NASA cancels its VIPER payload on Astrobotic’s Griffin lunar lander
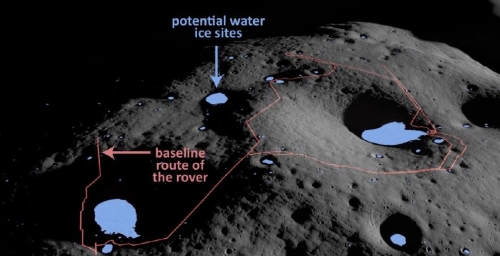
VIPER’s now canceled planned route at the Moon’s south pole
Late yesterday NASA announced it was canceling the VIPER rover that was the primary payload on Astrobotic’s Griffin lunar lander, scheduled for launch in the fall of 2025.
NASA stated cost increases, delays to the launch date, and the risks of future cost growth as the reasons to stand down on the mission. The rover was originally planned to launch in late 2023, but in 2022, NASA requested a launch delay to late 2024 to provide more time for preflight testing of the Astrobotic lander. Since that time, additional schedule and supply chain delays pushed VIPER’s readiness date to September 2025, and independently its CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) launch aboard Astrobotic’s Griffin lander also has been delayed to a similar time. Continuation of VIPER would result in an increased cost that threatens cancellation or disruption to other CLPS missions. NASA has notified Congress of the agency’s intent.
Knowing a bit of history is important to understand this decision. In the first half of the 2010s VIPER was called Resource Prospector, and was intended as an entirely NASA-built lunar lander and rover mission with a budget of about billion dollars. In 2018 however the Trump administration cancelled it as part of its decision to shift from missions designed, built, and owned by NASA to making NASA simply a customer buying products from private sector. Rather than spend a billion on one lunar lander/rover mission, NASA would use that money to buy multiple lunar landers from private companies, and put its instruments on those.
NASA then decided to repurpose the rover portion of Resource Prospector, turning it into VIPER to launch on Astrobotic’s Griffin lander. However, that project still carried with it all the problems that curse all government-designed, government-built, and government-owned projects. It had no fixed price contract but instead had the typical government unlimited checking account, and thus its costs kept rising with repeated delays in construction.
When then-NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine revealed the project at the 2019 International Astronautical Congress, the estimated cost was $250 million. By the time NASA was ready to make a cost commitment to Congress, that grew to $433.5 million with landing in 2023. That landing date slipped to 2024 with a cost of $505.4 million. Now it has slipped again to 2025 and with a cost of $609.6 million, more than 30 percent above the commitment. That triggered an automatic cancellation review, Kearns said, which took place last month.
Some of the cause of the 2023 delay was because Astrobotic’s Griffin lander wasn’t ready either. Now however it appears VIPER still won’t be ready for the 2025 launch, even though the lander will be ready.
NASA has therefore decided to stop throwing good money after bad, and kill the rover. It however has not killed its funding for Astrobotic’s Griffin, and the mission will go forward, with the company offering its now open payload space to others. It also may use this space to fly a demonstration mission of its own proposed LunarGrid solar power system.

VIPER’s now canceled planned route at the Moon’s south pole
Late yesterday NASA announced it was canceling the VIPER rover that was the primary payload on Astrobotic’s Griffin lunar lander, scheduled for launch in the fall of 2025.
NASA stated cost increases, delays to the launch date, and the risks of future cost growth as the reasons to stand down on the mission. The rover was originally planned to launch in late 2023, but in 2022, NASA requested a launch delay to late 2024 to provide more time for preflight testing of the Astrobotic lander. Since that time, additional schedule and supply chain delays pushed VIPER’s readiness date to September 2025, and independently its CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) launch aboard Astrobotic’s Griffin lander also has been delayed to a similar time. Continuation of VIPER would result in an increased cost that threatens cancellation or disruption to other CLPS missions. NASA has notified Congress of the agency’s intent.
Knowing a bit of history is important to understand this decision. In the first half of the 2010s VIPER was called Resource Prospector, and was intended as an entirely NASA-built lunar lander and rover mission with a budget of about billion dollars. In 2018 however the Trump administration cancelled it as part of its decision to shift from missions designed, built, and owned by NASA to making NASA simply a customer buying products from private sector. Rather than spend a billion on one lunar lander/rover mission, NASA would use that money to buy multiple lunar landers from private companies, and put its instruments on those.
NASA then decided to repurpose the rover portion of Resource Prospector, turning it into VIPER to launch on Astrobotic’s Griffin lander. However, that project still carried with it all the problems that curse all government-designed, government-built, and government-owned projects. It had no fixed price contract but instead had the typical government unlimited checking account, and thus its costs kept rising with repeated delays in construction.
When then-NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine revealed the project at the 2019 International Astronautical Congress, the estimated cost was $250 million. By the time NASA was ready to make a cost commitment to Congress, that grew to $433.5 million with landing in 2023. That landing date slipped to 2024 with a cost of $505.4 million. Now it has slipped again to 2025 and with a cost of $609.6 million, more than 30 percent above the commitment. That triggered an automatic cancellation review, Kearns said, which took place last month.
Some of the cause of the 2023 delay was because Astrobotic’s Griffin lander wasn’t ready either. Now however it appears VIPER still won’t be ready for the 2025 launch, even though the lander will be ready.
NASA has therefore decided to stop throwing good money after bad, and kill the rover. It however has not killed its funding for Astrobotic’s Griffin, and the mission will go forward, with the company offering its now open payload space to others. It also may use this space to fly a demonstration mission of its own proposed LunarGrid solar power system.

