariel as seen by Voyager-2 in 1986.
Click for original image.
The uncertainty of science: Using computer modeling based on our scant data of the surface features of the Uranus moon Ariel, scientists now posit that underground oceans, some of gigantic depth as much as 100 miles deep, were required to shape those features.
“First, we mapped out the larger structures that we see on the surface, then we used a computer program to model the tidal stresses on the surface, which result from distortion of Ariel from soccer ball-shaped to slight football-shaped and back as it moves closer and farther from Uranus during its orbit,” Patthoff said. “By combining the model with what we see on the surface, we can make inferences about Ariel’s past eccentricity and how thick the ocean might have been.”
The team found that, in the past, Ariel needed to have an eccentricity of about 0.04 [to create those surface structures]. This is about 40 times larger than its current value. While 0.04 may not sound dramatic, eccentricity can strengthen the effects of tidal stresses, and Ariel’s orbit would have been four times more eccentric than that of Jupiter’s moon Europa, which is wracked by the tidal forces that push and pull it to create its cracked and broken surface. Yet, to the eye, the orbit will still resemble a circle.
“In order to create those fractures, you have to have either a really thin ice on a really big ocean, or a higher eccentricity and a smaller ocean,” Patthoff said. “But either way, we need an ocean to be able to create the fractures that we are seeing on Ariel’s surface.”
This result does not prove an underground ocean now exists, or even if one existed in the past. The data is based on the few fly-by images taken by Voyager-2 when it passed close to Uranus in 1986. Coverage of the entire surface of Ariel was not complete, nor did the images have much resolution. The data is suggestive of this conclusion, but not conclusive by any means.
Using the Webb Space Telescope, scientists have detected a host of carbon molecules inside an accretion disk that surrounds an exoplanet circling a baby star 625 light years away.
Infrared observations of CT Cha b were made with Webb’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument) using its medium resolution spectrograph. An initial look into Webb’s archival data revealed signs of molecules within the circumplanetary disk, which motivated a deeper dive into the data.
…Ultimately, the team discovered seven carbon-bearing molecules within the planet’s disk, including acetylene (C2H2) and benzene (C6H6). This carbon-rich chemistry is in stark contrast to the chemistry seen in the disk around the host star, where the researchers found water but no carbon. The difference between the two disks offers evidence for their rapid chemical evolution over only than 2 million years.
You can read the original paper here [pdf]. The exoplanet itself is thought to have a mass 14 to 24 times that of Jupiter, making it almost a brown dwarf star. The NASA makes a big deal claiming this disk is forming a moon around the exoplanet, but that is not what the paper finds. This research did not find any evidence of a new moon exoplanet.
Instead, the paper found an accretion disk rich in carbon molecules, a finding that is significant on its own. It also found that that the accretion disk around the central star, while lacking carbon molecules, appears rich in water.
In other words, this baby solar system is packed with the right material for eventually producing life. Moreover, in this system’s relatively short life, two million years, these materials were able to sort themselves out so that the star has one concentration of material while the exoplanet has another. Both facts suggest that organic chemistry is common in the universe, and can evolve fast.
That is the important discovery here.
Two Japanese startups, the lunar landing company Ispace and the orbital capsule startup ElevationSpace, have signed an agreement to develop the first private mission to bring samples back to Earth from the Moon.
Based on the agreement, Ispace and ElevationSpace will jointly pursue development to undertake a lunar return mission. Ispace has already demonstrated the technology to deploy a lander into lunar orbit through its two lunar missions operated in 2023 and 2025. The company is currently considering the development of an Orbital Transfer Vehicle (OTV), derived from its existing lunar lander development technology.
The collaboration aims to conduct a technology demonstration to verify the feasibility of missions utilizing an and the sample return re-entry capsule being developed by ElevationSpace, as well as to evaluate the overall system characteristics.
