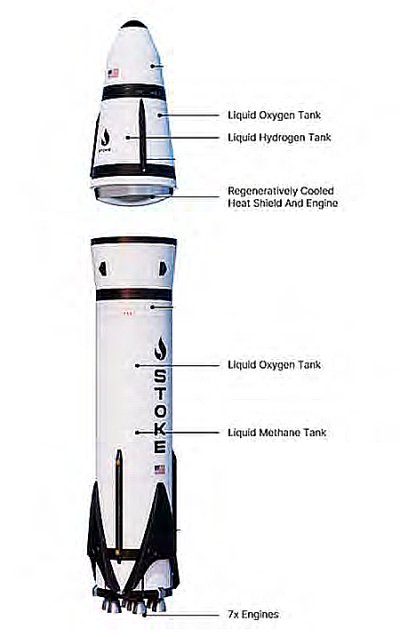
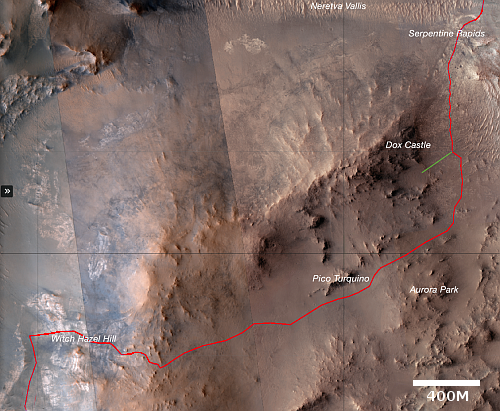
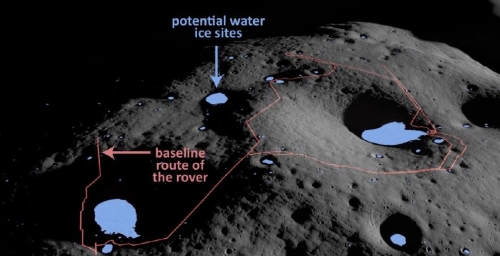
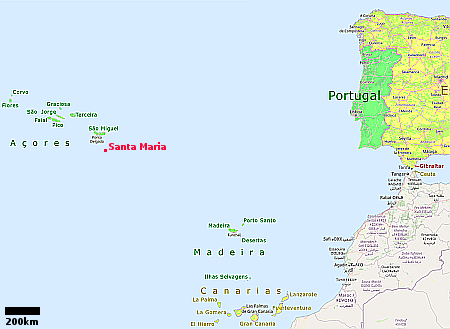
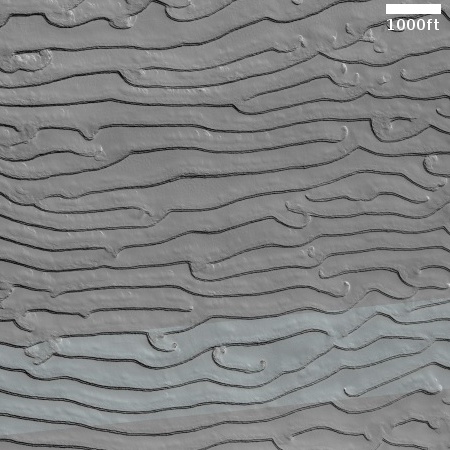
China launches new set of classified remote-sensing satellites
China today launched a new set of classified remote-sensing satellites supposedly designed to test “new technologies of low-orbit constellations, using its Long March 4B rocket lifting off from its Xichang spaceport in the southwest of China.
Almost no information was released about the satellites. Nor did China’s state-run press reveal where the rocket’s lower stages, carrying toxic hypergolic fuels, crashed within China.
The leaders in the 2024 launch race:
81 SpaceX
34 China
10 Rocket Lab
9 Russia
American private enterprise still leads the rest of the world combined in successful launches 96 to 52, while SpaceX by itself still leads the entire world combined, including American companies, 81 to 67.
These numbers will likely change in only a few hours, as SpaceX has another launch today, scheduled for 11:20 am (Pacific).
China today launched a new set of classified remote-sensing satellites supposedly designed to test “new technologies of low-orbit constellations, using its Long March 4B rocket lifting off from its Xichang spaceport in the southwest of China.
Almost no information was released about the satellites. Nor did China’s state-run press reveal where the rocket’s lower stages, carrying toxic hypergolic fuels, crashed within China.
The leaders in the 2024 launch race:
81 SpaceX
34 China
10 Rocket Lab
9 Russia
American private enterprise still leads the rest of the world combined in successful launches 96 to 52, while SpaceX by itself still leads the entire world combined, including American companies, 81 to 67.
These numbers will likely change in only a few hours, as SpaceX has another launch today, scheduled for 11:20 am (Pacific).