Chinese pseudo-commercial rocket industry gearing up to launch numerous times from interior spaceport
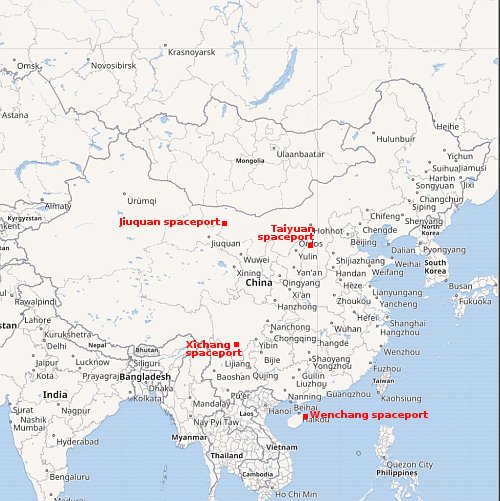
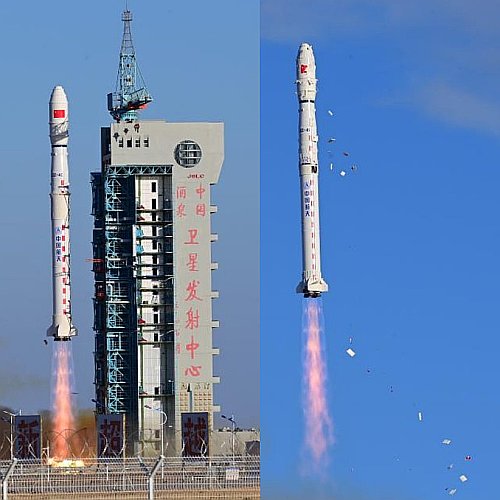
Even as China is presently building a commercial launch facility at its Wenchang spaceport on the coast, at least four of China’s pseudo-commercial rocket companies are gearing up to launch numerous times from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in the interior of China.
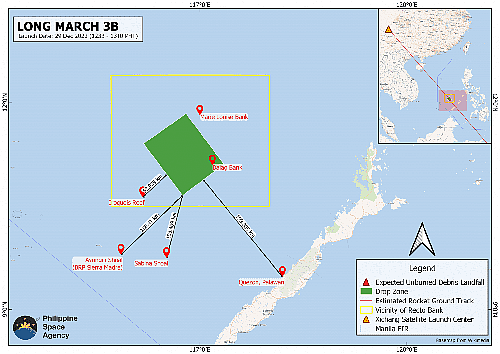
The link above shows the launch sites being built at Jiuquan by pseudo-companies Landspace, Expace, CAS Space, and Space Pioneer. The map to the right illustrates what these interior launches will mean. Since none of these pseudo-companies will be vertically landing their first stages — at least not for several years — it means that numerous first stages will be coming down in many areas in China and Mongolia, most of which will be uncontrolled descents.
Eventually the Wenchang launch facility on the coast will become available, but based on past Chinese actions, do not expect these pseudo-companies to end their operations at Jiuquan at that time. All are controlled by the Chinese government, which has made it very clear it really doesn’t care if first stages crash near habitable areas.
Hat tip to BtB’s stringer Jay for this story.

Even as China is presently building a commercial launch facility at its Wenchang spaceport on the coast, at least four of China’s pseudo-commercial rocket companies are gearing up to launch numerous times from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in the interior of China.
The link above shows the launch sites being built at Jiuquan by pseudo-companies Landspace, Expace, CAS Space, and Space Pioneer. The map to the right illustrates what these interior launches will mean. Since none of these pseudo-companies will be vertically landing their first stages — at least not for several years — it means that numerous first stages will be coming down in many areas in China and Mongolia, most of which will be uncontrolled descents.
Eventually the Wenchang launch facility on the coast will become available, but based on past Chinese actions, do not expect these pseudo-companies to end their operations at Jiuquan at that time. All are controlled by the Chinese government, which has made it very clear it really doesn’t care if first stages crash near habitable areas.
Hat tip to BtB’s stringer Jay for this story.