At the moment this project is only a PowerPoint proposal. Though Ispace has made two attempts to soft land an unmanned spacecraft on the Moon, neither was a success. It has three further contracts with NASA, ESA, and Japan’s space agency JAXA, but none has flown yet, and its orbital vehicle is only under development.
As for ElevationSpace, it has flown nothing yet as well. Its first demo satellite, designed to test re-entry and recovery, won’t fly until late next year, assuming its launch rocket, Isar’s new Spectrum, gets to orbit.
Nonetheless, this project illustrates the continuing shift to the private sector in space. The companies are doing this to demonstrate their capabilities in order to win contracts from both commercial and government customers.
In a result that could have a direct bearing on trying to understand the inexplicable geology of Mars, a new study has found that ice actually does a better job at releasing iron from mineral deposits than liquid water.
It was once believed that when iron-rich mineral deposits were locked in ice, the iron would stay put, but a new study from Sweden’s Umeå University shows that the ice itself is actually working better than permafrost melt to release the iron. The study showed that ice at -10 °C (14 °F) releases more iron from mineral deposits than liquid water at 4 °C (39.2 °F). “It may sound counterintuitive, but ice is not a passive frozen block,” says study co-author Jean-François Boily. “Freezing creates microscopic pockets of liquid water between ice crystals. These act like chemical reactors, where compounds become concentrated and extremely acidic. This means they can react with iron minerals even at temperatures as low as minus 30 degrees Celsius.”
The researchers also found that the seasonal freeze/thaw cycle helped this process, and that brackish fresh water did better in dissolving the iron than seawater.
The significance for Mars geology is that this suggests glacial ice in the alien Mars climate might be the catalyst for creating its meandering canyons that so much resemble features on Earth produced by liquid water. On Mars however no model yet has been convincingly successful in creating past conditions where liquid water could flow on the surface. Mars has either been is too cold or its atmosphere too thin to allow it.
This study suggests ice however could do the work. It also fits with other Martian data that suggests the same, that at the base of the Martian glaciers pockets of liquid water could exist that act to shape the canyons.
All of this is speculation on my part, but it seems that the planetary scientists who are studying Mars should take a close look at this research.
The Italian rocket company Avio has won $47 million study contract from the European Space Agency (ESA) to begin design work on a reusable upper stage rocket.
The contract runs for two years, with a goal to “assess and prepare the requirements, the design and the technologies for both the ground and flight segments required for an upper stage demonstrator that in the future could return to Earth and be reused on another flight.”
In other words, Avio is not yet building this upper stage, but will use this money to work up a design. The Avio graphic to the right suggests the lower stage will be based on the first stage of Avio’s solid-fueled Vega-C rocket. The upper stage concept appears to resemble Starship, which suggests Avio will be aiming for a vertical landing, using the methane-fueled engines it is developing for its not-yet-launched Vega-E rocket.
This ESA contract once again shows that agency’s shift to the capitalism model. Rather than develop this idea in-house, as it has done so poorly in the past, ESA has asked a private company to do it, and own what it develops.
SpaceX this evening successfully placed another 28 Starlink satellites into orbit, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
The first stage, B1063, completed its 28th flight, landing on a drone ship in the Pacific. (This booster had been listed as the first stage on a launch two days ago, but it turns out the booster on that flight was B1082, completing its 16th flight.) The present rankings for the most reflights of a rocket:
39 Discovery space shuttle
33 Atlantis space shuttle
30 Falcon 9 booster B1067
28 Columbia space shuttle
28 Falcon 9 booster B1071
28 Falcon 9 booster B1063
27 Falcon 9 booster B1069
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
126 SpaceX
57 China
13 Russia
12 Rocket Lab
SpaceX now leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 126 to 97. China has a launch scheduled for this evening, but nothing as yet has been published about its status as of this posting.
Since yesterday China successfully completed two launches from two of its interior spaceports.
First, it successfully launched what its state-run press described as a satellite that will “primarily support monitoring and research activities in weather forecasting, atmospheric chemistry and climate change”, its Long March 4C rocket lifting off yesterday from its Jiuquan spaceport in northwest China.
