Firefly successfully launches for the second time in 2023
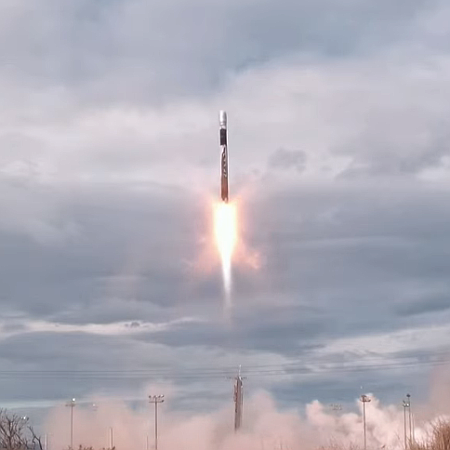

Alpha seven seconds after liftoff
UPDATE #2: According to a Firefly tweet on X, the second stage failed to fire its second burn. The satellite however was deployed, communications established, and mission operations started. Though its orbit will decay prematurely, it appears the customer, the Space Force, will achieve most of its mission objectives. This should be considered a successful launch, albeit not one that Firefly will want to repeat in this manner.
UPDATE: It appears the upper stage might have had a problem in its final engine burn intended to circularize the orbit for deployment. Either the burn failed to occur, or did not fire correctly. See this tweet. (Hat tip Jay.) I have found other reports that indicate the same question.
The question now is whether this is considered a successful launch. One of its main tasks was to demonstrate fast assembly and prelaunch procedures, for the Space Force. This was accomplished. If the satellite cannot function however is isn’t a full success. I will wait for more information before deciding whether to remove it from the launch stats.
Original post:
——————
Firefly today successfully completed its second launch in 2023, its third launch overall, its Alpha rocket lifting off from its launchpad at Vandenberg in California.
With this launch Firefly also met its launch prediction for 2023, two launches. The mission was its second for the Space Force this year, both designed to test quick launch procedures. As of posting the payload has not been deployed.
The leaders in the 2023 launch race remain the same:
92 SpaceX
61 China
18 Russia
8 Rocket Lab
7 India
American private enterprise now leads China in successful launches 106 to 61, and the entire world combined 106 to 97. SpaceX still trails the rest of the world (excluding other American companies) 92 to 97.

Alpha seven seconds after liftoff
UPDATE #2: According to a Firefly tweet on X, the second stage failed to fire its second burn. The satellite however was deployed, communications established, and mission operations started. Though its orbit will decay prematurely, it appears the customer, the Space Force, will achieve most of its mission objectives. This should be considered a successful launch, albeit not one that Firefly will want to repeat in this manner.
UPDATE: It appears the upper stage might have had a problem in its final engine burn intended to circularize the orbit for deployment. Either the burn failed to occur, or did not fire correctly. See this tweet. (Hat tip Jay.) I have found other reports that indicate the same question.
The question now is whether this is considered a successful launch. One of its main tasks was to demonstrate fast assembly and prelaunch procedures, for the Space Force. This was accomplished. If the satellite cannot function however is isn’t a full success. I will wait for more information before deciding whether to remove it from the launch stats.
Original post:
——————
Firefly today successfully completed its second launch in 2023, its third launch overall, its Alpha rocket lifting off from its launchpad at Vandenberg in California.
With this launch Firefly also met its launch prediction for 2023, two launches. The mission was its second for the Space Force this year, both designed to test quick launch procedures. As of posting the payload has not been deployed.
The leaders in the 2023 launch race remain the same:
92 SpaceX
61 China
18 Russia
8 Rocket Lab
7 India
American private enterprise now leads China in successful launches 106 to 61, and the entire world combined 106 to 97. SpaceX still trails the rest of the world (excluding other American companies) 92 to 97.