Dart changed the orbit of the Didymos/Dimorphos binary asteroids around the Sun

When the Dart spacecraft impacted the asteroid Dimorphos in September 2022, it not only shortened Dimophos’ orbit around its companion asteroid Didymos by about 33 minutes while reshaping the asteroid, a new study has found that it also changed very slightly the orbit of both asteroids around the Sun.
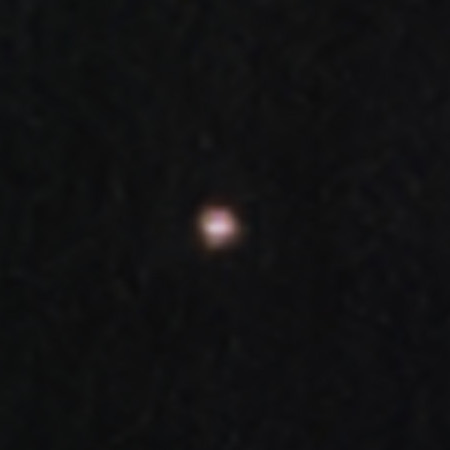
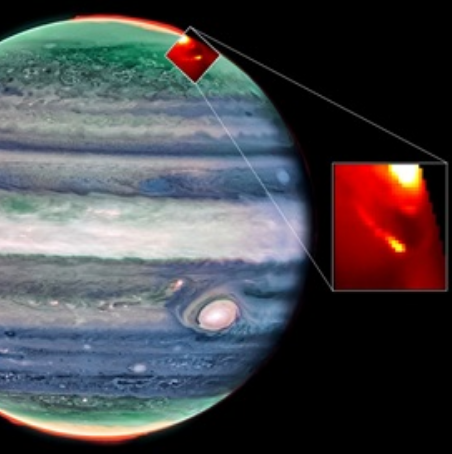
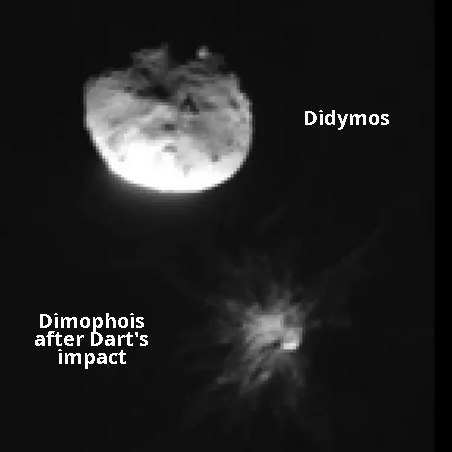
The image to the right, annotated to post here, was taken by the Italian LICIACube spacecraft moments after the September 26, 2022 impact.
The research paper describing this research can be found here. From the press release:
The new study shows the impact ejected so much material from the binary system that it also changed the binary’s orbital period around the Sun by 0.15 seconds. “The change in the binary system’s orbital speed was about 11.7 microns per second, or 1.7 inches per hour,” said Rahil Makadia, the study’s lead author at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign. “Over time, such a small change in an asteroid’s motion can make the difference between a hazardous object hitting or missing our planet.”
To be precise, the orbital speed was slowed 1.7 inches per hour, which while tiny would mean its solar orbit is now slightly lengthened.
The result proves that a similar impact could be used on some asteroids to deflect them from hitting the Earth, though we would need to know a lot about that asteroid prior to launching the mission to accurately predict the orbital change. Otherwise, any impact could be a dangerous crap shoot that could do more harm than good.

When the Dart spacecraft impacted the asteroid Dimorphos in September 2022, it not only shortened Dimophos’ orbit around its companion asteroid Didymos by about 33 minutes while reshaping the asteroid, a new study has found that it also changed very slightly the orbit of both asteroids around the Sun.
The image to the right, annotated to post here, was taken by the Italian LICIACube spacecraft moments after the September 26, 2022 impact.
The research paper describing this research can be found here. From the press release:
The new study shows the impact ejected so much material from the binary system that it also changed the binary’s orbital period around the Sun by 0.15 seconds. “The change in the binary system’s orbital speed was about 11.7 microns per second, or 1.7 inches per hour,” said Rahil Makadia, the study’s lead author at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign. “Over time, such a small change in an asteroid’s motion can make the difference between a hazardous object hitting or missing our planet.”
To be precise, the orbital speed was slowed 1.7 inches per hour, which while tiny would mean its solar orbit is now slightly lengthened.
The result proves that a similar impact could be used on some asteroids to deflect them from hitting the Earth, though we would need to know a lot about that asteroid prior to launching the mission to accurately predict the orbital change. Otherwise, any impact could be a dangerous crap shoot that could do more harm than good.