India’s Chandrayaan-2 lunar orbiter photographs Intuitive Machines’ Athena lander
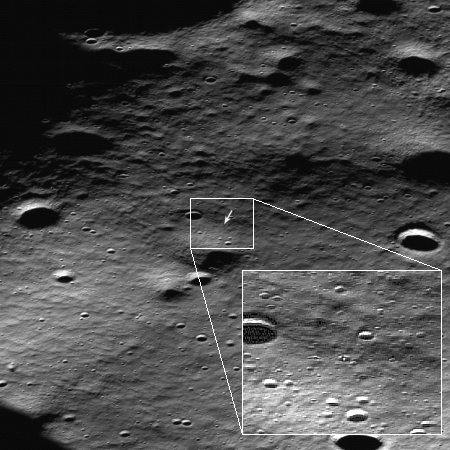
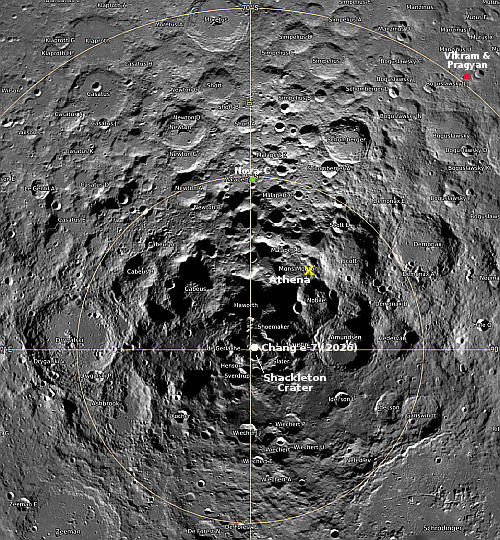
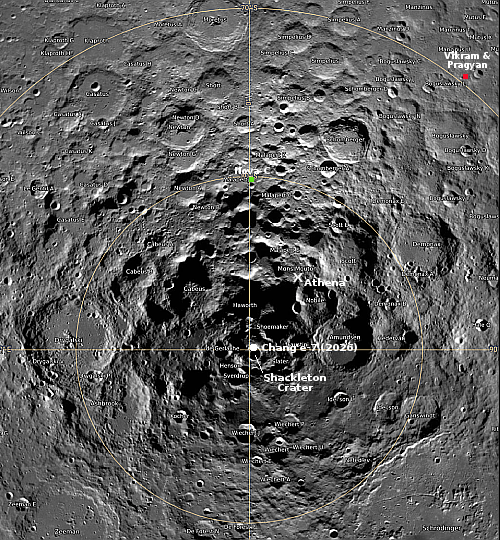
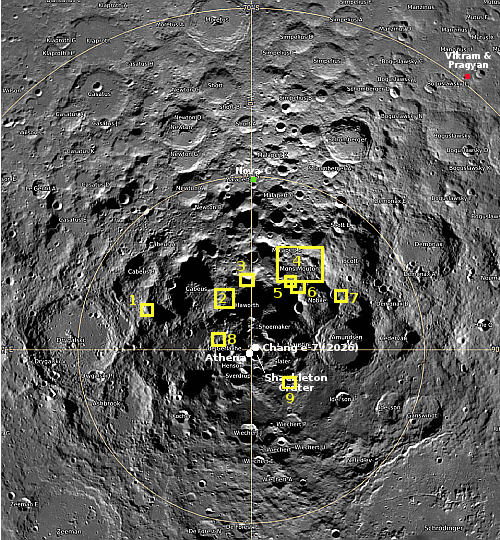
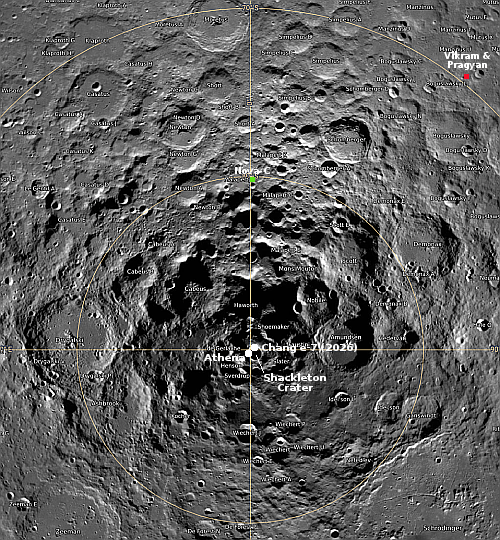
India’s Chandrayaan-2 lunar orbiter has now produced a new high resolution image of Intuitive Machines’ Athena lander, sitting on its side inside a small crater near the Moon’s south pole.
The IM-2 ‘Athena’ lander attempted a soft touchdown near the Moon’s South Pole on 6 March, 2025. Although the lander remained intact, it failed to reach its intended landing spot and ended up tipping over on its side inside a crater.
In the … images taken by the OHRC instrument on board the Chandrayaan-2 Orbiter, the Athena lander can be clearly seen lying on its side inside a crater.
This image, posted to the right, compares very favorably with the photos taken by Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) in March 2025. The lander’s legs can clearly be seen sticking out toward the top of the picture.
Hat tip BtB’s stringer Jay.
India’s Chandrayaan-2 lunar orbiter has now produced a new high resolution image of Intuitive Machines’ Athena lander, sitting on its side inside a small crater near the Moon’s south pole.
The IM-2 ‘Athena’ lander attempted a soft touchdown near the Moon’s South Pole on 6 March, 2025. Although the lander remained intact, it failed to reach its intended landing spot and ended up tipping over on its side inside a crater.
In the … images taken by the OHRC instrument on board the Chandrayaan-2 Orbiter, the Athena lander can be clearly seen lying on its side inside a crater.
This image, posted to the right, compares very favorably with the photos taken by Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) in March 2025. The lander’s legs can clearly be seen sticking out toward the top of the picture.
Hat tip BtB’s stringer Jay.