Click for original image.
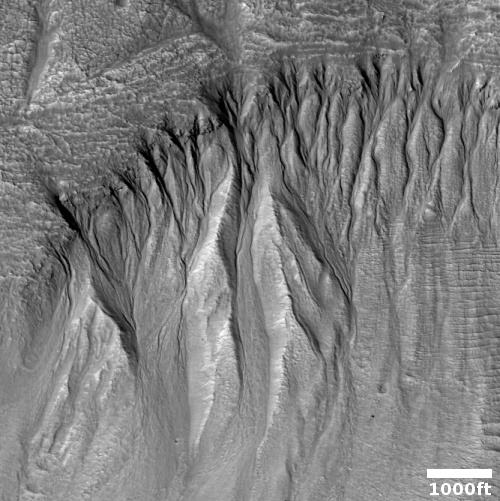
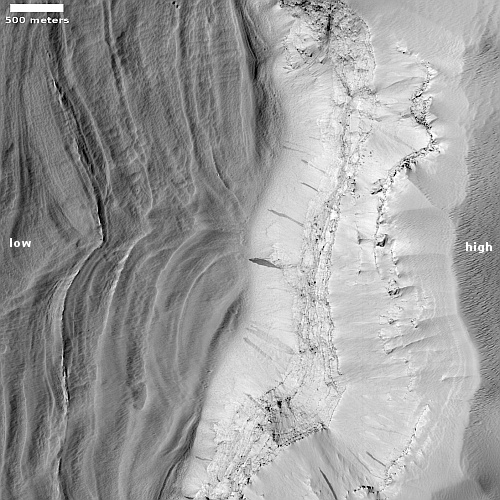
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on March 24, 2023 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) as part of a long term monitoring program of the many Martian gullies scientists have found above 30 degrees north latitude on a variety of slopes.
Martian gullies are small, incised networks of narrow channels and their associated downslope sediment deposits, found on the planet of Mars. They are named for their resemblance to terrestrial gullies. First discovered on images from Mars Global Surveyor, they occur on steep slopes, especially on the walls of craters. Usually, each gully has a dendritic alcove at its head, a fan-shaped apron at its base, and a single thread of incised channel linking the two, giving the whole gully an hourglass shape. They are estimated to be relatively young because they have few, if any craters.
…Most gullies occur 30 degrees poleward in each hemisphere, with greater numbers in the southern hemisphere. Some studies have found that gullies occur on slopes that face all directions; others have found that the greater number of gullies are found on poleward facing slopes, especially from 30° to 44° S. Although thousands have been found, they appear to be restricted to only certain areas of the planet. In the northern hemisphere, they have been found in Arcadia Planitia, Tempe Terra, Acidalia Planitia, and Utopia Planitia. In the south, high concentrations are found on the northern edge of Argyre basin, in northern Noachis Terra, and along the walls of the Hellas outflow channels.
Orbital data has identified almost 5,000 gullies on Mars. Based on their shape and the Martian climate, scientists generally think these gullies were formed by some form of water flow, possibly coming from an underground aquifer at their top.
» Read more