Firefly’s stock value far exceeds the predicted price
When Firefly announced it was going public at the end of July, it predicted the stock price would range from $35 to $39, with the initial public offering raising about $600 million in capital for the company. Less than a week later it revised these predictions upward to $45 and about $700 million.
When trading opened yesterday, these numbers were still too low, with the stock immediately trading at $70 per share> and raising almost $900 million.
The space and defense technology company reached a peak valuation of more than $9.84 billion during intraday trading, after its shares began trading at $70 — up more than 55% from the initial public offering price of $45. The stock climbed as high as $73.80 during the session before closing at $60.35.
Firefly sold more than 19 million shares in the offering, raising at least $868 million. By the end of trading Thursday, total volume had approached 30 million shares.
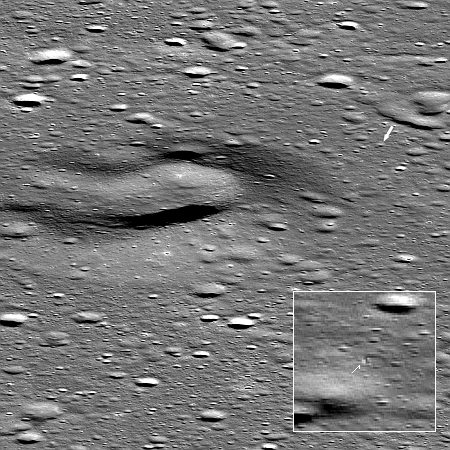
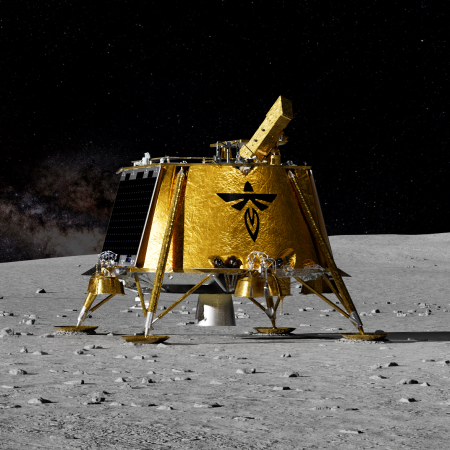
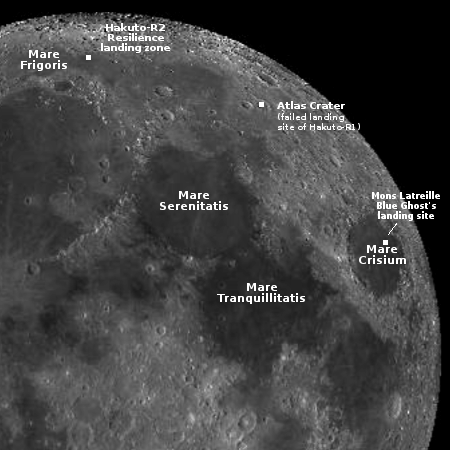
This confidence and enthusiasm by Wall Street reflects Firefly’s success this year in becoming the first private company to land an unmanned spacecraft softly on the Moon. It also suggests the market expects the company’s orbital tug and rockets to succeed. Though its Alpha rocket has had a mixed record of success, its new larger Eclipse rocket is being built in partnership with Northrop Grumman, which has invested $50 million into its development.
When Firefly announced it was going public at the end of July, it predicted the stock price would range from $35 to $39, with the initial public offering raising about $600 million in capital for the company. Less than a week later it revised these predictions upward to $45 and about $700 million.
When trading opened yesterday, these numbers were still too low, with the stock immediately trading at $70 per share> and raising almost $900 million.
The space and defense technology company reached a peak valuation of more than $9.84 billion during intraday trading, after its shares began trading at $70 — up more than 55% from the initial public offering price of $45. The stock climbed as high as $73.80 during the session before closing at $60.35.
Firefly sold more than 19 million shares in the offering, raising at least $868 million. By the end of trading Thursday, total volume had approached 30 million shares.
This confidence and enthusiasm by Wall Street reflects Firefly’s success this year in becoming the first private company to land an unmanned spacecraft softly on the Moon. It also suggests the market expects the company’s orbital tug and rockets to succeed. Though its Alpha rocket has had a mixed record of success, its new larger Eclipse rocket is being built in partnership with Northrop Grumman, which has invested $50 million into its development.