A new commercial smallsat space telescope is now operational and offering its data to scientists
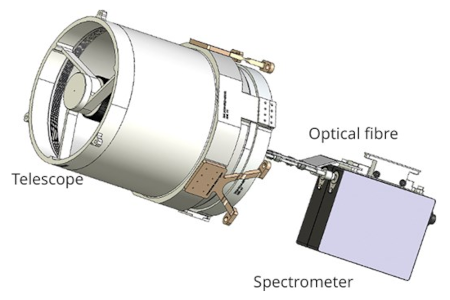
Mauve space telescope. Click for source.
Capitalism in space: A new commercial optical space telescope with a 5-inch-wide mirror and dubbed the Mauve Telescope is now operational in orbit, with its private owner, UK startup Blue Skies, offering its data to scientists for an annual subscription fee.
Blue Skies is in the process of commissioning the Mauve and plans to start delivering data to scientists in early 2026. Customers include Boston University, Columbia University, INAF’s Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri, Konkoly Observatory, Kyoto University, Maynooth University, the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, Rice University, Vanderbilt University, and Western University.
The spacecraft’s three-year mission is to study flares from stars and their impact on the habitability of planets around them. From low Earth orbit, it hosts a telescope that can collect data in the ultraviolet to visual light range (200-700 nm spectrum).
With such a small mirror Mauve is not going to be able to do a lot of ground-breaking work, though there are definitely observations of value it can accomplish, such as those listed above. Its main purpose is as a demonstration project to attract a bigger round of new investment capital, from universities like the ones listed above, for launching a larger private telescope with greater capabilities.
This is how all telescopes were funded in the U.S. until World War II, through private funds privately built. Blue Skies effort here suggests we are heading back to that model, with government budgets increasingly constrained. The company is already working on a second and larger space telescope, dubbed Twinkle with a 18-inch primary mirror. It hopes over time to continue to scale up its orbital telescopes until it is matching Hubble and Webb, and doing so faster and at far less cost.
And for profit no less!

Mauve space telescope. Click for source.
Capitalism in space: A new commercial optical space telescope with a 5-inch-wide mirror and dubbed the Mauve Telescope is now operational in orbit, with its private owner, UK startup Blue Skies, offering its data to scientists for an annual subscription fee.
Blue Skies is in the process of commissioning the Mauve and plans to start delivering data to scientists in early 2026. Customers include Boston University, Columbia University, INAF’s Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri, Konkoly Observatory, Kyoto University, Maynooth University, the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, Rice University, Vanderbilt University, and Western University.
The spacecraft’s three-year mission is to study flares from stars and their impact on the habitability of planets around them. From low Earth orbit, it hosts a telescope that can collect data in the ultraviolet to visual light range (200-700 nm spectrum).
With such a small mirror Mauve is not going to be able to do a lot of ground-breaking work, though there are definitely observations of value it can accomplish, such as those listed above. Its main purpose is as a demonstration project to attract a bigger round of new investment capital, from universities like the ones listed above, for launching a larger private telescope with greater capabilities.
This is how all telescopes were funded in the U.S. until World War II, through private funds privately built. Blue Skies effort here suggests we are heading back to that model, with government budgets increasingly constrained. The company is already working on a second and larger space telescope, dubbed Twinkle with a 18-inch primary mirror. It hopes over time to continue to scale up its orbital telescopes until it is matching Hubble and Webb, and doing so faster and at far less cost.
And for profit no less!
