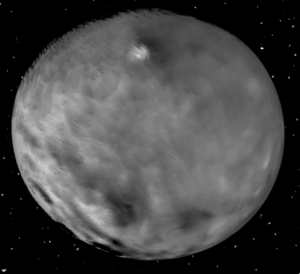
Water ice volcanoes on Ceres
Data collected by Dawn since it entered orbit around Ceres on March 6 now strongly suggests that the bright spots on the surface are produced by venting water,
Andreas Nathues, principal investigator for Dawn’s framing camera, says the feature has spectral characteristics that are consistent with ice. Intriguingly, the brightness can be seen even when the spacecraft is looking on edge at the crater rim, suggesting that the feature may be outgassing water vapor above the rim and into space. “Ceres seems to be indeed active,” he says. The feature brightens through the course of the day, and then shuts down at night. Nathues says the behavior is similar to that of comets.
More here. By mid-April Dawn should finally settle this with high resolution images.
Data collected by Dawn since it entered orbit around Ceres on March 6 now strongly suggests that the bright spots on the surface are produced by venting water,
Andreas Nathues, principal investigator for Dawn’s framing camera, says the feature has spectral characteristics that are consistent with ice. Intriguingly, the brightness can be seen even when the spacecraft is looking on edge at the crater rim, suggesting that the feature may be outgassing water vapor above the rim and into space. “Ceres seems to be indeed active,” he says. The feature brightens through the course of the day, and then shuts down at night. Nathues says the behavior is similar to that of comets.
More here. By mid-April Dawn should finally settle this with high resolution images.