Then today China’s Long March 6A lifted off from its Taiyuan spaceport in north China, placing in orbit the eleventh set of satellites in the Guowang internet constellation, eventually aiming to be 13,000 satellites strong. China’s state-run press did not specify the exact number of satellites. Based on previous launches using the Long March 6A, the number was likely five, bringing the number of this constellation’s satellites now in orbit to 87.
No word on where the the lower stages of both rockets crashed inside China. This is even more critical with the Long March 4C, since it uses very toxic hypergolic fuels that can dissolve your skin if it touches you.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
125 SpaceX
57 China
13 Russia
12 Rocket Lab
SpaceX now leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 125 to 97.
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
To listen to all of John Batchelor’s podcasts, go here.
» Read more
An evening pause: No visuals, no instruments, just their voices singing to heaven.
Hat tip Mike Nelson.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
If you think the left is tamping down its violent rhetoric and terrorist murder attempts of conservatives, think again. Earlier this week an independent group of conservatives wearing MAGA hats decided to set up a table at Tennessee State University (TSU), inviting anyone to debate the merits or failures of DEI.
Very quickly a mob formed, stealing their signs and becoming increasingly threatening, with at least one carrying a screwdriver in a threatening manner. The police arrived, but did literally nothing to protect the students.
Eventually the students closed up their table and attempted to drive away, only to have their car surrounded by the mob and blocked from leaving. It took an extensive effort for the police to clear a path to let these students escape.
Watch for yourself below. And note, such mob violence against conservatives on campuses is not new. I have been reporting such events now for years. The only difference now is that the mobs appear to becoming more violent and aggressive.
» Read more
A team of Japanese astronomers have used the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) in Chile to detect for the first time the rotation of the spiral accretion disk that surrounds a young star, rotation that showed the spiral was in the process of forming new planets.
Observations have revealed a spiral pattern in the disk of gas and dust around the young star IM Lup located 515 light-years away in the direction of the constellation Lupus. Spiral patterns are thought to be one of the signs that a new planet will form soon, but other things, such as an already formed planet, can also form spirals. These different types of spirals cannot be distinguished by visual inspection, but they are expected to move differently over time.
To determine the origin of the spirals around IM Lup, an international research team led by Tomohiro Yoshida, a graduate student at The Graduate University for Advanced Studies, SOKENDAI and the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ), created a stop-motion animation of the spiral pattern using four observations taken by ALMA over the course of seven years. The motion of the spirals in the stop-motion animation shows that they were not caused by an already formed planet, and instead the spirals might be helping to form a new planet.
The two images to the right, taken from the movie, show the spiral’s shift over seven years. I have added the vertical line down the center to help highlight that change.
This discovery once again illustrates the increasing sophistication of our astronomical tools, able to observe such changes at such a great distance.

Proposed Canadian spaceports
After trying twice earlier this week to launch its first suborbital test rocket from its Atlantic Spaceport in Newfoundland, the rocket startup Nordspace has decided to postpone that launch for at least several weeks, while it investigates the fuel leaks on the launchpad that caused fires during both launch attempts.
After detailed review over the last 15 hours, the root cause has been discovered to be related to our propellant quality slightly differing between vehicle tests at our test facility in Ontario, compared to our first launch test in Newfoundland and Labrador at our spaceport. This led to a fuel-rich scenario. All systems on the rocket and ground performed nominally after careful review. Personnel, rocket and the launch pad are perfectly safe and secure, and our safety systems operated nominally. As our company’s manufacturing and testing facilities are located in Ontario, there’s no expedient way to make the necessary modification with the temporary infrastructure and suppliers we have in place at our launch site.
This company is only about three years old, so this delay is hardly systematic to its operations. In that time they have established their own private spaceport, have built their first demo satellite (set to launch in June 2026), and developed a test suborbital rocket, Taiga, that is on the cusp of its first launch. The company is also developing its own rocket engines, as well as an orbital rocket dubbed Tundra.
