Congress: Let’s throw some more astronaut lives away so we can preen for the camera!

Jared Isaacman
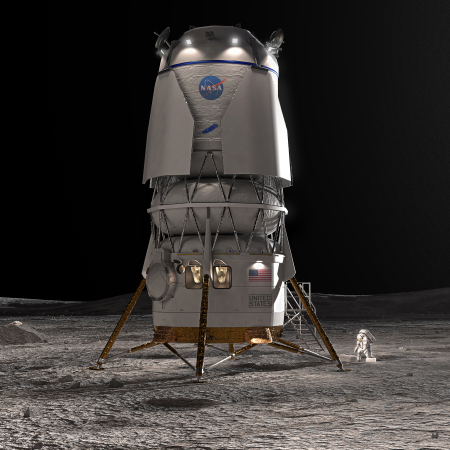
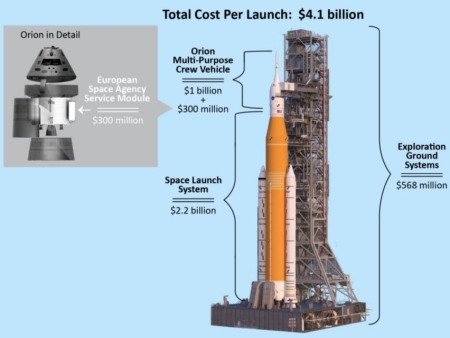
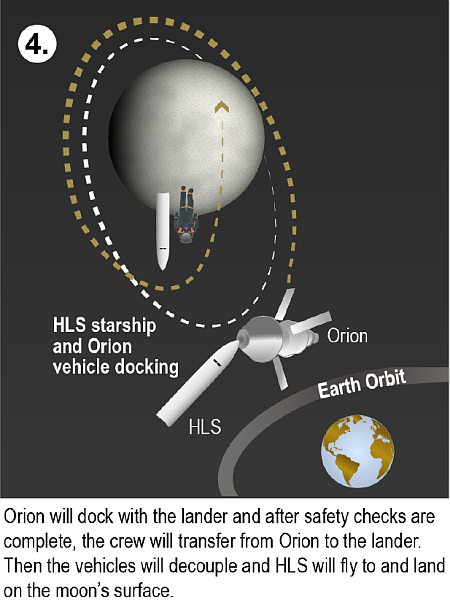
Here we go again: As I noted yesterday, the hearing this week of Jared Isaacman, Donald Trump’s nomination to become NASA’s next administrator, revealed almost nothing about what Isaacman plans to do once confirmed by the Senate. He very carefully kept his options open, even while he strongly endorsed getting Americans on the Moon as fast as possible in order to beat the Chinese there. When pressed by senators from both parties to commit to continuing the SLS, Orion, and Lunar Gateway projects to make that happen, Isaacman picked his words most cautiously. He noted that at the moment that plan seemed the best for getting to the Moon first. He also noted repeatedly that this same plan is years behind schedule and overbudget.
Like any smart businessman, Isaacman knows he cannot make any final decisions about SLS, Orion, or Gateway until he takes office and can aggressively dig into the facts, as administrator. He also knew he could not say so directly during this hearing, for to do so would antagonize senators from both parties who want those programs continued because of the money it pours into their states. So he played it coy, and the senators accepted that coyness in order to make believe they were getting what they want.
But what do these senators want? It appears our politicians (including possibly Trump) want NASA to launch humans to the Moon using SLS and Orion and do so as quickly as possible, despite knowing that both have real engineering issues of great concern. Instead, our elected officials want politics to determine the lunar flight schedule, instead of engineering, the same attitude that killed astronauts on Apollo 1 in 1967, on Challenger in 1986, and on Columbia in 2003. The engineering data then said unequivocally that things were not safe and that disaster was almost guaranteed, but NASA and Congress demanded the flights go on anyway, to serve the needs of politics.
With SLS and Orion it is now the same foolishness all over again. » Read more