Chinese scientists say the lunar far side appears drier than the near side
Based on a comparison of samples brought back by two Chinese unmanned lunar landers, Chinese scientists believe the lunar far side contains far less water in its mantle than the near side.
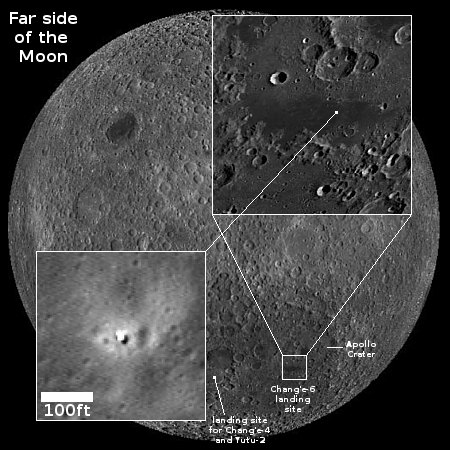
…the research team focused on analyzing water content and hydrogen isotopes in melt inclusions and apatite within [Chang’e-6] mare basalts—the first samples returned from the farside SPA Basin.
The team’s results indicate that the parent magma of these basalts contain 15–168 μg.g⁻¹ of water. Additionally, the team estimated that the mantle source of the CE6 basalts has a water content of 1–1.5 μg.g⁻¹, significantly lower than that of the nearside mantle. This disparity points to a potential hemispheric dichotomy in the Moon’s internal water distribution, mirroring many of the asymmetrical features observed on the lunar surface.
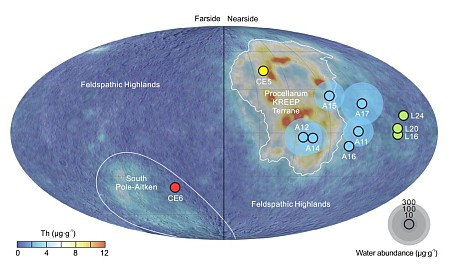
The map to the right, figure 1 in the scientists’ paper, shows the water content from the samples that have so far been brought back from the Moon. Note how the Chang’e-6 sample shows far less water content than all the near side samples.
Note however also that this is just one data point from the far side. To confirm these conclusions will require many more samples.
Based on a comparison of samples brought back by two Chinese unmanned lunar landers, Chinese scientists believe the lunar far side contains far less water in its mantle than the near side.
…the research team focused on analyzing water content and hydrogen isotopes in melt inclusions and apatite within [Chang’e-6] mare basalts—the first samples returned from the farside SPA Basin.
The team’s results indicate that the parent magma of these basalts contain 15–168 μg.g⁻¹ of water. Additionally, the team estimated that the mantle source of the CE6 basalts has a water content of 1–1.5 μg.g⁻¹, significantly lower than that of the nearside mantle. This disparity points to a potential hemispheric dichotomy in the Moon’s internal water distribution, mirroring many of the asymmetrical features observed on the lunar surface.
The map to the right, figure 1 in the scientists’ paper, shows the water content from the samples that have so far been brought back from the Moon. Note how the Chang’e-6 sample shows far less water content than all the near side samples.
Note however also that this is just one data point from the far side. To confirm these conclusions will require many more samples.