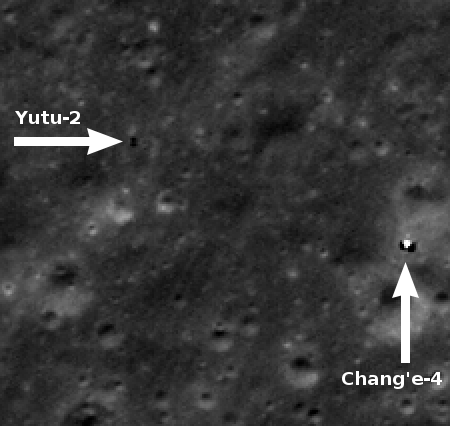
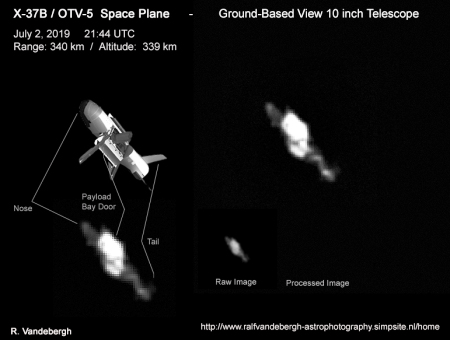
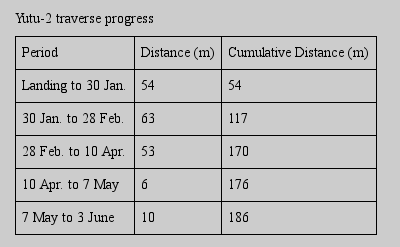
Branson sells 49% of Virgin Galactic, stock to be publicly listed
Capitalism in space: Richard Branson has sold 49% of Virgin Galactic in a deal that will have the company’s stock publicly listed by the end of 2019.
The firm will list its shares as part of a merger deal with Social Capital Hedosophia, a special-purpose acquisition company (SPAC) created by venture capitalist Chamath Palihapitiya. Social Capital Hedosophia, formed by Palihapitiya’s Social Capital and venture capital firm Hedosophia in 2017, will invest $800 million for a 49% stake in the combined company. The firm will have an enterprise value of $1.5 billion, Virgin Galactic said.
…Branson’s space venture would be the first publicly-listed human spaceflight firm, with the stock market listing slated to take place in the second half of 2019.
Branson had been in talks with Palihapitiya since he suspended talks over a Saudi investment in his space companies last year. Riyadh had planned to invest a total of $1 billion into Virgin Galactic and Virgin Orbit, which focuses on small satellites, but the deal fell through over the murder of journalist Jamal Khashoggi.
Branson was the person who said the Saudis backed out because of Khashoggi, but I personally do not believe that story. What I think happened was that, after 15 years of empty promises and no tourist flights, the Saudis suddenly realized that Virgin Galactic was a bad investment, and backed out. Branson now needs cash to keep the company afloat.
I am honestly unfamiliar with the ways of Wall Street. I do not know whether being “publicly listed” means the stock will be available for trade. If so, I expect the stock value to quickly plunge.
Capitalism in space: Richard Branson has sold 49% of Virgin Galactic in a deal that will have the company’s stock publicly listed by the end of 2019.
The firm will list its shares as part of a merger deal with Social Capital Hedosophia, a special-purpose acquisition company (SPAC) created by venture capitalist Chamath Palihapitiya. Social Capital Hedosophia, formed by Palihapitiya’s Social Capital and venture capital firm Hedosophia in 2017, will invest $800 million for a 49% stake in the combined company. The firm will have an enterprise value of $1.5 billion, Virgin Galactic said.
…Branson’s space venture would be the first publicly-listed human spaceflight firm, with the stock market listing slated to take place in the second half of 2019.
Branson had been in talks with Palihapitiya since he suspended talks over a Saudi investment in his space companies last year. Riyadh had planned to invest a total of $1 billion into Virgin Galactic and Virgin Orbit, which focuses on small satellites, but the deal fell through over the murder of journalist Jamal Khashoggi.
Branson was the person who said the Saudis backed out because of Khashoggi, but I personally do not believe that story. What I think happened was that, after 15 years of empty promises and no tourist flights, the Saudis suddenly realized that Virgin Galactic was a bad investment, and backed out. Branson now needs cash to keep the company afloat.
I am honestly unfamiliar with the ways of Wall Street. I do not know whether being “publicly listed” means the stock will be available for trade. If so, I expect the stock value to quickly plunge.