Its speed puts to shame Canada’s other proposed spaceport in Nova Scotia, which was first proposed in 2016, and has far accomplished little. Many of its problems stemmed from the Ukraine War, which lost it the rocket it had hoped to market. Even so, it only signed its first launch customer in August of this year.
In another sign that the member nations of the European Space Agency (ESA) are increasingly going their own way, Germany’s defense minister announced yesterday that his agency plans to spend $41 billion on space through 2030.
According to a 25 September Bundeswehr (German Armed Forces) release published following the minister’s address, the €35 billion investment will cover five main priorities: hardening against data disruptions and attacks, improved space situational awareness, redundancy through several networked satellite constellations, secure, diverse, and on-demand launch capabilities, and a dedicated military satellite operations centre.
This commitment is going to definitely benefit the three German rocket startups, Isar Aerospace, Rocket Factory Augsburg, and Hyimpulse. It will also likely benefit the North Sea launch platform — based in Germany — that is being built by a German consortium that has already received almost one million from the government.
While the European partners in ESA have generally kept their military spending separate from that agency, in the past a large bulk of this defense spending would have been committed to ESA joint projects, such as funding the agency’s commercial launch operation, Arianespace, to do the launches. No more.

Tenacity grounded in a warehouse, with the
Shooting Star small cargo capsule attached to
its aft port.
NASA today announced it has modified its fixed-price cargo contract with Sierra Space, canceling the planned seven cargo missions as well as a demo docking mission, replacing this with one test flight that will simply go into orbit and then return to Earth.
After a thorough evaluation, NASA and Sierra Space have mutually agreed to modify the contract as the company determined Dream Chaser development is best served by a free flight demonstration, targeted in late 2026. Sierra Space will continue providing insight to NASA into the development of Dream Chaser, including through the flight demonstration. NASA will provide minimal support through the remainder of the development and the flight demonstration. As part of the modification, NASA is no longer obligated for a specific number of resupply missions, however, the agency may order Dream Chaser resupply flights to the space station from Sierra Space following a successful free flight as part of its current contract.
The first launch of Tenacity, the only Dream Chaser so far constructed, has been repeatedly delayed for the past two years, with no explanation from either the company or NASA. Those delays started in 2023 as engineers began the final ground testing before launch, so though we do not know what the issue is it is likely that testing found something fundamentally wrong with the spacecraft that Sierra could not afford to fix.
According to Sierra’s own press release, the company will target a late 2026 launch for that free flyer mission. The company still hopes that mission will make further flights possible, either purchased by NASA or by others wishing to use Tenacity for in-orbit manufacturing, something it first proposed last year.
In the past two years, Sierra has shifted its focus away from commercial manned space and more towards winning military defense contracts. Part of that decision might have come from the problems with Dream Chaser. The decision might have also been fueled by the company’s generally unsatisfactory experience working with Blue Origin on their proposed Orbital Reef space station. While Sierra committed cash to develop and test its LIFE inflatable module, including a full scale prototype, Blue Origin appeared to do nothing at all. As early as September 2023 there were rumors the partnership was falling apart.
SpaceX this evening successfully placed 24 additional Starlink satellites into orbit, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
The first stage completed its 28th flight, landing on a drone ship in the Pacific, moving it up into the top rankings for the most reuse by a rocket:
39 Discovery space shuttle
33 Atlantis space shuttle
30 Falcon 9 booster B1067
28 Columbia space shuttle
28 Falcon 9 booster B1071
28 Falcon 9 booster B1063
27 Falcon 9 booster B1069
As for the 2025 launch race, this is the present leader board:
125 SpaceX
55 China
13 Russia
12 Rocket Lab
SpaceX now leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 125 to 95.
An evening pause: Taken from the album Viva Elvis, which is the soundtrack remix of Presley’s Cirque du Soleil show. From the youtube webpage:
Viva Elvis features new backing instrumentation on each track in an attempt to modernize the arrangements. This has met with a mixed critical response, with some reviewers praising the production quality and others opining that Elvis’s music is best left untampered with.
Hat tip Cotour.
For those interested in hearing Robert Pratt and I discuss the non-stop ugliness we are presently seeing from the left side of the political spectrum, I will be on his show, Pratt on Texas, starting tomorrow at 5 pm (Central).
We taped the show today. Three out of the four segments focused on that tragic and very horrible madness that seems cool with the idea of killing people because of their opinions. The last segment focused on the space industry.
You can listen live at either the “listen live” button at the website of the country station KORQ 96.1, or here, or at the Pratt on Texas website.
If you can’t listen live, the podcast is now embedded below.
» Read more
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) and downloaded on August 3, 2025. Labeled as a “terrain sample,” such images are usually taken not as part of any specific research request but because the camera team needs to fill a gap in the camera’s schedule so as to maintain its proper temperature. When they do this, they always try to pick interesting targets within the time window, and usually succeed.
In this case, the camera team picked a location in the middle of Isidis Planitia, one of Mars’ four biggest basins thought to have been formed from a major impact several billion years ago, focusing on an area covered with these strange knobs that have craterlike depressions at their peaks.
According research published in 2010 [pdf], it is believed these cones — all of which are only a few feet high — are the result of volcanic activity following the impact that formed Isidis four billion years ago. In a sense, they are leftover pimples from that impact and the subsequent volcanic activity within that melted basin.
» Read more
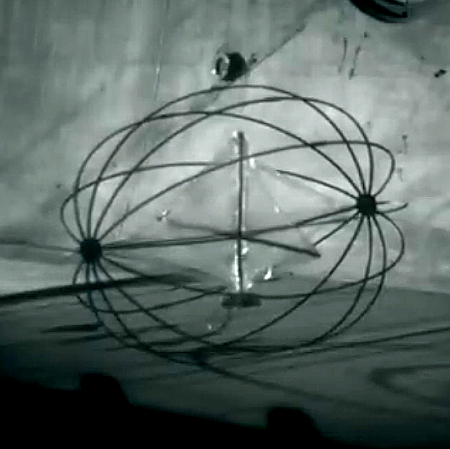

Tumbleweed being tested on sandy ground. Click for video.
European engineers at Aarhus University in Denmark have now developed and tested a tumbling rover design that is propelled solely by the Martian wind. You can read their most recent paper here.
Not surprisingly, they call it “Tumbleweed.” The screen capture to the right comes from a video of a wind tunnel test proving the Martian atmosphere could move a prototype on sandy ground. The engineers also did similar tests successfully on rocky and coarse ground.
In July 2025, Team Tumbleweed conducted a week-long experimental campaign, supported by Europlanet, at Aarhus University’s Planetary Environment Facility. Using scaled prototypes with 30-, 40- and 50-centimetre diameters, the team carried out static and dynamic tests in a wind tunnel with a variety of wind speeds and ground surfaces under a low atmospheric pressure of 17 millibars.
Results showed that wind speeds of 9-10 metres per second were sufficient to set the rover in motion over a range of Mars-like terrains including smooth and rough surfaces, sand, pebbles and boulder fields. Onboard instruments successfully recorded data during tumbling and the rover’s behaviour matched fluid-dynamics modelling, validating simulations. The scale-model prototypes were able to climb up a slope of 11.5 degrees in the chamber – equivalent to approximately 30 degrees on Mars – demonstrating that the rover could traverse even unfavourable slopes.
Their concept is to send a swarm of Tumbleweeds to Mars, where they could cheaply document prevailing wind and speeds globally. More sophisticated versions could act as full weather stations, as well as provide in situ data about the landscapes they traverse.
The concept is still in its development stage. The next stage of testing will see if Tumbleweed will work with some science sensors attached.